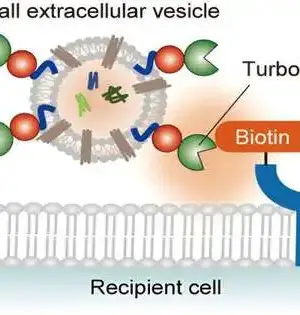
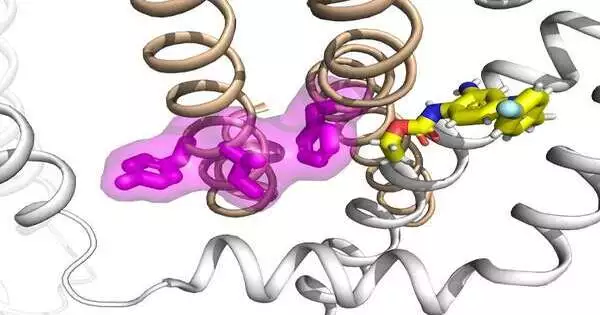
Numerous therapeutics for asthma and other obstructive lung illnesses focus on the 2-adrenergic receptor (2AR), a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that quickly upholds aviation route unwinding when invigorated. However, abuse of these specialists is related to unfriendly well-being results, including death, which has restricted their utility as front-line treatments. A mouse model review distributed in the present issue of Molecular Cell by examiners at University Hospitals (UH) and Case Western Reserve University, recognizes a clever system to detach the useful impacts of 2AR feeling. This proposes another helpful way to deal with aviation route illnesses as well as various different
Biochemistry
Epilepsy is a neurological problem that arises from strange electrical movements in the cerebrum, prompting seizures. These seizures can be caused by a variety of factors, including hereditary variations in a group of proteins that regulate potassium particles in the brain.Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis have led a worldwide group to investigate the instruments behind the capability and brokenness of these proteins, as well as their communication with an antiepileptic drug, to foster a possible new system to treat epilepsy. Jianmin Cui, teacher of biomedical design in the McKelvey School of Engineering, and Nien-Du Yang, a doctoral understudy
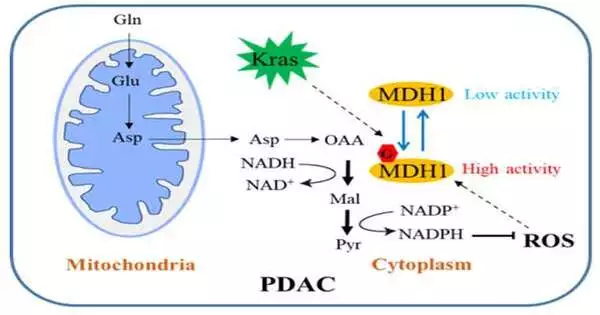
Pancreatic disease is a really harmful cancer in the stomach-related framework, and its five-year endurance rate is minimally over 10%. Metabolic changes are one of the signs of cancer cells. Oncogenic Kras-enacted pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells rely intensely upon an unusual glutamine (Gln) catabolic pathway to support cell development. In the regular pathway, Gln is first changed over completely to aspartate (Asp), which is moved from the mitochondria into the cytosol where it is changed over successively by aspartate transaminase 1 (GOT1), MDH1 and malic protein 1 (ME1) to pyruvate and NADPH. This pathway is basic for PDAC cells
PFAS synthetics appeared to be smart right away. Like Teflon, they made pots simpler to clean beginning in the 1940s. They made coats waterproof and covered stains-safe. Food coverings, firefighting froth, and even cosmetics appeared to be better with perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Then tests began recognizing PFAS in individuals' blood. Today, PFAS are unavoidable in soil, residue, and drinking water all over the planet. The review proposes they're in 98% of Americans' bodies, where they've been related to medical issues including thyroid illness, liver harm, and kidney and testicular disease. There are presently north of 9,000 kinds of PFAS.
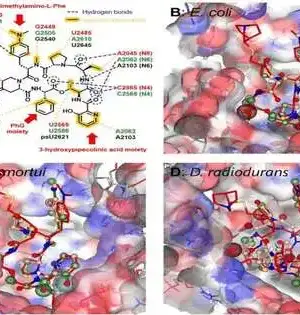
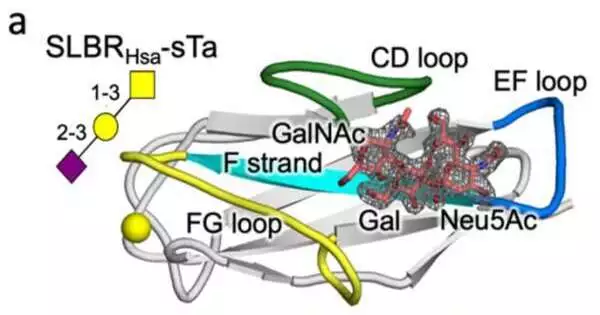
Microbes in our bodies dilemma to different host cell surface receptors, which figure out where the microorganisms reside and how they act. These receptors, comprised of chains of sugar atoms called glycans, are more than going on behind the scenes. Cells in moderate disease states, such as disease, can have an increased number of glycan receptors on their surfaces. The lab of Tina Iverson, Louise B. McGavock Chair and teacher of pharmacology, revealed the primary system by which streptococcus microbes bind to cell glycans, making the way for better approaches for utilizing bacterial atoms to identify disease cells possibly. Past
Unsaturated fats and their subsidiaries are promising unrefined components for assembling refined biofuels, cleansers, oils, surfactants, etc. The ongoing stock of unsaturated fats is, for the most part, through extraction from plants, which requires a lot of arable land. Methanol is an ideal and inexhaustible feedstock for biomanufacturing. Methanol biotransformation could give a reasonable course to unsaturated fat creation with freedom from arable land and new water. As of late, an examination group led by Prof. Zhou Yongjin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has designed yeast Ogataea polymorpha for the
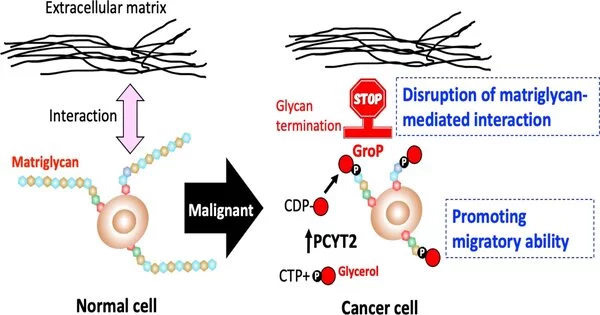
Dystroglycans on epithelial cell surfaces communicate with the extracellular grid via long sugar chains known as matriglycans, and they are responsible for cell grip.Matriglycan development errors can weaken cell grip and cause solid dystrophy. The cooperative gatherings, including scientists at Nagoya City University and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences, have recently found the presence of a clever post-translational change, in which glycerol phosphate (GroP) covers the center piece of matriglycan, in this way impeding its extension. In this new review published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, the analysts have shown that GroP change is improved in disease
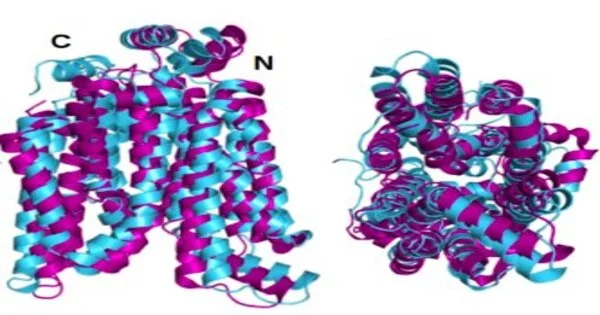
All cell films in the human body have implanted proteins that act as sensors, couriers, or for moving and managing substances going all through the cell. Transport proteins specifically are inadequately perceived due to their primary intricacy and their hydrophobic nature that makes them impervious to study. Simultaneously, these vehicle proteins, particularly those that direct glucose, play a crucial part in the development of harmful cancers. In another review, researchers led by Dr. Shuguang Zhang, Ph.D. of the MIT Media Lab, show a strategy for rapidly foreseeing the plans of hydrophilic variation designs of the 14 glucose transport film proteins
A characteristic little particle got from a cypress tree can move iron in live mice and human cells without the protein that regularly finishes the work, facilitating a development of iron in the liver and reestablishing hemoglobin and red platelet creation, another review found. Coming from a coordinated effort between scientists at the University of Illinois Urbana Champaign, the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor and the University of Modena in Italy, the review showed that the little particle hinokitiol possibly could work as a "sub-atomic prosthetic" when the iron-shipping protein ferroportin is absent or imperfect, offering a potential treatment way
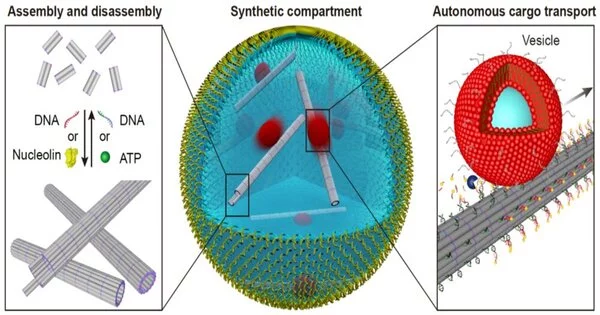
Developing practical manufactured cells from the ground up is a never-ending effort by researchers all over the world.Their application in focusing on cell systems in a highly controlled and pre-defined environment provides an excellent incentive for comprehending nature and developing new useful methodologies.Researchers from the Second Physics Institute at the University of Stuttgart and associates from the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research were currently ready to make the next stride towards manufacturing cells. They brought useful DNA-based cytoskeletons into cell-sized compartments. Cytoskeletons are fundamental parts of every cell that control their shape, inside association, and other essential capabilities like