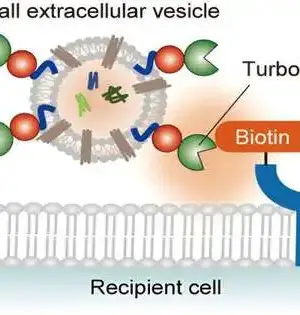
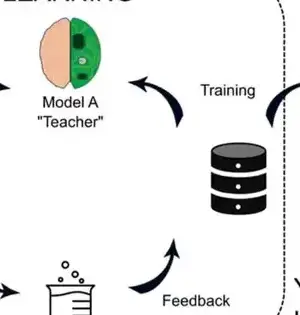
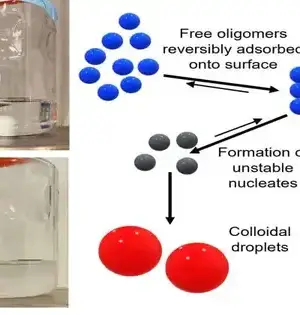
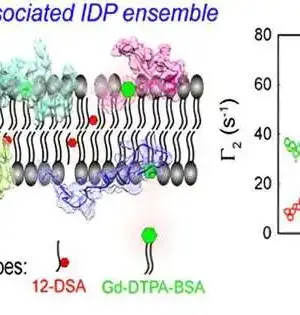
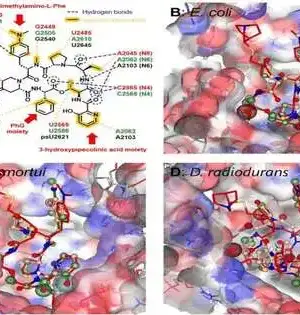
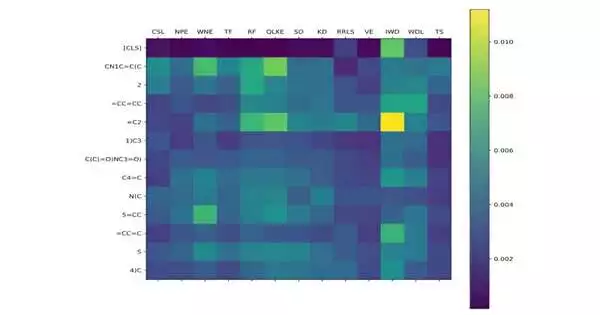
Precisely anticipating the medication protein communication (DPI) is vital in virtual medication screening. Be that as it may, current strategies will generally designate equivalent weighting to amino acids and iotas in encoding protein and medication groupings, consequently disregarding the changing commitments from particular themes. To handle this issue, a gathering of scientists headed by Juan Liu have distributed their concentrate in Wildernesses of Software Engineering. Their exploration presented a strategy, FragDPI, for the expectation of medication-protein-restricting fondness. This approach addresses the underlying undertaking to consolidate part coding and union the succession data of the two medications and proteins, subsequently safeguarding
Biochemistry
Peptides are biomolecules shaped when at least two amino acids that carry out key roles in the human creature, for example, chemicals, synapses, pain relievers, and anti-microbials, tie together. Consequently, they are greatly contemplated and utilized by the drug business, for instance. A review directed by researchers in the Division of Biophysics at the Government College of São Paulo's Clinical School (EPM-UNIFESP) in Brazil distinguished massive changes in the physicochemical properties of peptides during an unconstrained course of compound change called pyroglutamination. Pyroglutamination is a change coming about because of the unconstrained transformation of glutamine into pyroglutamic corrosive, with a
College of Maryland specialists concentrated on synaptic changes in a creature model when it created vision, which assumes a critical role in the circadian beat. In another review highlighted on the front of the journal Scientific Science, named "Microanalytical Mass Spectrometry with Super-Goal Microscopy Uncovers a Proteome Change During Improvement of the Mind's Circadian Pacemaker," a group of College of Maryland specialists utilized state-of-the-art advancements to concentrate on a little-figured-out visual pathway in a creature model. The exploration group set off to comprehend what the improvement of vision means for proteins in a piece of the mind called the suprachiasmatic
Lead enhancement in drug discovery is a difficult cycle that vigorously depends on speculation and the experience of restorative physicists. This frequently prompts questionable results and failure. Moreover, the interaction is tedious and requires critical assets. Hence, the presentation of man-made consciousness (simulated intelligence) and prescient apparatuses to speed up this cycle would be exceptionally significant in the field of medication disclosure. Silico strategies like free energy irritation (FEP) and atomic mechanics summed up conceived surface region (MM-GB/SA) have demonstrated valuable in lead streamlining by computing restricting free energy. Be that as it may, their complicated planning process, restricted atom
The adequacy of any medication atom depends on how well it associates with the inward climate inside our body. Its pharmacokinetic (PK) properties determine how effectively it evades corrupting chemicals as it goes through the stomach-related framework or the circulation system, crosses natural hindrances like the cell film, and arrives at the ideal objective. In a review distributed in Nature Correspondences, scientists at the Sub-atomic Biophysics Unit (MBU), Indian Foundation of Science (IISc), depict a clever technique for working on the pharmacokinetic properties of "macrocyclic peptides"—drug particles that are sought after vigorously by drug enterprises around the world. The IISc
A College of Alberta scientist has grown better ways of changing over carbon dioxide, an unsafe ozone-depleting substance, and glycerol, an extra of biodiesel creation, into value-added materials with boundless purposes, including fluid hydrogen stockpiling. The sets of methodologies, which will be tried for a wider scope of industry-level reasonability, address a significant step in the right direction in supportability, says Yanet Rodriguez Herrero, who led the work to procure a Ph.D. in bioresource innovation and food design from the Personnel of Horticultural, Life, and Ecological Sciences. "We've broken a boundary as far as further developing troublesome transformation cycles and
Most medications are little particles that stick solidly to a particular objective—some atom in human cells that is engaged with an illness—to work. For instance, a disease medication's objective may be a particle that is bountiful within malignant growth cells. The medication ought to speculatively travel uninhibitedly all through the cell until it comes to its objective and then lock onto it, prompting a helpful activity. Nonetheless, little particle drugs don't go in such an unhindered way; all things considered, they will generally move in unambiguous districts of the cell. This is on the grounds that each medication is equipped
Spent espresso beans (SCG) make up the biggest piece of waste created from getting ready espresso refreshments and making instant espresso, delivering near 6 million metric tons of waste overall every year. To deal with this tremendous amount of waste, researchers are tracking down approaches to changing SCG into value-added items for different applications, from modern materials to biofuels. A group of specialists led by academic administrator Liu Shao Quan from the NUS Division of Food Science and Innovation under the Workforce of Science took a more imaginative course to make a cocktail from matured SCG as an approach to
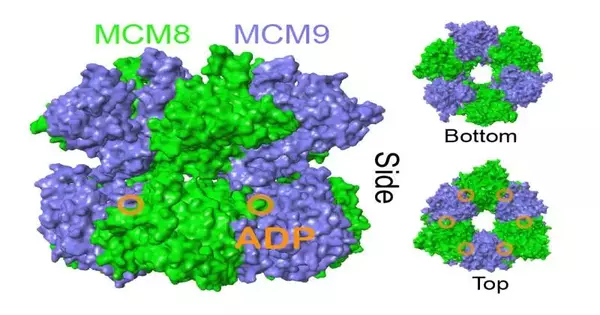
Logical examination requires tolerance. The prizes are not generally quick, and the innovation required doesn't necessarily exist in every case. Michael A. Trakselis, Ph.D., teacher and overseer of graduate undertakings for the Branch of Science and Organic Chemistry at Baylor College, figures this out. For quite a long time, Trakselis has been keen on the MCM8/9 protein. Part of the minichromosomal support protein (MCM) family, MCM8/9 is straightforwardly connected to ovarian inadequacy, fruitlessness, and malignant growths, including ovarian, testicular, and colon tumors, yet little is known about the way this functions and its association with illness. There was no comprehension
Enzymes are increasingly being used in environmentally friendly and sustainable processes to produce key chemical building blocks for a variety of industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and biofuels. These enzymes have several advantages over traditional chemical methods, such as milder reaction conditions, higher selectivity, and lower environmental impact. Using light energy to activate natural enzymes can assist scientists in developing novel enzymatic reactions that support environmentally friendly biomanufacturing - the production of fuels, plastics, and valuable chemicals from plants or other biological systems. Using this photoenzymatic approach, researchers created a clean, efficient method for synthesizing critical chemical building blocks known as