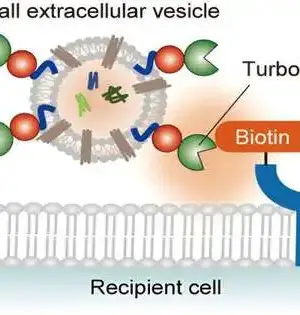
Electrical charges play a crucial role in the human body. The majority of biological processes are dependent on electrical ions traveling across the membranes of each of our body's cells, which send pulses of energy through the brain and nerves that resemble lightning. These electrical signs are conceivable, to some extent, due to a lopsidedness in electrical charges that exists on one or the other side of a cell layer. Until recently, scientists believed that the membrane was a key factor in this imbalance. However, when Stanford University researchers discovered that microdroplets of water and air can have similar unbalanced
Biochemistry
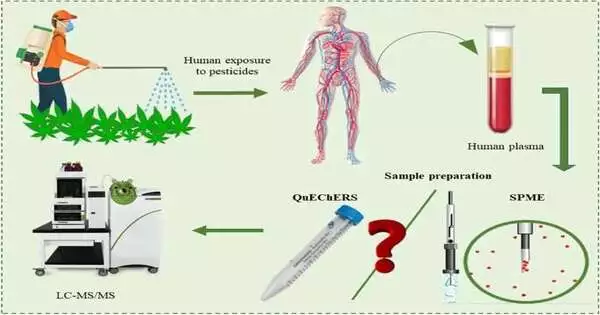
A chemical analyst and micro-extraction specialist at The University of Toledo developed a more dependable, strong, and effective way to monitor pesticide exposure and safeguard the health and safety of agricultural workers, especially in developing industries like the cannabis industry. Dr. Analytical Chemistry Assistant Professor Emanuela Gionfriddo as well as Nipunika H. Godage, a Ph.D. candidate in the Dr. Nina McClelland Laboratory for Water Chemistry and Environmental Analysis at the University of Toledo, published a paper in the journal Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry outlining their ground-breaking technique that can identify 79 pesticide residues in human blood plasma at "ultra-trace" levels,
By using an improved mechanochemical method, the formerly time-consuming but frequently used Birch reduction can now be completed in the air in under a minute. The Birch reduction is a reaction that is frequently used to produce drugs and bioactive compounds, but the strenuous procedure frequently necessitates that chemists handle liquid ammonia, use cryogenic temperatures, and complete time-consuming steps. A streamlined technique for carrying out the Birch reduction has been created by researchers at the Institute for Chemical Reaction Design and Discovery (WPI-ICReDD) in Hokkaido University. This technique can be used at room temperature or in ambient air and is
The first industrially scalable surface modification method for bioabsorbable magnesium alloy wires has been created by researchers from the IMDEA Materials Institute and the German company Meotec GmbH. The results could significantly affect how such wires are used in biomedical applications in the future, according to two recent scientific papers published in the journal Biomaterials Advances. Magnesium wires with surface modifications have a lot of potential in the biomedical field, including applications as polymer reinforcement in trauma fixation plates, wound closure, cardiovascular stents, nerve regeneration, and implants. "There are presently no commercially authorized magnesium wire-based medical devices on the market
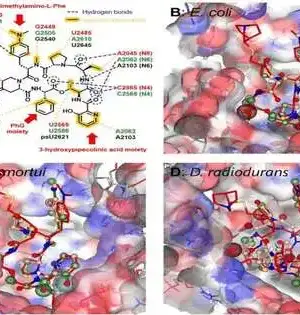
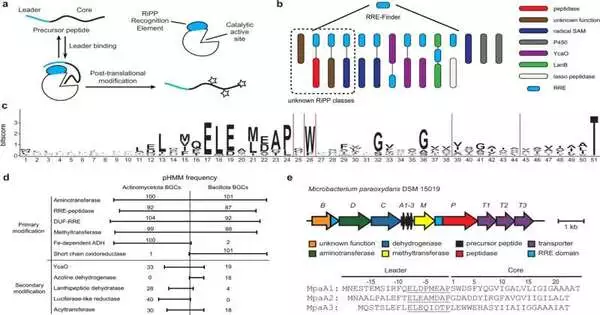
Living things produce a wide range of organic compounds that are useful in contemporary therapeutics and medicine. The majority of natural products now come from bacteria and other microbes, including the expanding family of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides, or RiPPs. The chemistry laboratories of Huimin Zhao (CABBI/BSD/GSE/MMG), Steven L. and Margaret Witt Professor of Computer Science, and Douglas Mitchell (MMG), John and Margaret Witt Professor of Chemistry, are located in the same building. Miller Chair of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have been collaborating to find and assess fresh RIPs that might
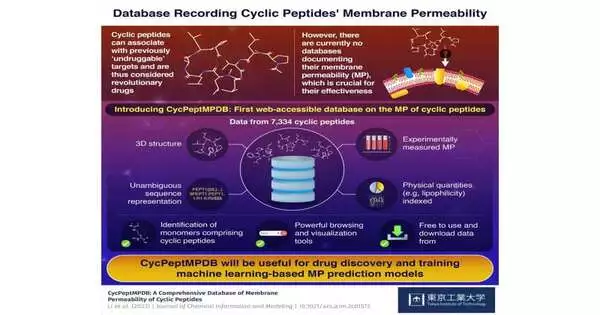
Researchers at Tokyo Tech have developed a novel database called CycPeptMPDB that focuses on the permeability of cyclic peptides to membranes. This database could hasten the development of drugs based on these intriguing compounds. This database was made by compiling published data on thousands of cyclic peptides and neatly organizing it on an online-accessible platform. CycPeptMPDB could open the door to new computational and machine learning methods for screening and designing drugs with cyclic peptides because of its search and visualization capabilities. Finding compounds that meet a number of seemingly incompatible requirements is one of the biggest challenges in modern
A study on the effects of combining two common ultraviolet light filters, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate (against UVB) and avobenzone (against UVA), with the active antioxidant rosmarinic acid was published in the journal Cosmetics. By adding rosmarinic acid at 0 percent, a very small amount when compared to those of conventional UV filters, the research team improved the sunscreen's photoprotective efficacy. They believe their research indicates that adding natural molecules with antioxidant properties to sunscreens may reduce the amount of conventional UV filters in the finished product while also adding other useful properties. The performance of the product increased without the need
Being as close to the source material as possible is ideal when studying the microbiology of any object, be it a molecule or a dolphin. When you're looking into the Rube Goldberg environment of a cell's nucleus, that can be especially difficult. However, Princeton chemists from the Muir Lab and the MacMillan Lab used two renowned technologies in research that was published this week in Nature to direct light in the precise direction they desired. In the process, they discovered crucial, unanticipated changes in interactions surrounding chromatin, a DNA-protein complex that functions as a sort of architecture that permits the
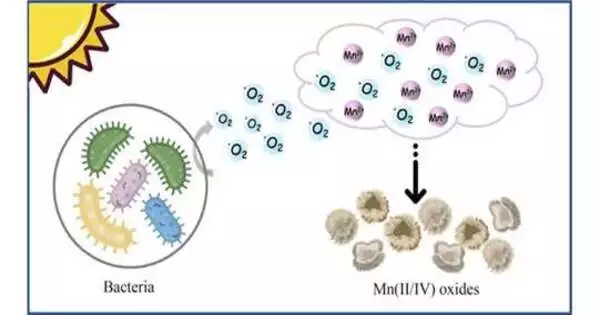
Manganese oxides are naturally reactive minerals that are common in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. Through adsorption and oxidation in sewage treatment, they have an impact on the fate of metals (like As3 and Cd2) and organic pollutants (like phenols and diclofenac). Most of the time, it is believed that dissolved Mn(II) is oxidized by abiotic or biotic processes to produce manganese (III or IV) oxides in the environment. Although the reaction between dissolved Mn(II) and Mn(III/IV) oxides has a high energy barrier, it is thermodynamically advantageous to oxidize aqueous Mn(II) by dissolved oxygen. However, the reaction's kinetics are slow.
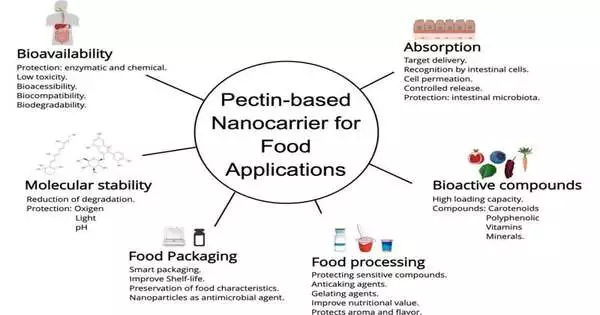
Bioactive mixtures present for the most part in products of the soil carry out various substantial roles connected with wellbeing and prosperity. Antioxidant, diabetes, anti-aging, and cancer-fighting properties are among their effects. Bioactive compounds' bioavailability—the percentage that enters the bloodstream after being absorbed—is the subject of numerous studies aimed at improving the organism's ability to absorb them and increasing their bioavailability. The compounds can be packaged on the nanometric scale (a nanometer is one billionth of a meter) by coating them with another material. The term "nanoencapsulation" refers to the method that guarantees the compounds' slow release, allowing them to