A gadget has been made that could complete clinical breast assessments (CBE). The controller, planned by a group at the College of Bristol and based at the Bristol Advanced Mechanical Research Center, can apply quite certain powers over a range, like powers utilized by human inspectors, and can distinguish irregularities utilizing sensor innovation at deeper levels than previously. This could reform how ladies screen their bosom wellbeing by giving them access to safe electronic CBEs situated in effectively open spots, for example, drug stores and wellbeing focuses, which give precise outcomes. Accuracy, repeatability, and precision are of vital significance in
Biomedical technology
Depending on what a test is looking for, getting results from a blood test can take anywhere from an hour to a week. The same holds true for examinations of food and water contamination. The majority of the time, lengthy procedures in sample processing and analysis are what cause the delay. In a popular class of magnetic beads, MIT engineers have now discovered a novel optical signature that might be utilized to quickly detect impurities in various diagnostic procedures. For example, the team showed the signature could be used to detect signs of the food contaminant Salmonella. The so-called “Dynabeads”
Specialists from the College of Salerno, Italy, have found that a basic blood test for tTG-IgA concentrations could be utilized as a demonstrative edge in anticipating duodenal villous decay, a sign of celiac sickness. In their paper, "Serum hostile to tissue transglutaminase IgA and expectation of duodenal villous decay in grown-ups with thought celiac illness without IgA lack (Bi.A.CeD): a multicentre, planned companion study," distributed in The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the specialists detail the discoveries of the review directed on a partner with associated celiac sickness and contrast the demonstrative capacity and blood serum edges with endoscopy biopies. After
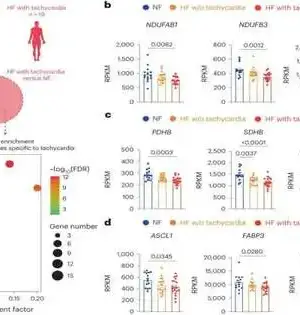
Breast cancer recurrence is a complicated and multifaceted process with multiple underlying causes. While chemotherapy is a popular treatment for breast cancer, it is crucial to highlight that chemotherapy does not cause recurrence. Chemotherapy, on the other hand, is used to target and kill cancer cells in the body. According to a recent study published in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Ramya Ganesan of Emory University, US, and colleagues, a common chemotherapy treatment injures surrounding non-cancer cells, which can then awaken dormant cancer cells and encourage cancer growth. The discovery is significant for understanding cancer recurrence and may point
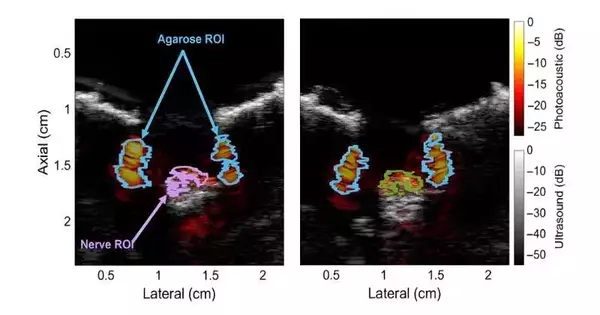
Intrusive operations, for example, medical procedures requiring neighborhood sedation, frequently imply the risk of nerve injury. During activity, specialists may incidentally cut, stretch, or pack nerves, particularly while confusing them with another tissue. This can prompt enduring side effects in the patient, including tangible and engine issues. Also, patients getting nerve barricades or different sorts of sedation can experience the ill effects of nerve harm on the off chance that the needle isn't set at the right distance from the designated fringe nerve. Thusly, specialists have been attempting to foster clinical imaging strategies to moderate the risk of nerve harm.
A delicate ball intended to help emotional well-being by 'embodying' breath has been developed by a software engineering understudy at the College of Shower. A delicate ball that 'represents' breath, extending and contracting in synchronicity with an individual's inward breaths and exhalations, has been imagined by a Ph.D. understudy at the College of Shower. The ball is intended to help with psychological wellness by providing clients with an unmistakable portrayal of their breath to keep them centered and assist them with directing their feelings. Alexz Farrall, the understudy in the branch of software engineering who developed the gadget, said, "By
Reflection practices can frequently and emphatically impact the existence of specialists, for example, by further developing their profound prosperity, lessening feelings of anxiety, and expanding their emphasis on everyday exercises. While some meditators practice peacefully with no outer direction or signs, many use sound accounts and cell phone applications or go to meetings driven by reflection instructors. Analysts at the Hong Kong Polytechnic College and Hong Kong Science Park have as of late investigated the expected worth of robots as guides for two unique sorts of reflection: cherishing benevolence and strolling contemplations. Their discoveries, distributed in the Global Diary of
Attractive reverberation imaging (X-ray) machines can obviously see non-hard aspects of the body—ddelicate tissue like the cerebrum, muscles, and tendons—aas well as distinguish growths, making it conceivable to analyze numerous sicknesses and different circumstances. However, conventional MRI machines are only used in hospitals and other large facilities due to their high cost and bulk caused by their powerful magnets. Companies are creating new portable versions with magnetic fields of lower strength as an alternative. The applications of MRI may be extended by these new models. For example, low-field X-ray frameworks could be sent in ambulances and other portable settings. They
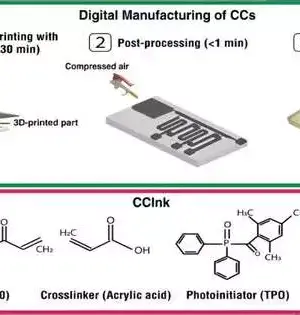
Research suggests that printed tablets have reached a level of quality comparable to that of conventionally manufactured tablets, suggesting that 3D-printed medicine could be the future of personalized health care. The promise that 3D-printed medicines hold for patients is highlighted in our new study, which was published in the International Journal of Pharmaceutics. The nearly limitless potential to have medicines tailored to your specific health requirements may become a reality sooner than you think if we can scale up 3D printing for everyday use. A "one-size-fits-all" approach to medicine production has existed for a long time, with tablets and capsules
You are not alone if you have ever considered taking a temperature but been unable to locate a thermometer. The most frequently cited COVID-19 symptom is a fever, which is also an early sign of many other viral infections. A temperature check can be very important for quick diagnoses and to prevent the spread of viruses. Despite the rise of telehealth consultations, precise at-home thermometers are still uncommon. There are a couple of possible explanations behind that. The gadgets can cost anywhere from $15 to $300, and many people only use them occasionally throughout the year. The COVID-19 pandemic's early