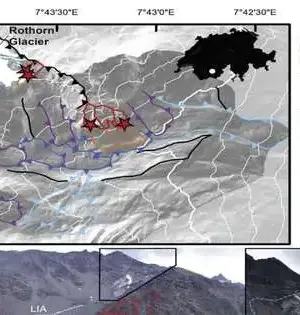
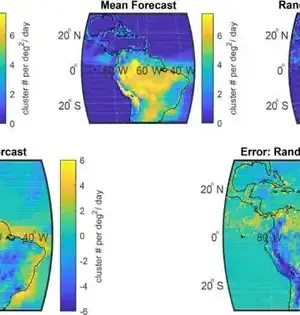
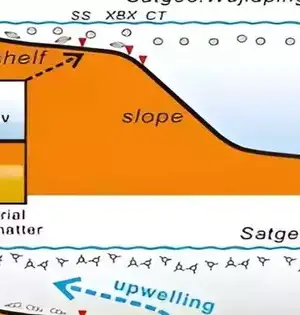
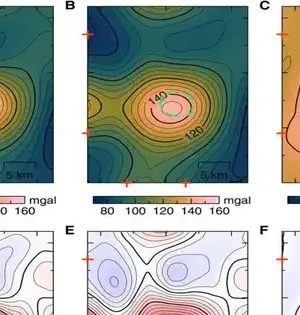
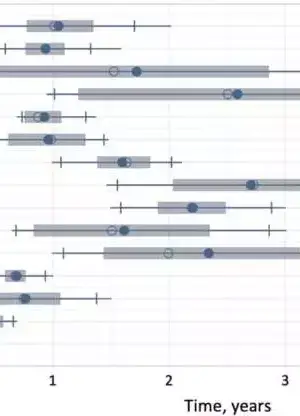
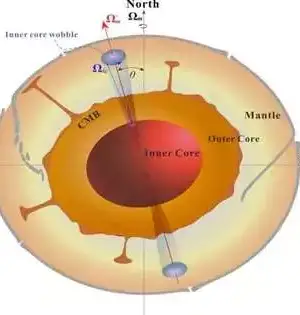
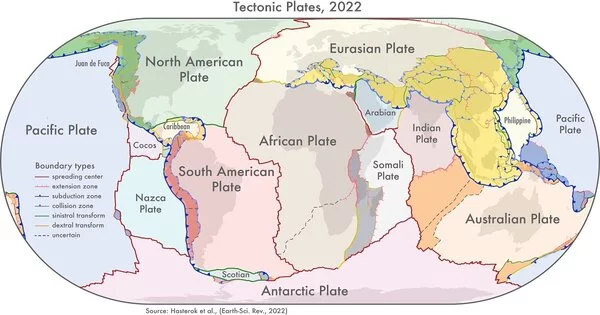
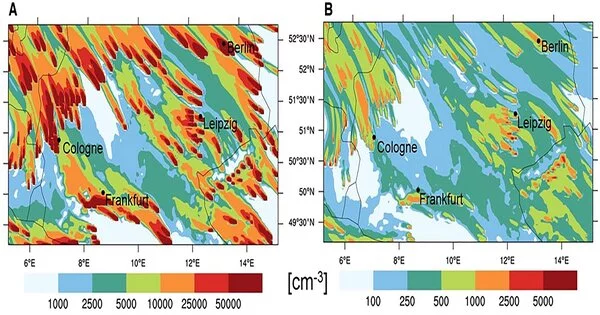
New models that show how the continents were collected are providing new insights into the Earth's historical background and will aid in providing a better understanding of common hazards such as earthquakes and volcanoes. "We took a gander at the ongoing information on the design of plate limit zones and the previous development of the mainland covering," said Dr. Derrick Hasterok, Lecturer, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Adelaide, who led the group that delivered the new models. "The mainlands were gathered a couple of pieces all at once, a piece like a jigsaw, but each time the riddle was
Earth Sciences
For a really long time, researchers have attempted to figure out the design of the Earth. One of these researchers is University of Twente geophysicist Dr. Juan Carlos Afonso (Faculty of ITC). He has as of late fostered another strategy to examine the Earth's mainland covering that lays the foundation to anticipate geothermal energy sources and other basic assets for the Earth and different planets. He published his exploration in the logical journal Nature Geoscience. To limit the effect of normal perils and accelerate the change to environmentally friendly power energy innovations, it is vital to figure out how the
In the fall of 2017, geography teacher Patricia Gregg and her group had recently set up another volcanic determining demonstrating program on the Blue Waters and iForge supercomputers. At the same time, one more group was checking action at the Sierra Negra fountain of liquid magma in the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador. One of the researchers on the Ecuador project, Dennis Geist of Colgate University, reached out to Gregg, and what occurred next was the chance figure of the June 2018 Sierra Negra ejection five months before it happened. Initially developed on an iMac PC, the new displaying method had proactively
In the middle between Earth's unbending structural plates above and its convecting mantle beneath is a hot and delicate layer known as the asthenosphere. At mid-sea edges, upwelling of the hot asthenosphere to the outer layer of the ocean bottom structures a new sea outside. With time, the sea outside layer ages significantly, becomes colder and denser, and is at long last reused down into the mantle at subduction zones. Along these lines, the maritime environment is normally under 200 million years old. "These recently discovered rocks from the Indian Ocean are as old as 2.7 billion years and belong
Whether it's heavy rain or a severe drought, the frequency of extreme weather events is increasing around the world. Existing environmental models, be that as it may, don't show their elements well enough. Scientists at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) expect that ultrafine particles in the environment affect cloud material science and, thus, climate. Their plane estimates confirm an increase in molecule emanations despite a decrease in coarse fine residue focus and blame it on the ignition of petroleum derivatives in fume gas cleaning frameworks. Their outcomes are distributed in Scientific Reports. According to the most recent reports of
The Hunga volcano ushered in 2022 with a boom, destroying the island nation of Tonga and causing a frenzy of activity among aid groups and Earth scientists. It had been nearly 140 years since an eruption of this magnitude had jolted the planet. UC Santa Barbara's Robin Matoza led a group of 76 researchers, from 17 countries, to record the emission's air waves, the most grounded recorded from a spring of gushing lava since the 1883 Krakatau ejection. The collaboration, incorporated in an abnormally short measure of time, subtleties the size of the waves starting from the ejection, which the
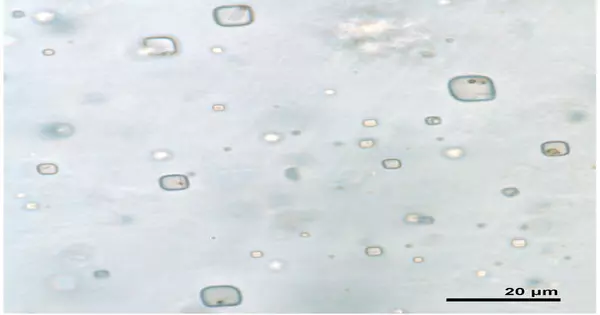
Essential liquid incorporations in halite from the 830-million-year-old Browne Formation of central Australia contain natural solids and fluids, as reported with communicated light and UV-vis petrography. These articles are reliable in size, shape, and fluorescent reaction to cells of prokaryotes and green growth, and totals of natural mixtures. This study demonstrates how microorganisms from saline depositional conditions can survive in halite for many years and be distinguished in situ using only optical techniques.This review, published in Geology, has suggestions for the quest for life in both earthly and extraterrestrial synthetic sedimentary rocks. As halite precious stones fill in saline surface