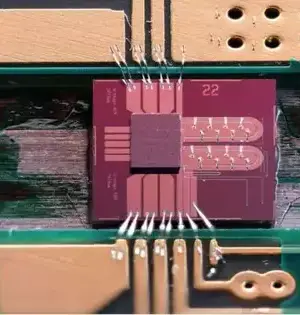
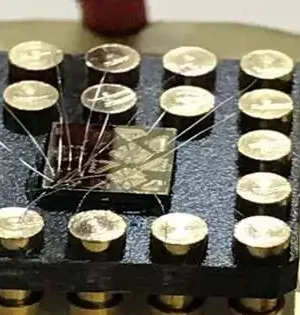
Engineers at Caltech and the University of Southampton in the United Kingdom collaborated to design a gadget chip that is coordinated with a photonics chip (which uses light to move information), resulting in a firm end result capable of sending data at ultrahigh speed while producing negligible intensity. However, the two-chip sandwich is probably not going to find its way into your PC, and the new plan could impact the fate of server farms that oversee extremely high volumes of information correspondence. "Each time you are on a video call, transfer a film, or play a web-based computer game, you're
Electronics & Semiconductors
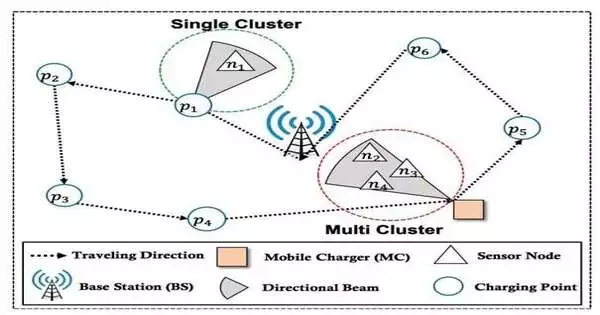
Brilliant industrial facilities, vehicles, and urban areas progressively utilize remote battery-powered sensor organizations (WRSNs) for correspondence. A particular benefit of WRSNs is that they can be set in remote, out of reach, or even naturally or synthetically polluted regions for correspondence, observation, and surveillance in military and ecological applications. In any case, the capability of these WRSNs is limited by their dependence on restricted energy sources like batteries, which can obstruct their smooth working. The essential test of WRSNs is their ability to charge and keep up with the batteries of the sensors in the organization successfully. The charging effectiveness
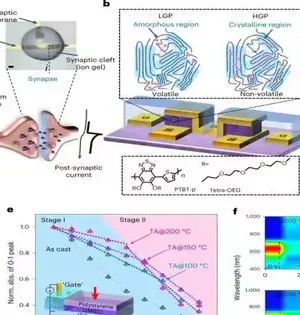
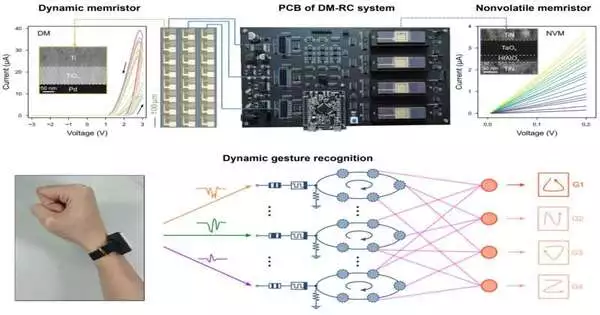
Supply registering (RC) is a methodology for building PC frameworks motivated by current information on the human cerebrum. Neuromorphic registering structures in light of this approach contain powerful actual hubs, which when joined can handle spatiotemporal signs. Tsinghua University researchers in China have recently developed another RC framework based on memristors, electrical components that control the progression of electrical flow in a circuit while also recording how much charge has recently passed through it.This RC framework, presented in a paper distributed in Nature Gadgets, has been found to accomplish wonderful outcomes, both with regard to execution and proficiency. "The basic
Field-impact semiconductors (FETs) are semiconductors in which the opposition of the majority of the electrical flow can be constrained by a cross-over electric field. Throughout the last 10 years or something like that, these gadgets have ended up being truly important for controlling the progression of current in semiconductors. To additionally promote FETs, gadget engineers overall have as of late been attempting to reduce their size. While these down-scaling endeavors have been found to speed up and bring down the power utilization, they are likewise connected with short-channel impacts (i.e., ominous impacts that happen when a FET's channel length is
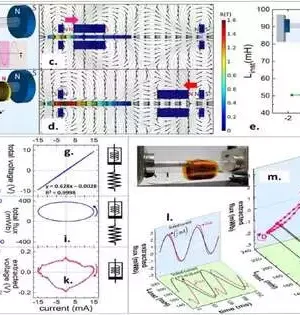
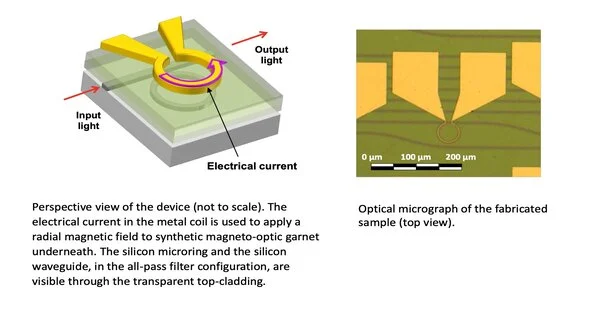
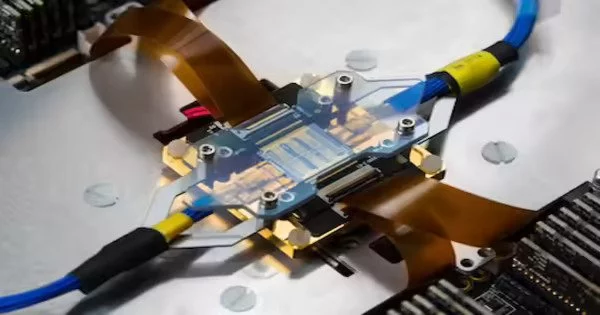
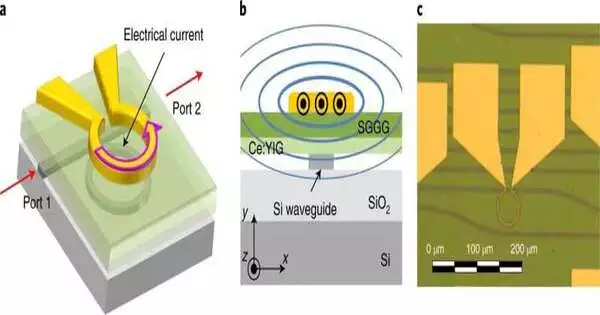
Later on, numerous PCs will no doubt be based on electronic circuits made of superconductors. These are materials through which an electrical flow can stream without energy misfortunes. This could be extremely encouraging for the advancement of elite execution supercomputers and quantum PCs. Scientists at the University of California, Santa Barbara, Raytheon BBN Innovations, the University of Cagliari, Microsoft Exploration, and the Tokyo Foundation of Innovation recently developed a magneto-optic modulator—a device that controls the properties of a light bar via an attractive field.This gadget, presented in a paper distributed in Nature Hardware, could add to the execution of huge
Gallium nitride (GaN) is causing an innovative shift in the world of power electronics. For decades, silicon-based MOSFETs (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors) have been an essential component of modern life, converting energy to power. However, we are approaching the theoretical limit of how much silicon MOSFETs can be improved in terms of power efficiency. Silicon is failing to meet modern demands for increasing power density and efficiency, as well as environmental pollution regulations. Gallium nitride is on the rise as a replacement for silicon as the backbone of power switching technology due to its ability to meet growing
Millions of quantum bits are required for quantum computers to prove useful in practical applications. Scalability is one of the greatest challenges in the development of future devices. One problem is that the qubits have to be very close to each other on the chip in order to couple them together. Researchers at Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University have now come a significant step closer to solving the problem. They succeeded in transferring electrons, the carriers of quantum information, over several micrometers on a quantum chip. Their "quantum bus" could be the key component to master the leap to
Many cutting-edge advances work at amazingly low temperatures. To protect their fragile states, researchers must keep them just above absolute zero (-459.67° Fahrenheit).In any case, super cool parts need to connect with room-temperature frameworks, giving both a test and a chance for engineers. A global group of researchers, led by UC St. Nick Barbara's Paolo Pintus, has planned a gadget to assist cryogenic PCs with chatting with their fair-climate partners. The system utilizes an attractive field to change information from electrical flow completely to beats of light. The light can then travel through fiber-optic links, which can send more data
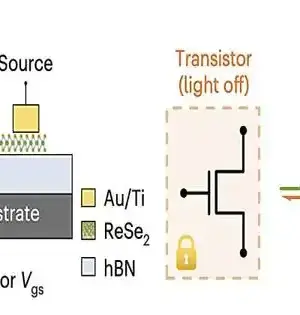
Lately, gadgets and compound specialists have concocted different substance doping strategies to control the sign and centralization of charge transporters in various materials. Synthetic doping strategies basically involve introducing contamination into materials or substances to change their electrical properties. These promising strategies have been effectively applied to a few materials, including van der Waals (vdW) materials. VdW materials are structures described by firmly reinforced 2D layers, which are bound in the third aspect through more fragile scattering powers. Specialists at the University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley), the Kavli Energy Nanosciences Institute, Beijing Institute of Technology, Shenzhen University, and Tsinghua
Convolutional brain organizations (CNNs) have ended up being profoundly important for many applications, going from PC vision to the examination of pictures and the handling of human language. However, to handle further developed errands, these models are turning out to be progressively intricate and computationally demanding. Recently, many device engineers have been attempting to create devices that can support the capacity and computational heap of complex CNN-based models.This incorporates denser memory gadgets that can uphold a lot of loads (i.e., the teachable and non-teachable boundaries thought about by the various layers of CNNs). Scientists at the Chinese Academy of Sciences,