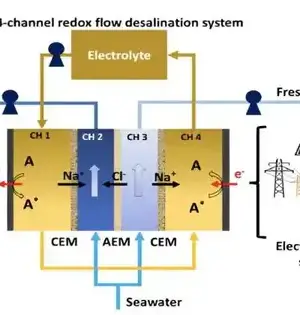
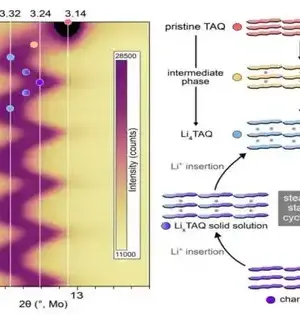
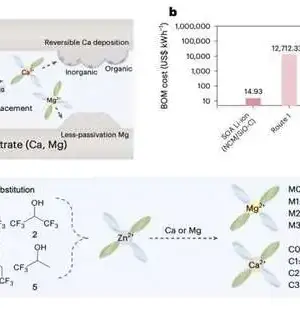
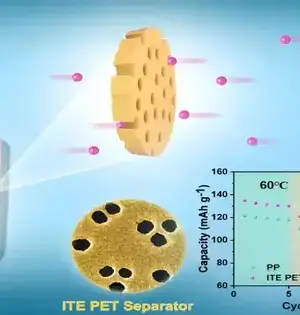
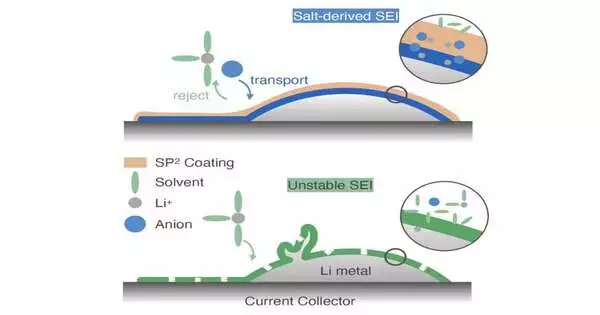
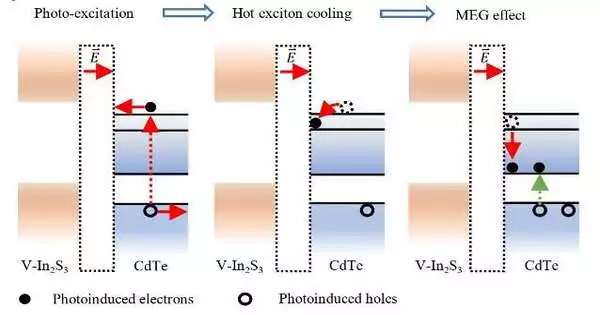
The promising battery solutions that make use of metallic lithium as the anode are lithium metal batteries. They use a single layer of lithium close to the anode rather than electrode materials that store lithium ions, as is the case with most lithium-ion batteries (LiBs), which can significantly reduce their size and weight. While these batteries could outflank LiBs concerning limit and energy thickness, to work dependably, the layer between their Li metal anode and electrolyte ought to be powerful and stable over the long haul. The solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer has been difficult to stabilize up to this
Energy & Green Tech
The unprecedented COVID-19 flight ban has caused a rapid recovery in the global airline industry. Even more rapidly than before the pandemic, airlines are expanding in some parts of the world, like the Middle East. In any case, how might the business keep on developing while at the same time doing its reasonable portion for environmental change? Except if worldwide avionics changes tack, its ozone-depleting substance emanations are projected to cause around 0.1 °C of an all-out Earth-wide temperature boost by 2050. The aviation and energy industries are promoting so-called "sustainable aviation fuels" as the best option. These fuels can
Because of its excellent power-conversion efficiency and low price, perovskite solar cells (PVSCs) are a possible replacement for conventional silicon-based solar cells. Nevertheless, ensuring long-term stability has been one of the main obstacles in their development. A research team from the City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently achieved a breakthrough by creating a novel, multifunctional, non-volatile additive that can enhance the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells by controlling the growth of the perovskite film. The commercialization of PVSCs has a lot of potential because to this straightforward and successful technique. “This type of multifunctional additive can be
Even if you haven't heard of piezoelectric materials, you have probably used them to your advantage. Solid materials like crystals, bones, and proteins are known as piezoelectric materials because, when subjected to mechanical stress, they generate an electric current. Solar cells, wearable and implantable electronics, and even spacecraft are incorporating materials that use light, heat, and motion as sources of energy. They let us keep gadgets charged for longer, perhaps perpetually, without the need to connect them to a power source. However, in order for these energy harvesters to function properly, we need to know precisely how much energy they
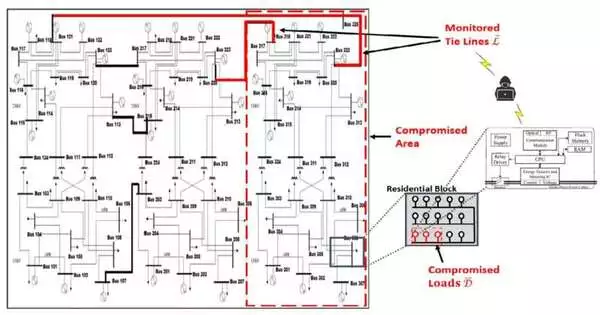
Researchers from the Oregon State University College of Engineering have demonstrated that hackers can destabilize a power transmission grid by manipulating smart meters to generate an oscillation in electricity demand. IEEE Access published the findings. According to associate professor of electrical engineering and computer science Eduardo Cotilla-Sanchez, who led the project with graduate student Falah Alanazi, the study is important because understanding where a grid's vulnerabilities lie and what they look like is the first step in designing protection mechanisms. A smart meter is a digital device that uses a telecommunications connection to send electricity usage data to a local
Scalable methods to reliably split water into hydrogen and oxygen could have important repercussions for the energy sector, as hydrogen inside fuel cells can generate electrical power. These techniques may contribute to the reduction of Earth's emissions of greenhouse gases by producing a lot of hydrogen for more environmentally friendly energy sources. Photocatalysts, which are substances that are able to absorb light and use the energy of that light to start chemical reactions, are one method for splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. This method basically involves shining light on these materials, which starts the reaction that turns water
In a world that is gradually reducing most, if not all, connections with carbon-based energy, there has been a fleeting ascent in the utilization of lithium-particle batteries as a cutting-edge energy capacity arrangement. However, this has led to yet another issue: more lithium battery waste has been generated. Over 500 charging and discharging cycles, lithium-ion batteries gradually degrade, losing anywhere from 12 to 24 percent of their total capacity. The electrolyte and different materials inside the battery can likewise corrupt, causing a decline in capacity over the long run. Due to the potential for toxic elements to leach into the
Reza Arghandeh from the Western Norway College of Applied Sciences (HVL), Hossein Farahmand (NTNU), and their group are concentrating on how hydropower makers can utilize normal assets and flex with the market at some random time. The researchers have created concrete artificial intelligence methods for figuring out how producers should control how much water is put in water reservoirs. Hossen Farahmand, a professor at NTNU and the head of the research group for electricity markets and energy system planning, is in charge of the research project on hydropower production. Mojtaba Yousefi from HVL, Jayaprakash Rajasekharan from NTNU, and Jinghao Wang
At the point when Doc Earthy took care of his DeLorean food scraps in Back to the Future as fuel, it seemed like insane sci-fi. Now that UBC Okanagan researchers are looking into the possibility of using solid and liquid fruit waste to power fuel cells, science is taking over that fiction. Researchers are working to purify and enhance the energy output of discarded food, particularly fruit waste, which is abundant in the agricultural belt of the Okanagan Valley, despite the fact that the energy extracted from food scraps still pales in comparison to solar or wind power. The BC
A group accumulates around a dark wooden box that looks like a short fridge, hanging tight for the movement of a couple of mechanical arms sitting right there. At Idaho National Laboratory, when the arms move, a wave of excited energy in the room shows how this simple action may alter the removal and disposal of international radioactive sources in the future. The group was attending the very first demonstration of a mobile hot cell that had the potential to fundamentally alter the handling of a particular class of radioactive materials. The hot cell's robotic and mobile nature has the