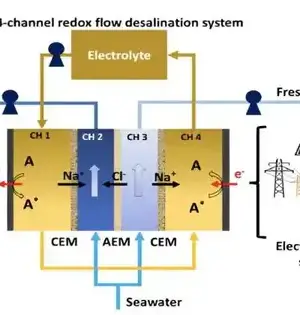
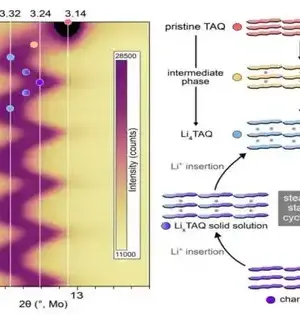
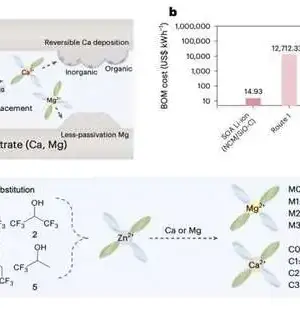
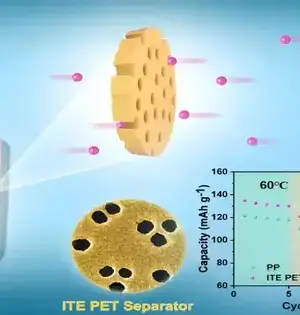
At the point when the intensity of summer hits, forced air systems turn on and energy requests skyrocket, stressing the matrix. In a hotter world, more effective cooling choices will play a significant part in limiting the increment of cooling-related energy requests. This will be especially valid for the almost 80% of the worldwide populace residing in nations encompassing the equator, where even small temperature increments could cause life-undermine. New exploration from Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) gives a guide framing how more effective cooling frameworks are doable with improvement and backing from industry. The welcomed research focus was published
Energy & Green Tech
Involving sun-powered chargers in the travel industry in nations like Greece and Cyprus won't just assist with lessening fossil fuel byproducts but, in addition, altogether decrease costs, research has found. A contextual investigation carried out on a normal Greek Island traveler's inn on Rhodes challenges the familiar way of thinking that "the travel industry is difficult to decarbonize" and "renewables are excessively costly." Involving novel mathematical displays for electric energy utilization and creation, the examination shows there will be immense money-saving advantages for the Mediterranean economy, especially when the cost of imported energy from petroleum products is at an all-time
A study led by UCLA experts could help accelerate the use of hydrogen as an environmentally safe source of energy in transportation and other applications. The group fostered a technique for anticipating platinum composites' strength and security — two vital marks of how they will proceed as impetuses in hydrogen energy units. Then, utilizing that procedure, they planned and delivered a combination that yielded amazing outcomes under conditions approximating true use. The discoveries are published in the journal Nature Catalysis. "For the maintainability of our planet, we can't continue to experience the manner in which we do, and reexamining energy
A low-cost "optofluidic" framework planned by University of Toronto scientists—and motivated by marine life like fish, crab, and krill—could assist structures with saving energy by progressively changing the presence of their outsides. "I don't believe it's extending the similarity a lot to view structures as living creatures," says Raphael Kay, an expert's understudy in the branch of materials science and design in the Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering, who's directed by Professor Ben Hatton in a similar division. "They have a digestion as far as internal and outward energy streams." Furthermore, they must adapt to changing natural circumstances in
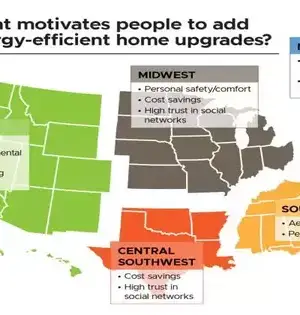
Weakening energy requests overall can assume a basic part in gathering worldwide environmental targets and successfully handling environmental change. As discharges are reduced, such efforts may eventually relieve some of the pressure on state-run administrations to decarbonize the energy supply. In any case, even after the consenting to of the Paris Arrangement in 2015, energy demand has kept on developing. From the year 2000, requests have developed at a normal pace of 1.9% consistently, and with the extension of numerous megacities around the world, its increment isn't probably going to dial back at any point in the near future. In
Shortening—or, what happens when more environmentally friendly power is free than can be conveyed to clients—has acquired a dreadful underlying meaning in the energy industry for wasting perfect, free power. In a new explainer video, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) utilizes the force of similarity to require a change in outlook, as the diminishing of wind and sun-based energy can be utilized to assist in making the matrix more adaptable and dependable. "Reduction has been seen as a hindrance to coordinating variable renewables like breeze and sunlight into the power framework, yet our examination shows it can offer some
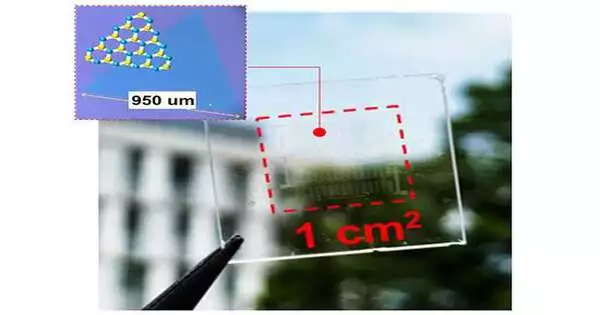
Solar-based chargers frequently get unfavorable criticism for ruining the presence of homes and organizations. However, this might be about to change. An exploration group has created a profoundly straightforward sun-oriented cell with a 2D nuclear sheet. These close-imperceptible sun-oriented cells accomplished a normal apparent straightforwardness of 79%, meaning they can, in principle, be put all over the place — building windows, the front boards of vehicles, and, surprisingly, human skin. Researchers have long attempted to develop simple solar power cells, but the necessary materials have not yet been developed. "The method by which we built the solar cell resulted in
In 2016, specialists writing in Nature recorded seven forward leaps in the way we process synthetic compounds that could impact the world and improve things. We accept we've quite recently ticked one of those off the rundown. In our review distributed in Materials Today, we tracked down an exceptionally effective and completely original method for isolating, cleansing, storing, and transporting tremendous measures of gas securely, with no waste. For what reason is this advancement so significant? We accept it will assist with conquering the critical test of hydrogen stockpiling by permitting us to securely store and transport tremendous amounts of
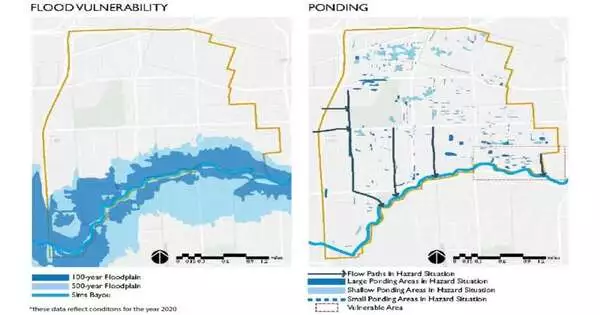
Texas A&M Superfund Research Center specialists have fostered a clever green framework intending to decrease stormwater spillover in Houston's Sunnyside neighborhood by particularly consolidating the consequences of three separate scene execution devices. The Green Foundation (GI) is an organization of interconnected green spaces that diminishes the effect of flooding in metropolitan regions. GI can also reduce the amount of foreign substances in stormwater runoff. A few devices have been made to quantify the effect of GI, flooding, and overflow. However, by joining these devices in a way never finished, Superfund scientists had the option to assemble an arrangement that wouldn't
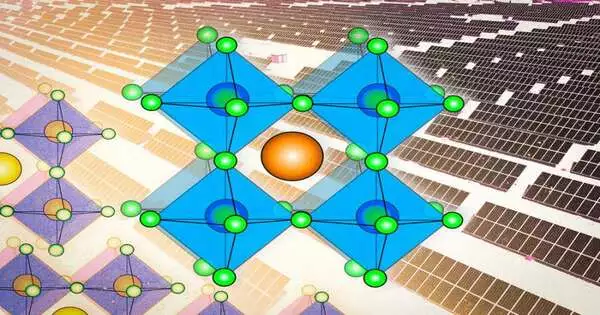
Perovskites hold the guarantee for making sun-powered chargers that can be effortlessly kept on most surfaces, including adaptable and finished ones. These materials would likewise be lightweight, modest in delivery, and as effective as the present driving photovoltaic materials, which are essentially silicon. They're the subject of expanding examination and speculation, yet organizations hoping to scale their true capacity in all actuality do need to address a few extra obstacles before perovskite-based solar power cells can be financially cutthroat. The term perovskite alludes not to a particular material, similar to silicon or cadmium telluride, other driving competitors in the photovoltaic