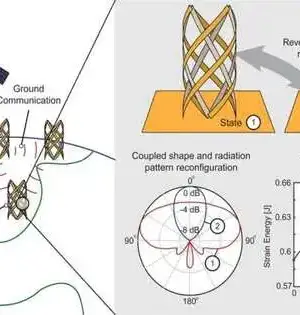
A disclosure by MIT specialists could at long last open the way to the development of another sort of battery-powered lithium battery that is more lightweight, minimized, and protected than current renditions, and that has been sought after by labs all over the planet for quite a long time. The way to achieve this likely jump in battery innovation is by replacing the fluid electrolyte that sits between the positive and negative cathodes with a much more slender, lighter layer of strong earthenware material and by replacing one of the terminals with strong lithium metal. This would enormously reduce the
Engineering
In the computer game Minecraft, everything including creatures and characters is made of little 3D blocks called voxels. Materials researchers at the College of Virginia School of Designing and Applied Science have fostered a Minecraft-like, voxelated approach that involves drops as the fundamental structure blocks to make confounded structures equivalent to human tissues and organs. Liheng Cai, an associate teacher of materials science and designing, substance designing and biomedical designing, drives the group. Jinchang Zhu, a Ph.D. understudy in Cai's Delicate Biomatter Research facility, fosters their bioprinting strategy, computerized get together of round bio-ink particles (DASP). "On a basic level,
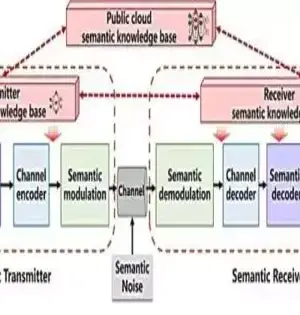
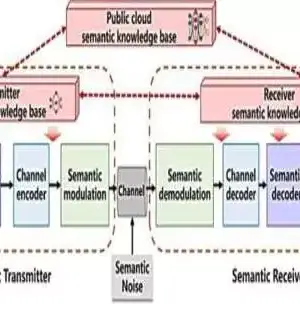
Machine learning methods enable researchers to find statistical patterns in large datasets to solve a wide range of problems, including those in neuroscience. Recent advancements have resulted in an explosion in the scope and complexity of problems to which machine learning can be applied, with accuracy that rivals or exceeds that of humans in some domains. Last year, MIT researchers announced the development of "liquid" neural networks inspired by the brains of small species: a class of flexible, robust machine learning models that learn on the job and can adapt to changing conditions for real-world safety-critical tasks such as driving
Because of the large amount of energy that lithium-particle (Li-particle) batteries can store in small spaces, they are used to power everything from smart watches to electric vehicles.When overheated, in any case, they're inclined to burst into flames or, in any event, detonate. However, a late examination distributed in Nano Letters offers a potential arrangement with another innovation that can quickly slow down a lithium-ion battery, shutting it down when it gets excessively hot. The science found in numerous batteries is basically something very similar: Electrons are moved through an electronic gadget in a circuit, starting with one terminal in
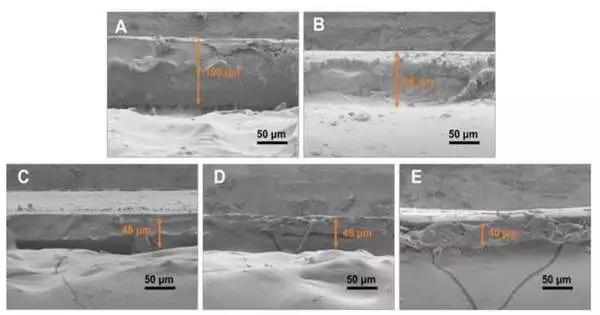
Another MIT-created heat treatment changes the tiny design of 3D-printed metals, making the materials more grounded and stronger in outrageously warm conditions. The method could enable 3D printing of elite execution edges and vanes for power-creating gas turbines and fly motors, enabling new plans with improved fuel utilization and energy proficiency. The present gas turbine edges are made through regular projecting cycles in which liquid metal is filled into complex molds and directionally set. These parts are produced using the absolute highest-intensity safe metal amalgams on the planet, as they are intended to turn at high rates in very hot
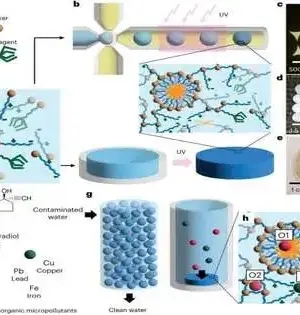
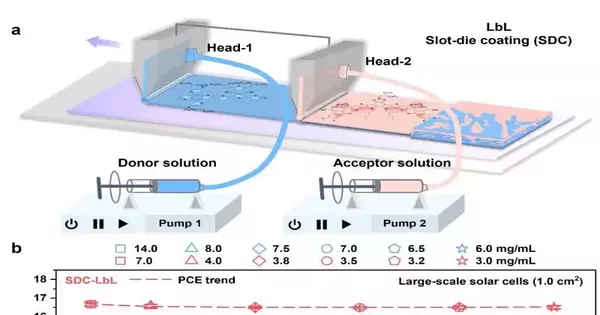
Natural photovoltaics, or sun-powered energy gadgets in view of natural semiconductors, have up to this point accomplished extremely encouraging outcomes in trial settings, both regarding proficiency and strength. However, engineers have not yet devised solid systems to manufacture these devices for a wide range of applications at a reasonable cost. Scientists at Wuhan College in China have as of late recognized a methodology that could work with the fast creation of photoactive layers for natural sun-based cells without compromising the cells' proficiency and security. Their proposed system, presented in a paper distributed by Nature Energy, depends on successive testimony, a
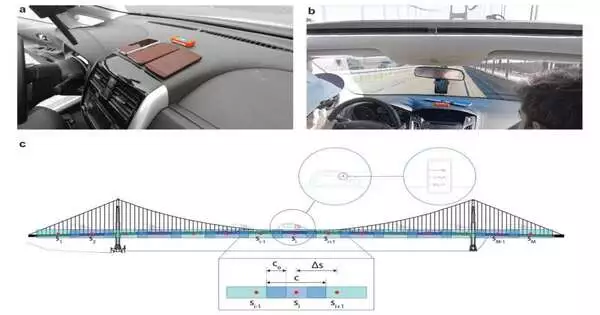
Want to find out whether the Brilliant Door Scaffold is holding up well? There could be an application for that. Another review including MIT analysts shows that cell phones set in vehicles, outfitted with unique programming, can gather helpful primary honesty information while crossing spans. In this manner, they could turn into a more affordable option in contrast to sets of sensors joined to spans themselves. "The center finding is that data about the primary strength of scaffolds can be removed from cell phone-gathered accelerometer information," says Carlo Ratti, head of the MIT Sensable City Lab and co-creator of another
Diodes permit coordinated progressions of current. Without them, current hardware would be incomprehensible. As of not long ago, they must be made from two materials with various attributes. An exploration group at the Specialized College of Munich (TUM) has now found a material that makes it conceivable to make a diode with a basic change in temperature. Producing a diode, for the most part, involves joining two semiconducting materials with various properties. By and large, these are altered types of silicon, to which various components are added to make the ideal attributes. This cycle is known as doping. Doping with
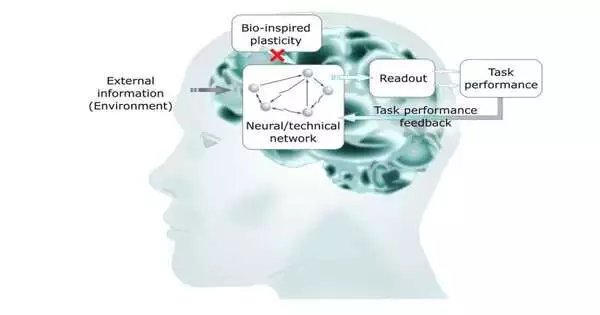
With numerical display, an examination group has now prevailed in better figuring out how the ideal functioning condition of the human mind, called criticality, is accomplished. Their outcomes represent a significant step toward naturally motivated data handling and new, exceptionally productive PC advancements and have been distributed in logical reports. "Specifically for errands, supercomputers are superior to people, for instance in the field of man-made reasoning." However, they can't deal with the range of errands in regular day-to-day existence—driving a vehicle first, then, at that point, making music and recounting a story at a party at night," makes sense to
Throughout the previous few decades, battery research has generally centered around battery-powered lithium-particle batteries, which are utilized in everything from electric vehicles to convenient gadgets and have been worked on decisively with regards to reasonableness and limit. However, nonrechargeable batteries have seen little improvement during that time, in spite of their urgent job in numerous significant applications, for example, implantable clinical gadgets like pacemakers. Presently, scientists at MIT have concocted a method for further developing the energy density of these nonrechargeable, or "essential," batteries. They say it could empower up to a half expansion in valuable lifetime, or a corresponding