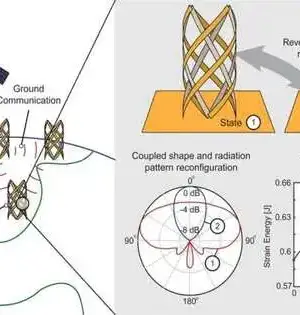
The up and coming age of telephones and remote gadgets will require new radio wires to get to increasingly high recurrence ranges. One method for making radio wires that work at many gigahertz — the frequencies required for 5G and higher gadgets — is to mesh fibers at around 1 micrometer in width. Yet, the present modern creation methods won't deal with strands that small. Presently, a group of scientists from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Designing and Applied Sciences (Oceans) has fostered a basic machine that utilizes the surface strain of water to get and control tiny
Engineering
Plastics utilized in home decorations and development materials could be supplanted with another sort of wood-based degradable plastic with semi-primary strength. Not at all like thermoplastic, the material can be separated without damage to the climate, specialists in Sweden have revealed. One of the objectives of sustainable wood composite improvement is to make materials sufficiently able to supplant fossil-based materials utilized in home development and outfitting, for example, washroom cupboards, entryways, wall-sheets, and ledges. What's more, it should be supportable, or round. "Degradability empowers circularity," says Peter Olsén, a specialist at KTH Imperial Establishment of Innovation in Stockholm. "By corrupting
Materials researchers Nicole Kleger and Simona Fehlmann have fostered a 3D printing process for making salt layouts that they can load up with different materials. One area of use is the making of profoundly permeable lightweight metal parts. This cycle is currently being attempted by the two Trailblazer colleagues. Quite recently, materials scientists scored an upset: they utilized a 3D printer to make a system out of salt, which they then loaded up with fluid magnesium. After the lightweight metal had cooled and solidified, the scientists drained out the salt system, bringing about an item made of profoundly permeable magnesium
MIT engineers designed basic microparticles that can all in all create complex behaviors, similar to how insects dig passages or gather food. Cooperating, the microparticles can create a beating clock that sways at a low recurrence. The motions can then be outfitted to drive small automated gadgets, the analysts showed. "As well as being fascinating according to a material science perspective, this conduct can likewise be converted into an on-board oscillatory electrical sign, which can be strong in microrobotic independence. There are a ton of electrical parts that require such oscillatory information, "says Jingfan Yang, a new MIT Ph.D. beneficiary
A huge group of scientists at the Maximum Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung GmbH, working with partners from Technische Universität Darmstadt, Delft College of Innovation, and KTH Regal Organization of Innovation, has observed that it is feasible to utilize AI to assist metallurgists with tracking down the ideal combination of metals to make an ideal compound. In their paper distributed in the journal Science, the gathering depicts their three-step cycle and how well it functioned when tried. Qing-Miao Hu and Rui Yang, with the Chinese Foundation of Sciences, Organization of Metal Exploration, have distributed a Viewpoints piece in a similar diary issue
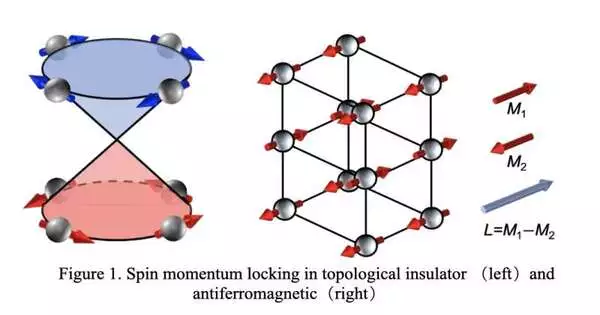
Antiferromagnetic materials, in which iotas are organized so that all adjoining particles are hostile to resemble (i.e., pointing the other way) to them, can have a few beneficial properties for the improvement of gadgets. Because of their quick twist elements and unimportant wanderer fields, they could be especially good for making rapid memory gadgets with a ton of capacity and low power utilization. In any case, engineers should have the option to proficiently recognize and control the electrical flow and pivot of minutes (i.e., the proportion of a power's propensity to make a body turn) in antiferromagnetic materials. This has
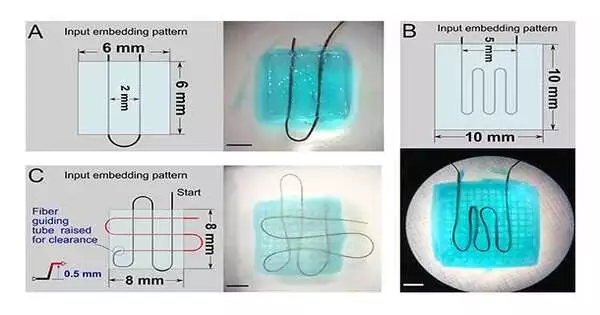
Scientists in Carnegie Mellon College's School of Design have made an open-source, monetarily accessible fiber extruder to help future examinations with hydrogels and delicate advanced mechanics. As their name suggests, hydrogels start in fluid structures as monomers. This gooey fluid, which can be made of engineered or normal materials ranging from polyester to sodium alginate, can be utilized as ink for 3D printing. The ink is first stacked into a needle, then siphoned through the needle as a slim fiber and set following 3D printing to shape a complex design, similarly that Harden O is stirred up first as a
Analysts have thought about how flooding from rising ocean levels and tempest floods will harm the assembled climate along the coast, yet what might be said about environmental change's less observable effects underneath the surface? Another focus of Colorado State University structural designers examines the hidden costs to building establishments caused by rising sea levels.They propose a strategy for review and fixing to bring down the expense related to decay from saltwater erosion. The analysts, who are essential for the NIST Place for Hazard Based People group Strength Arranging at CSU, say it means a lot to prepare — particularly
Another Northwestern College-led study discovers that high-performing water filtration frameworks, which are critical for reducing water scarcity, can also reduce cost and energy consumption. In the new review, scientists carried out an undeniable level examination of film filtration frameworks to assess cost, energy utilization, and ozone-harming substance discharges related to desalination and wastewater treatment. The specialists explicitly inspected the antifouling layers, an elite presentation filtration framework that opposes the gathering of pollutants. Although foul-safe layers might cost more cash when bought, they cost less over their lifetimes than less expensive non-foul-safe films, which require regular cleaning and should be supplanted
Designing analysts have created new high-power electronic gadgets that are more energy-effective than past advances. The gadgets are made conceivable by a novel method for "doping" gallium nitride (GaN) in a controlled way. According to Dolar Khachariya, the main creator of a paper on the work and a previous Ph.D. understudy at North Carolina State College, numerous innovations necessitate power change — where power is transferred from one organization to the next."For instance, the innovation could have to switch AC over completely to DC, or convert power into work—like an electric engine." Also, in any power change framework, most power