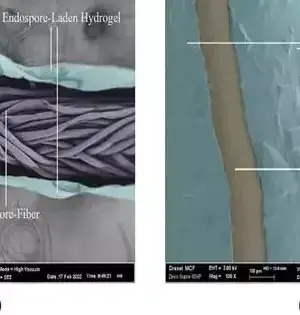
In order to deliver substantial designs that can fix their breaks, specialists from Drexel College's School of Designing are putting another curve on an old stunt for working on the solidity of cement. Fiber support has been around since the primary bricklayers blended horsehair into their mud. Anyway, the Drexel research group is taking this strategy to a higher level by transforming building-up strands into a living tissue framework that surges concrete-mending microorganisms to the site of breaks to fix the harm. As of late revealed in the diary Development and Building Materials, Drexel's "BioFiber" is a polymer fiber encased
Hi Tech & Innovation
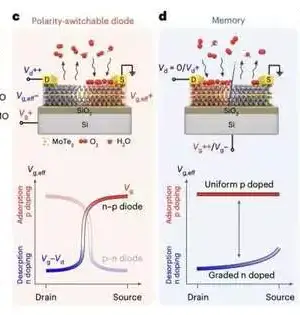
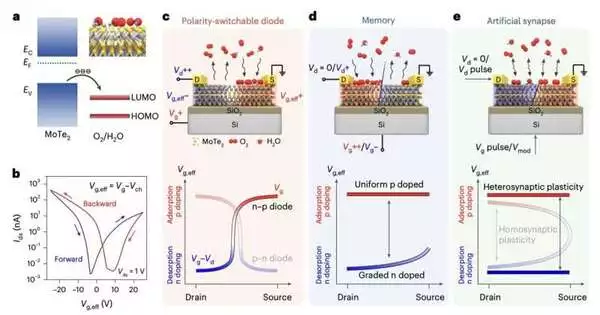
Over the course of the last many years, gadget engineers have been attempting to grow progressively more modest and exceptionally performing field-impact semiconductors (FETs) with different capabilities. FETs are urgent parts of most hardware available today that have some control over the electrical flow coursing through gadgets. Downscaling FETs to arrive at sizes beneath 10nm, nonetheless, has demonstrated extremely testing. A few examinations have in this way been investigating the capability of reconfigurable gadgets, gadgets that can change their capability as they are working, as options in contrast to traditional FETs. A significant number of the reconfigurable gadgets created lately
Over the course of the last many years, gadget engineers have been attempting to grow progressively more modest and exceptionally performing field-impact semiconductors (FETs) with different capabilities. FETs are urgent parts of most hardware available today that have some control over the electrical flow coursing through gadgets. Downscaling FETs to arrive at sizes beneath 10nm, nonetheless, has demonstrated extremely testing. A few examinations have in this way been investigating the capability of reconfigurable gadgets, gadgets that can change their capability as they are working, as options in contrast to traditional FETs. A significant number of the reconfigurable gadgets created lately
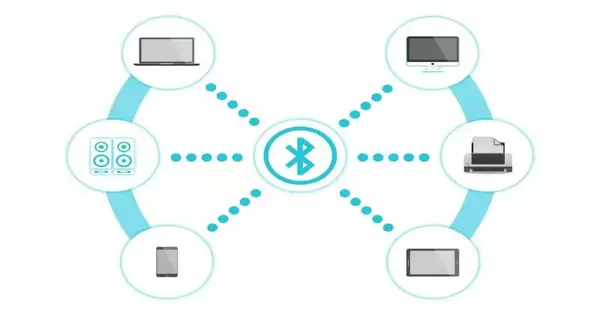
College of Sussex specialists have fostered a more energy-efficient choice to communicate information that might actually supplant Bluetooth in cell phones and other tech gadgets. With increasingly more of us possessing cell phones and wearable tech, scientists at the College of Sussex have tracked down a more productive approach to interfacing our gadgets and further developing battery duration. Applied to wearable gadgets, it really might see us opening entryways by contact or trading telephone numbers by shaking hands. Teacher Robert Skip and Teacher Daniel Roggen of the College of Sussex have fostered the utilization of electric waves, as opposed to
Your telephone might have in excess of 15 billion little semiconductors stuffed into its microchip chips. The semiconductors are made of silicon, metals like gold and copper, and protectors that together take an electric flow and convert it to 1s and 0s to impart data and store it. The semiconductor materials are inorganic, essentially derived from rock and metal. Be that as it may, imagine a scenario in which you could make these crucial electronic parts part of nature, ready to respond straightforwardly to climate change like living tissue. This is the very thing that a group at Tufts College
The eventual fate of human-machine connection points is on the cusp of an upset with the uncovering of a pivotal innovation—a stretchable high-goal multicolor synesthesia show that creates synchronized sound and light as information and yield sources. An examination group, led by Teacher Moon Kee Choi in the Branch of Materials Science and Designing at UNIST, has prevailed with regards to fostering this state-of-the-art show utilizing move printing methods, pushing the field of multifunctional shows into new domains of probability. The group's exploration is distributed in the journal Progressed Useful Materials. Customarily, multifunctional shows have been restricted to envisioning mechanical
Another Monash College project programs food to "dance" across platters, opening energetic and intuitive culinary doors for cafes and gourmet experts. The examination paper, distributed in the Procedures of the 2023 ACM Planning Intuitive Frameworks Gathering, investigates the use of food as a material through which PC projects can be sanctioned. Food connection plan specialist and lead creator of the exploration, Jialin Deng, from Monash College's Workforce of Data Innovation (IT), planned a framework enveloping a plate fitted with cathodes that can be modified to move different food components like sauces and fixings around all alone, making new blends or
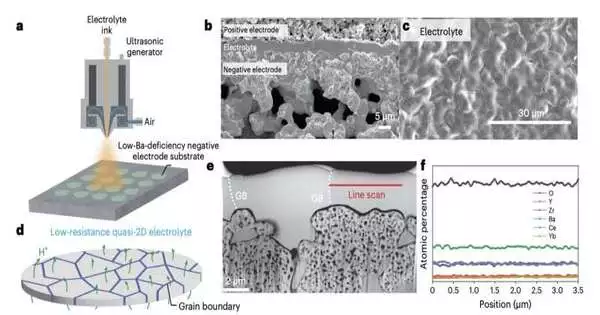
Protonic ceramic electrochemical cells (PCECs) are emerging energy advances containing electrolytes in view of proton-leading oxides and oxygen-particle guides. These gadgets could contribute to the continuous shift towards maintainable energy arrangements by helping the worldwide creation of green hydrogen and electrical power. PCECs enjoy various advantages over regular low-temperature electrochemical cells with polymer-based electrolytes. For example, they can achieve higher energy efficiencies and are viable with various kinds of fills. Notwithstanding their great execution and invaluable qualities, these cells have so far demonstrated hard work to create and carry out a huge scope. The critical justification behind this is that
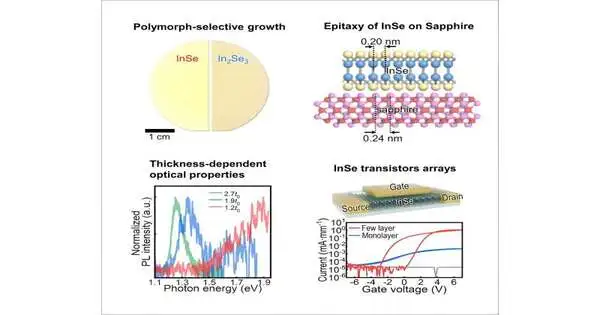
The semiconductor business today is attempting to answer a triple order: expanding processing power, diminishing chip measures, and overseeing power in thickly stuffed circuits. To satisfy these needs, the business should look beyond silicon to deliver gadgets proper for the developing job of figuring. While it is far-fetched to leave the workhorse material in the near or far future, the innovation area will require imaginative improvements in chip materials and structures to create gadgets fitting for the developing job of registering. One of the greatest inadequacies of silicon is that it must be made so flimsy in light of the
In order to extract communication signals from background noise and minimize undesirable interference over the whole radio frequency spectrum, researchers have created a novel chip-sized microwave photonic filter. The gadget is anticipated to assist next-generation wireless communication technologies in efficiently transmitting data in a space that is growing crowded with signals from gadgets like cell phones, self-driving cars, internet-connected appliances, and smart city infrastructure. “This new microwave filter chip has the potential to improve wireless communication, such as 6G, leading to faster internet connections, better overall communication experiences and lower costs and energy consumption for wireless communication systems,” said researcher