Researchers have created an algorithm that reliably measures trees five times faster than manual approaches using computer vision techniques. The method was created by academics from the University of Cambridge and provides a precise measurement of tree diameter, a crucial indicator used by scientists to track the health of forests and levels of carbon sequestration. The program produces results that are just as accurate as manual measuring techniques, but significantly faster thanks to the use of low-cost, low-resolution LiDAR sensors found in many smartphones. The results are reported in the journal Remote Sensing. Tree diameter at chest height is the
Hi Tech & Innovation
Interestingly, specialists have prepared an AI model in space, on board a satellite. This accomplishment could empower ongoing observation and decision-making for a scope of utilizations, from calamity across the board to deforestation. "Fast model inference and training on-board satellites," a summary of this project, is available on the pre-print server arXiv. Additionally, on July 21, 2023, the work was presented at the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) conference. Information gathered by remote-detecting satellites is crucial for the overwhelming majority of key exercises, including airborne planning, climate expectations, and observing deforestation. The majority of satellites cannot currently make
Adaptable, attractive sensors have acquired prevalence because of their adaptability and possible applications in significant areas of adaptable gadgets, including delicate advanced mechanics, shopper hardware, medical care, and cars. From there, the sky is the limit. They are generally used for errands, for example, route, strain and tension detection, stance, and movement following. Due to their bendability, flexible sensors outperform rigid ones in that they can adapt to a wide range of surfaces, including soft and irregularly shaped ones. Nonetheless, this benefit has come at an expense, as adaptable attractive sensors have displayed a fundamentally mediocre capacity for recognizing little
The components in electronics of the next generation will be smaller and more powerful, necessitating novel cooling strategies. According to the researchers, a new thermoelectric cooler developed by Penn State researchers outperforms commercial thermoelectric units in terms of cooling power and efficiency. The cooler also has the potential to help regulate heat in future high-power electronics, the researchers stated. "Our new material can furnish thermoelectric gadgets with exceptionally high cooling power thickness," said Bed Poudel, research teacher in the Branch of Materials Science and Designing at Penn State. "We had the option to show the way that this new gadget
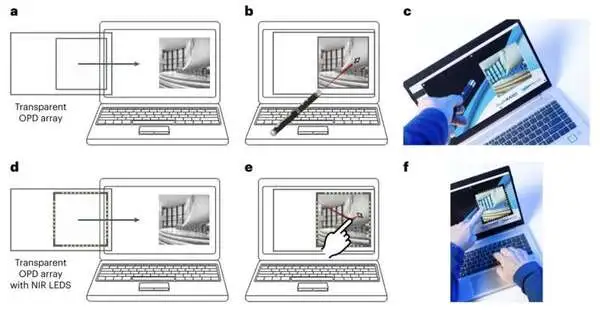
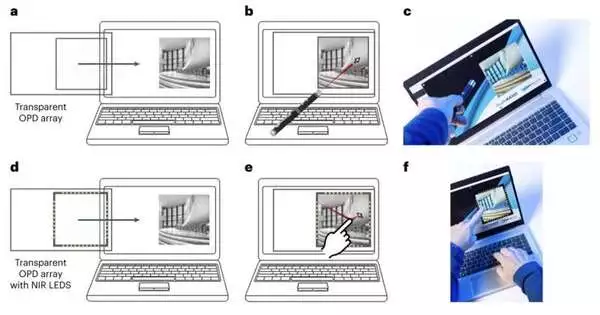
The majority of current devices, including touchscreens, mice, remote controls, keyboards, and other equipment, are operated using the sense of touch. A few specialists, in any case, have been attempting to present elective connection points that don't expect clients to contact anything, as these could be more clean. Past investigations showed that cell phones, for example, are frequently dirtier and more stacked with microbes than the typical latrine, as they are contacted frequently yet seldom cleaned. Touchless connection points would permit clients to work their gadgets without contacting them, undoubtedly restricting the microbes amassing on them. Specialists at the Dutch
The majority of current devices, including touchscreens, mice, remote controls, keyboards, and other equipment, are operated using the sense of touch. A few designers, nonetheless, have been attempting to present elective points of interaction that don't expect clients to contact anything, as these could be more sterile. As smartphones are frequently touched but rarely cleaned, previous research demonstrated that they are frequently dirtier and more contaminated with bacteria than the typical toilet. Touchless points of interaction would permit clients to work their gadgets without contacting them, no doubt restricting the microbes amassing on them. Specialists at the Dutch Association for
Parts of the world around us shift into and out of focus as we perceive it. This visual cue is one that humans use naturally, but it can be difficult for technology to mimic, especially in 3D displays. The Split-Lohmann multifocal display is a new technique developed by Carnegie Mellon University researchers for creating natural focal blur in virtual reality headsets. The eye has a lens that can change its focal length to focus on objects at a certain depth and resolve them to their finest details, while points at other depths become blurry. A crucial cue that needs to
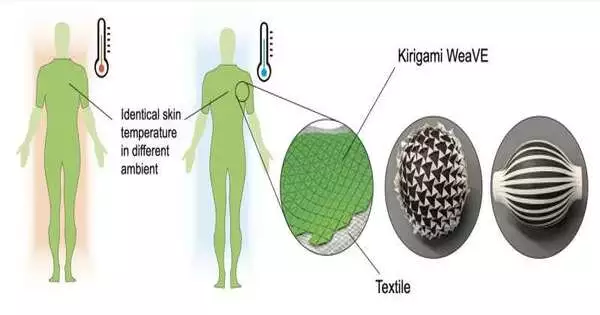
A fabric that can be switched between two different states to stabilize radiative heat loss and keep the wearer comfortable across temperature ranges is the subject of a study that was published in PNAS Nexus. Po-Chun Hsu, Jie Yin, and partners planned a texture made of a layered, semi-strong electrochemical cell sent on a nylon slice in a kirigami example to permit it to stretch and move with the wearer's body. Although a variety of breathable or insulating fabrics are used in modern clothing, each one only offers one thermal mode, which is determined by the emissivity of the fabric—the
Over the past decade, virtual reality (VR) technology has significantly improved in performance and realism, making it possible for users to immerse themselves in digital content in previously inaccessible ways. Over the next few years, the technology will most likely continue to develop, introducing new features and components that further engage the five senses. A new haptic device has recently been developed by researchers at Westlake University, the Westlake Institute for Advanced Study, and other universities in China. This device has the potential to improve the fidelity and realism of virtual experiences. The Asian art of paper folding known as
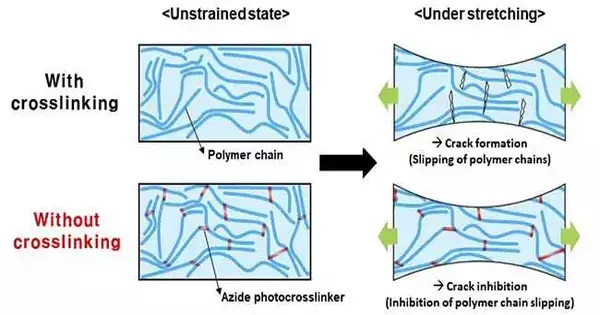
Similar to car brakes, a molecular brake exists that prevents semiconductor chains from slipping, allowing for the development of novel devices. As of late, a joint examination group led by Teacher Kilwon Cho and Ph.D. up-and-comers Seung Hyun Kim and Sein Chung from the Branch of Substance Designing at POSTECH and Teacher Boseok Kang from the Division of Nano Designing at Sungkyunkwan College (SKKU) has fostered an innovation for elite execution of natural polymer semiconductors that show both stretchability and electrical usefulness. This study was distributed in the journal Progressed Practical Materials. Rather than rigid materials, stretchable semiconductors must be