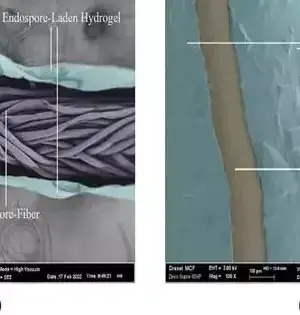
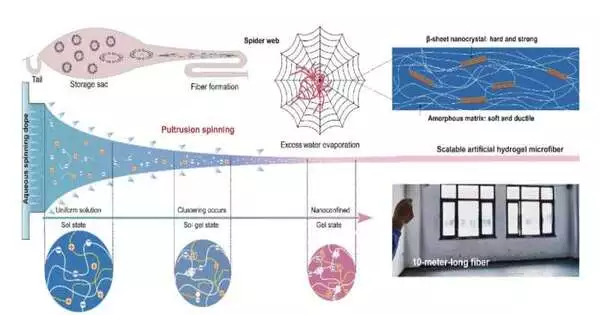
Material scientists have recently developed novel materials with a variety of advantageous properties that have the potential to improve the performance of various devices and technologies. Hydrogel-based fibers and synthetic skins, which could be used to make soft humanoid robots, prosthetics, and even comfortable smart clothes or wearable devices, are included in this category. New robust, self-healing, and crack-resistant hydrogel-based microfibers were recently developed by researchers at Donghua University in China. A method that was influenced by the way spiders spin their webs was used to create these microfibers, which were first published in Nature Communications. Shengtong Sun, one of
Hi Tech & Innovation
Flip phones are everywhere these days. Engineers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison and the University of Texas at Austin used a model that predicts how well flexible electronics will fit on spherical surfaces, ushering in a new era of seamless integration of these flexible devices with parts of the human bodyle devices with parts of the human body. body. In the future, for example, flexible bioelectronic artificial retinas implanted in human eyes could help restore vision, or smart contact lenses could continuously measure glucose levels in the body. "With a robust simulation model, we can immediately predict compliance, which can
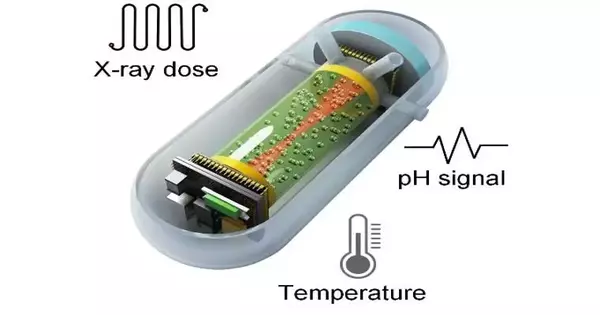
The ability to precisely target tumor tissue while minimizing damage to healthy tissue is essential in radiotherapy. Observing the portion of radiation conveyed and assimilated continuously, especially in the gastrointestinal tract, presents huge trouble. Also, existing techniques utilized for checking biochemical markers, for example pH and temperature, are lacking for a thorough assessment of radiotherapy. To address this test, a joint exploration group from the Shenzhen Organization of Trend Setting Innovation (SIAT) of the Chinese Foundation of Sciences, the Public College of Singapore (NUS), and Tsinghua University has fostered a case-formed swallowable X-beam dosimeter (with a width of 5 mm
Thanks to researchers and businesspeople who have been attempting to tap into the potential of brain-computer interfaces for enhanced cognitive abilities, interacting with computers by brain activity seems less far-fetched today. Recently, researchers at the University of Glasgow, Gao Wang, and Daniele Faccio showed that it is possible to perform basic computational imaging tasks by connecting a human brain and a computer. Similar developments may one day increase the sensing capacity of human vision and open up fresh perspectives on the neurophysics of human perception. Intelligent Computing published the results of this study. Wang and Faccio computationally reconstructed images of
In the context of technology, “SnS interface” could refer to several different things depending on the specific field or application. Solar cells will be crucial in the world's transition to renewable energy as the quest for carbon neutrality grows and as a concerning pattern of rising temperatures and natural disasters brought on by global warming continues. Now, a research group has laid the path for achieving higher open-circuit voltage in tin sulfide (SnS) solar cells, thus realizing their latent potential as a thin-film solar material. Compound semiconductors with high light absorption that are used in thin-film solar cells make them
Software and hardware for a 4D printer with applications in the biomedical industry have been developed by researchers at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M). This machine also enables the control of additional functions, such as programming the material's response to change shape in response to an external magnetic field or its electric properties to change in response to mechanical deformation. This makes it possible to create soft robotics, intelligent sensors, and substrates that send signals to various cellular systems, among other things. This research area focuses on the creation of soft multifunctional structures made of materials whose mechanical characteristics
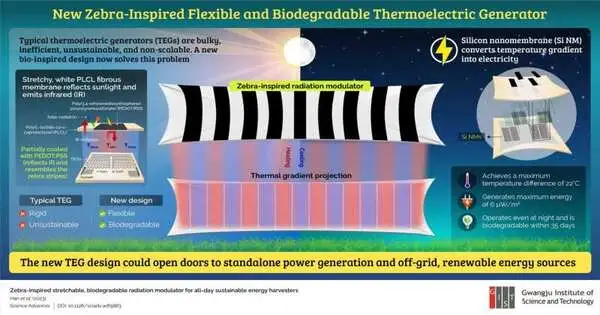
Thermoelectric generators (TEG) are gadgets that can switch temperature inclinations over completely to power. Such gadgets are very helpful for creating power for distant sensors that can't be associated with the primary power matrix. A customary TEG is made out of one side (top or base) that transmits intensity to cool off and the other side that retains heat from the sun or the climate. This, thus, creates an out-of-plane temperature inclination, which is converted into power. Notwithstanding, such prerequisites frequently lead to plans that are massive, complex, and wasteful. This, thus, makes TEGs hard to coordinate with different parts
Remember iron-on decals? All you had to do was use a home printer and special paper to print something, then use an iron to transfer it to a T-shirt. Scientists have now created a very similar method, although it prints circuits rather than images or logos. The technique can print functioning circuits onto a variety of objects, including ukuleles and teacups, as described in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Circuit boards that manage electronics are developing at the same rate as electronics themselves. Today's boards are typically robust and constructed with strong fiberglass backings. Electronics must be flexible because they
Throughout the course of recent years, material researchers and hardware engineers have been attempting to manufacture new adaptable inorganic materials to make stretchable and exceptionally performing electronic gadgets. These gadgets can be founded on various plans, like inflexible island dynamic cells with serpentine-shape or fractal interconnections, nonpartisan mechanical planes, or bunched structures. In spite of the critical advances in the manufacture of stretchable materials, a few difficulties have proven challenging to overcome. For example, materials with wavy or serpentine interconnect patterns generally have a restricted region thickness, and it is frequently both troublesome and costly to create proposed stretchable materials.
Autonomous vehicles, often known as self-driving automobiles, have long been hailed as the transportation of the future. Many diverse technologies related to signal processing, image processing, artificial intelligence deep learning, edge computing, and IoT need to be developed in order to enable the autonomous navigation of such vehicles in various contexts. The popularity of autonomous vehicles has raised many questions about their reliability and safety. An autonomous vehicle must precisely, effectively, and efficiently monitor and differentiate its surroundings as well as possible risks to passenger safety in order to guarantee a safe driving experience for the user. Autonomous cars use