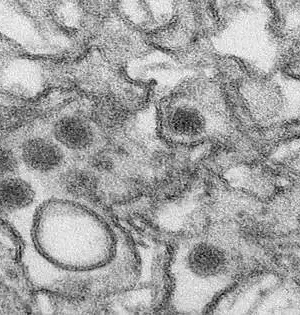
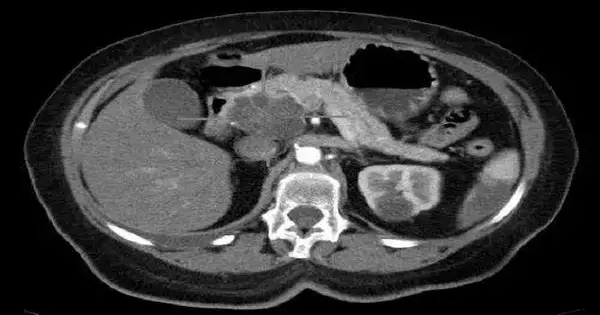
Scientists at The College of Texas MD Anderson Malignant Growth Community have found a clever immunotherapy mix, focusing on designated spots in both lymphocytes and myeloid silencer cells, that effectively reconstructed the growth-safe microenvironment (TIME) and essentially further developed the enemy of growth reactions in preclinical models of pancreatic disease. In this review, published today in Nature Malignant Growth, researchers used extensive safe profiling in mouse and human pancreatic diseases to efficiently recognize immunotherapy obstruction systems and explore potential helpful targets.They found that killing a few particular immunosuppressive components of the TIME decisively further developed endurance rates in lab models,
Immunology
Courier RNA immunization innovation, which was previously an obscure area of research, has now become family phrasing in light of the Coronavirus pandemic, and researchers are currently dealing with a mRNA influenza antibody system that, in this review, includes a first portion directed as a shot yet a second portion regulated as a mRNA nasal splash. The immunization is known as a self-intensifying mRNA antibody that targets the flu's viral nucleoprotein. That flu constructionBecause it is difficult to transform contrasted and viral surface proteins, an infection is an exceptionally moderate multifunctional protein that is a critical goal in immunization and
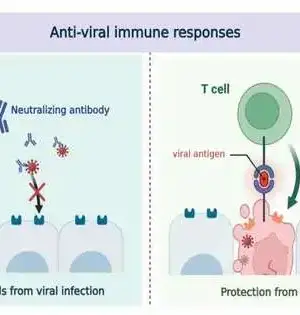
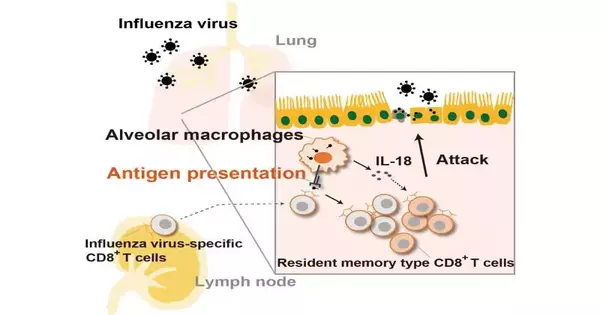
The human safe framework is a profoundly intricate organization of cells, signs, and reactions that is firmly managed to guarantee that the body can ward off disease without harming its own tissues. Presently, scientists from Japan report another manner in which the safe framework shields lung tissue from viral diseases. In a review distributed in Cell Reports, scientists from the Nara Foundation for Science and Innovation (NAIST) have uncovered that antigen-explicit executioner lymphocytes (CD8+ immune system microorganisms) quickly grow in the lungs when they experience antigen-introducing alveolar macrophages (AMs) to safeguard against viral disease. CD8+ lymphocytes give defensive resistance against
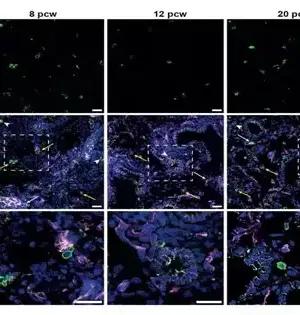
Late pressure to improve antibody adequacy has resulted in numerous new discoveries in immunology, revealing various standards with previously unknown beneficial potential.One developing part of the examination is centered around tissue-occupant memory lymphocytes (TRM cells), a sort of safe cell that gives durable security against microbes going after unambiguous organs and tissues. In another review distributed December 28, 2022, in Resistance, researchers at the College of California San Diego Institute of Medication uncovered a formerly neglected intricacy of TRM cell science in the stomach, which might usher in another age of accuracy therapeutics against contamination, malignant growth, and auto-safe illness.
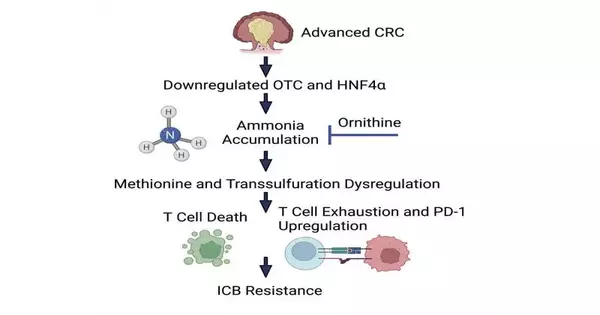
Elevated degrees of alkali in growths prompt fewer lymphocytes and immunotherapy resistance in mouse models of colorectal disease, according to new discoveries from the College of Michigan Rogel Disease Center. Analysts found that alkali hinders the development and capability of lymphocytes, which are crucial for fighting cancer resistance. The discoveries show up in cell digestion. "We identified the system of how smelling salts dysregulate lymphocyte capability and demonstrated that decreasing alkali levels utilizing FDA-approved hyperammonemia drugs can decrease growth size in a few distinct models, including metastatic colorectal disease," says Hannah Chime, Ph.D., a postdoctoral individual in disease science and
Ten small kids brought into the world without working safe frameworks and coming up short on the capacity to battle diseases are on target for better lives thanks to another quality treatment spearheaded at UC San Francisco, reports a Dec. 22 concentrate in the New Britain Diary of Medication. The kids have Artemis-SCID, an uncommon hereditary problem that is commonly treated with a bone marrow transplant from a healthy donor, preferably a matched sibling or sister. The new quality treatment permits scientists to treat recently determined children to have their own cells—adding a sound duplicate of the Artemis quality to
The presence of food-explicit IgA antibodies in the stomach doesn't keep nut or egg sensitivities from developing in kids, as per a Northwestern Medicine concentrate distributed in Science Translational Medication. Researchers examined feces samples from over 500 babies across the country and discovered that the presence of immunoglobulin A, the most well-known immunizer found in mucous films in the gastrointestinal system, does not prevent nut or egg sensitivities from developing further down the road. This revelation raises doubt about the job of immunoglobulin A, or IgA, which was recently remembered to be a defensive element against the improvement of food
According to new research published in Cell Host and Microorganism, three omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 — including two that now account for nearly half of all detailed Coronavirus contaminations in the United States — are better at evading immunization and disease-created killing antibodies than previous omicron variants. For their review, researchers tried killing antibodies in blood serum tests from immunized and once-helped or, as of late, contaminated medical care experts against a few subvariants available for use. Three subvariants stood apart for their protection from the immunizer-resistant reaction: BQ.1, BQ.1.1, and BA.2.75.2. BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 are subvariants of the BA.4
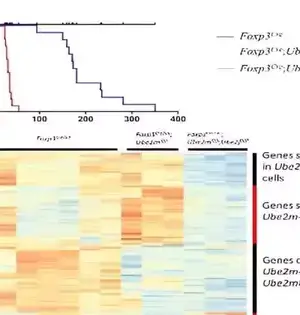
Another study discovered that patients with head and neck cancer who have more hereditary material on chromosome 9 in their disease cells live significantly longer after receiving immunotherapy than those who have less hereditary material there.Inside both typical and malignant cells, chromosomes are the 23 superstructures that house, put together, and safeguard the DNA code. Driven by scientists from the NYU Grossman Institute of Medication and the UC San Diego Moores Malignant Growth Community, the new review revolves around the human resistant framework, which can perceive disease cells as strange and assault them. Disease cells stow away from the framework
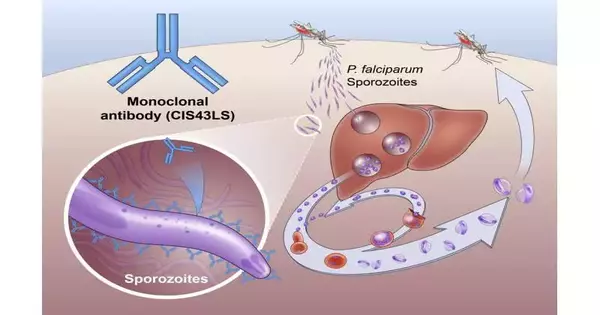
A clinical preliminary of Public Organizations of Wellbeing has been discovered.The immunizer depended on 88.2% viable at forestalling disease north of a 24-week term, showing interestingly that a monoclonal neutralizer can forestall jungle fever contamination in an endemic locale. These discoveries were distributed today in The New Britain Diary of Medication and introduced at the American Culture of Tropical Medication and Cleanliness 2022 Yearly Gathering in Seattle. "We want to grow the armory of accessible mediations to forestall jungle fever contamination and speed up endeavors to kill the illness," said Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., head of the Public Foundation of