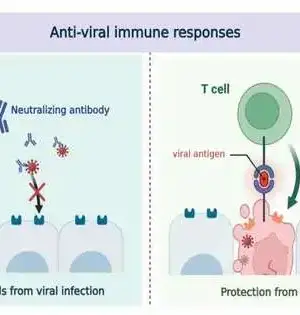
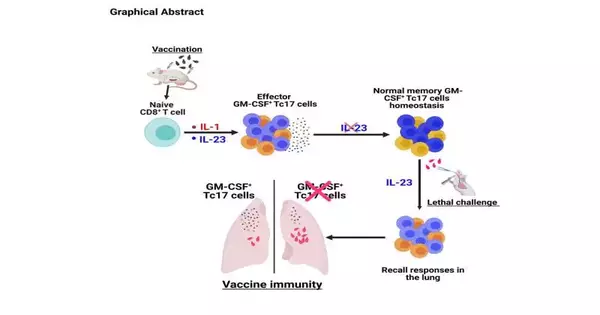
Antibodies do something amazing by really making safe cells that are enduring, frequently for many years. These safe cells create both a defensive boundary that can forestall or limit re-contamination and a memory that permits us to perceive an old intruder like an infection and to kill it before it causes illness. The immunizer in our blood that is the boundary is made by "enduring plasma cells" and, keeping in mind that the significance of these phones has forever been known, how and when they are created following an immunization has stayed a secret as of recently. An exploration group
Immunology
Scientists at the College of Colorado Institute of Medication have found that a novel microbe found in the stomach could be liable for setting off rheumatoid joint pain (RA) in individuals as of now in danger of the immune system illness. Kristine Kuhn, MD, Ph.D., academic partner of rheumatology, led a group of scientists from the Division of Rheumatology on the review, which was published on October 26 in the journal Science Translational Medication. Meagan Chriswell, an understudy at the CU Institute of Medication, is the lead creator of the paper. "Work driven by co-creators Drs. Kevin Deane, Kristen Demoruelle,
Specialists at the College of Illinois School of Veterinary Medication have shown in a mouse model that a particular kind of white blood cell, one of the body's powerful safe guards, produces cytokines that are vital for the body to obtain resistance against contagious microbes. This finding could be instrumental in creating novel, compelling parasitic antibodies. Regardless of antibodies being hailed as one of the best accomplishments of medication, responsible for controlling or killing various perilous irresistible sicknesses, no immunizations have been authorized to forestall or control human contagious diseases. This need was demonstrated to be particularly lethal during the
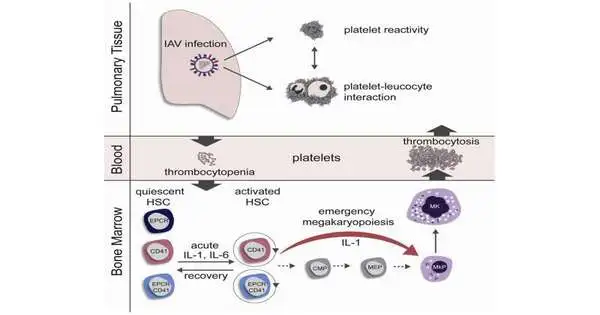
Infection-prompted respiratory diseases can become perilous. A group at the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, along with scientists in Heidelberg, has found that seasonal infection contamination restricted to the lungs likewise prompts the enactment of blood immature microorganisms and the expanded development of platelets. Platelets can cause apoplexy, as has been demonstrated in extreme instances of coronavirus. The messenger substances interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 are associated with the initiation. Cell Reports accounts for the outcomes in its web-based release from October 4, 2022. Influenza flare-ups of varying power happen consistently in the cold weather months. They are brought about by flu infections. Serious instances of
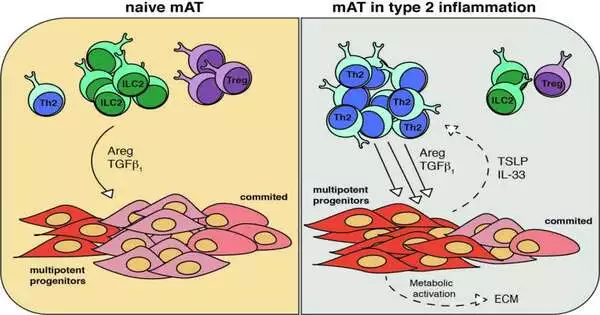
A group of scientists at the Maximum Planck Organization for Immunobiology and Epigenetics, working with partners from the Washington College Institute of Medication, the Clinical College of Vienna, the Van Andel Exploration Establishment and the USDA, have found that greasy tissue encompassing the digestive systems of mice helps to launch stomach-plaguing worms. Their paper is distributed in the journal Science Immunology. Earlier exploration has shown that mesenteric fat tissue helps the safe framework in responding to microbes and, furthermore, specific sorts of disease. In this new study, the analysts found that it likewise helps with fighting parasitic diseases. The work
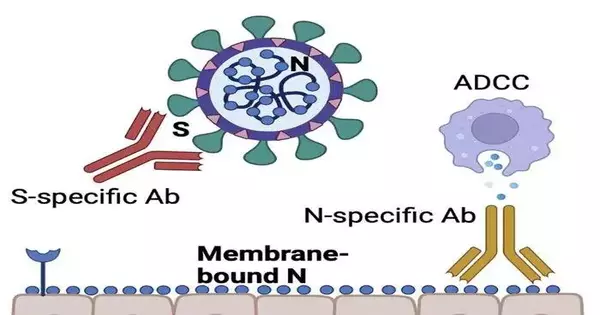
A completely new way to deal with monoclonal immunization treatment shows that focusing on the more hereditarily stable inner protein of the SARS-CoV-2 infection as opposed to the surface spike protein can likewise clear SARS-CoV-2, reports a review from Northwestern Medication and the College of Illinois at Chicago (UIC), distributed in the Diary of Clinical Examination. Some monoclonal immunizer medicines have quit working on the grounds that the spike viral protein goes through high rates of change, delivering a few viral variations impervious to current neutralizer treatments. The clever methodology could give another weapon in medicine that could save adequacy
Scientists rethink the role of ‘zombie’ cells, which anti-aging medicine has attempted to eradicate.
Not all senescent cells are unsafe "zombies" that ought to be cleared on a mission to forestall age-related illness, as per a new examination from UC San Francisco, which observed that some of them are implanted in youthful, sound tissues and advance typical fix from harm. Researchers have now seen these cells in real life in lung tissue, as well as different organs that act as hindrances in the body, like the small digestive tract, colon, and skin. When they utilized drugs called senolytics to kill these cells, wounds to lung tissues mended more leisurely. "Senescent cells can possess specialties
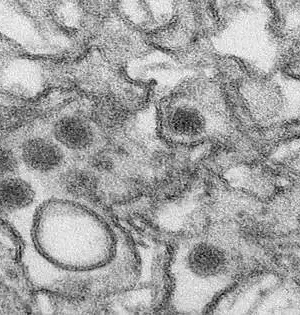
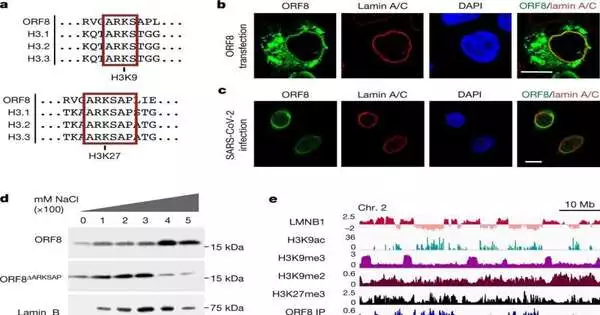
A group of scientists at the College of Pennsylvania, working with a partner from the College of Texas Clinical Branch and one more from Boston College and Boston Clinical Center, has found that the SARS-CoV-2 infection creates a protein that copies a protein that bundles DNA, forestalling a record that would normally play a part in a safe reaction. In their paper published in Nature, the gathering depicts how they contrasted proteins that bundle human DNA with proteins created by the SARS-CoV-2 infection and what doing so showed them. Lisa Thomann and Volker Thiel with the Foundation of Virology and
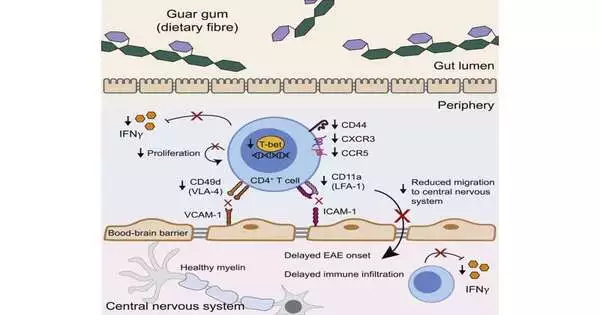
Eats lower in guar gum, a typical food additive and dietary fiber, limited irritation and delayed the beginning of various sclerosis (MS) side effects in mice, as per a new examination by individuals from the College of British Columbia (UBC) Microbial Science and Immunology division. The group's discoveries were distributed in Cell Reports. "The fast increment of immune system and fiery issues in industrialized nations over the most recent couple of decades shows dietary decisions are one natural element adding to the rate," said Dr. Lisa Osborne, senior scientist on the review and an associate teacher with UBC Microbial Science
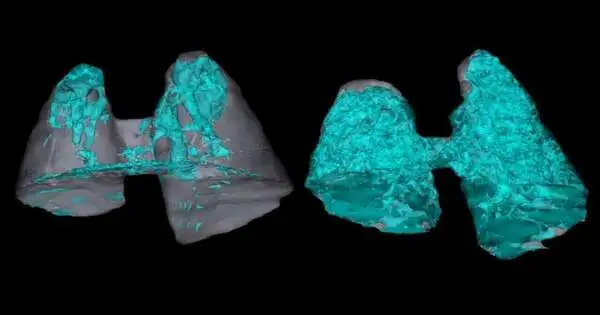
Neutrophils, the most plentiful sort of white platelet, are the body's most memorable line of defense against disease. Unfamiliar microbes can pressure the body and enact neutrophils. When enacted, neutrophils utilize different weapons to safeguard the body. Yet, in the event that they are overactivated, these weapons can harm the body's own tissues. Lung tissue is soaked with veins, making them truly helpless to neutrophil assaults. Assuming adequate extreme, intense lung wounds can prompt intense respiratory pain disorder (ARDS), the main source of death because of coronavirus. Nicholas Tonks, Caryl Boies teacher of disease research at Cold Spring Harbor Lab