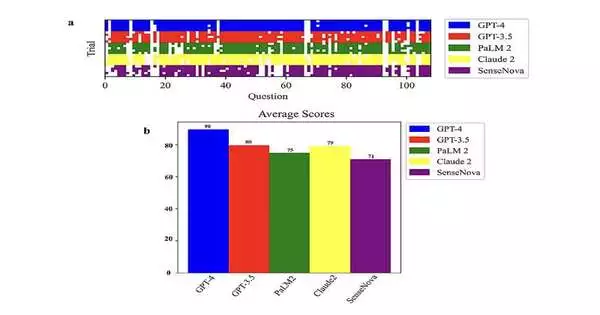
Enormous language models (LLMs) are profound learning calculations that can cycle composed or spoken prompts and create texts in light of these prompts. These models have, as of late, become progressively well known and are currently assisting numerous clients with making outlines of long reports, gaining motivation for brand names, tracking down fast responses to basic inquiries, and producing different sorts of texts. Researchers from the Mayo Clinic and the University of Georgia recently set out to evaluate the biological knowledge and reasoning abilities of various LLMs. Their paper, pre-distributed on the arXiv server, recommends that OpenAI's model GPT-4 performs
Machine learning & AI
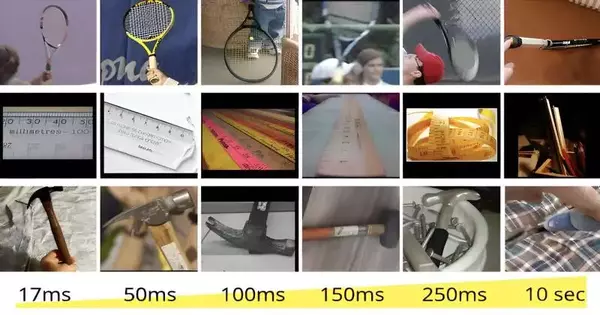
Imagine you're looking through your phone's photos when you come across an image you don't immediately recognize. On the couch, something seems to be fuzzy; might it at any point be a cushion or a coat? Of course, it clicks after a few seconds. That wad of cushion is your companion's feline, Mocha. While a portion of your photographs could be perceived in a moment, for what reason was this feline photograph considerably more troublesome? MIT Software Engineering and Computerized Reasoning Lab (CSAIL) specialists were amazed to find that notwithstanding the basic significance of understanding visual information in vital regions
A digital twin technology that could potentially improve human-robot product assembly collaboration.
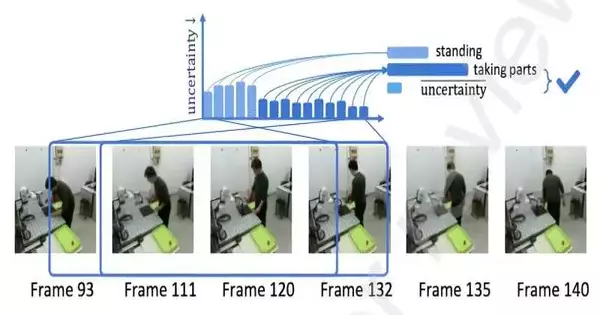
Systems based on robotics have already been implemented in a number of real-world settings, including some manufacturing and industrial facilities. In these establishments, robots can assist human workers on the assembly line and in the warehouse by assembling some product components with high precision and then handing them over to human agents, who are tasked with carrying out additional tasks. Researchers in the fields of robotics and computer science have been attempting to create increasingly sophisticated systems over the past few years with the goal of enhancing these interactions between robots and humans in industrial settings. The so-called "digital twin"
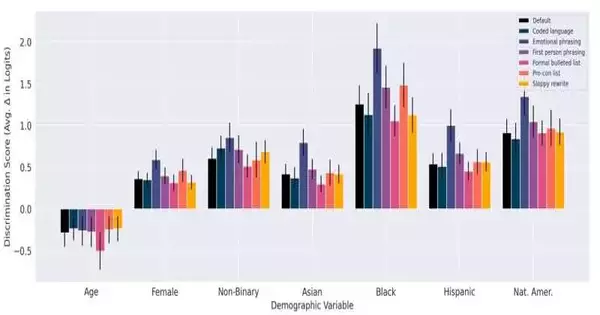
Many people were under the impression that racial bias in AI output could be contained more easily. Researchers at the simulated intelligence research organization Human-Centered say a little courteousness may simply get the job done, in some measure, on certain occasions. The authors of a report titled "Evaluating and Mitigating Discrimination in Language Model Decisions," which was posted to the preprint server arXiv on December 6, claim that using precisely crafted prompts allowed them to "significantly reduce" the number of AI-generated decisions that displayed evidence of discrimination. They made various true situations and asked Claude 2.0, a model made by
Computerized reasoning (simulated intelligence) frameworks are, in many cases, portrayed as conscious specialists ready to eclipse the human brain. However, man-made intelligence falls short of the pivotal human capacity for advancement, specialists at the College of California, Berkeley, have found. While youngsters and adults alike can tackle issues by finding novel purposes for ordinary items, artificial intelligence frameworks frequently miss the mark on capacity to see devices in another manner, as per discoveries distributed in Viewpoints on Mental Science. Man-made intelligence language models like ChatGPT are latently prepared for informational collections containing billions of words and pictures created by people.
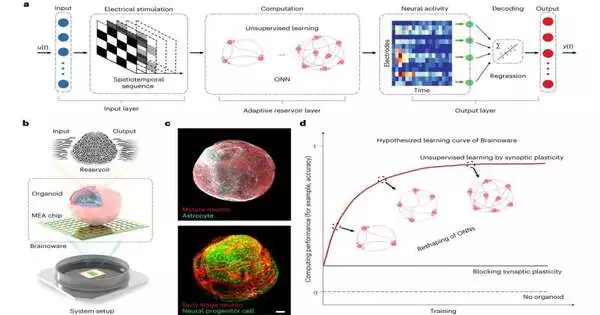
Bunches of lab-raised synapses associated with a PC are fit for rudimentary discourse acknowledgment and numerical statements. Feng Guo, a bioengineer in the Branch of Keen Frameworks Designing at Indiana College, Bloomington, said his review is a significant stage in exhibiting how cerebrum-motivated PC brain organizations can progress man-made consciousness capacities. Guo and his group developed heaps of specific undeveloped cells that formed into neurons, the principal part of the cerebrum. A commonplace cerebrum comprises 86 billion neurons, with every neuron associated with upwards of 10,000 different neurons. The bundle of neurons, known as an organoid, made in Guo's lab
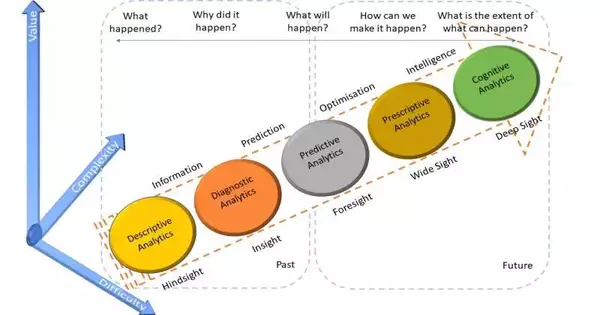
In the present information-driven world, information examination has turned into a foundation of direction. Be that as it may, regardless of the extraordinary potential, countless examination projects come up short. In a new article distributed in Importance, we dug into the complexities of information examination, underscoring the significance of issue-driven speculation in achieving effective results. A thorough examination systemInformation examination is a wide field, including information, devices, and cycles that incorporate both computational and executive cycles to extract significant experiences from handled information to pursue information-informed choices. The difficulties in information examination are amplified in the period of enormous information,
An algorithm developed by EPFL researchers can train analog neural networks with the same accuracy as digital ones, making it possible to develop more energy-efficient alternatives to power-hungry deep learning hardware. With their capacity to handle huge amounts of information through algorithmic 'learning' as opposed to customary programming, it frequently seems like the capability of profound brain networks like Visit GPT is boundless. In any case, as the degree and effect of these frameworks have developed, so have their size, intricacy, and energy utilization—the last option of which is adequately critical to raising worries about commitments to worldwide fossil fuel
A group of man-made intelligence scientists at Google's DeepMind project have fostered a sort of simulated intelligence framework that can show social learning capacities. In their paper distributed in the diary Nature Correspondences, the gathering portrays how they fostered a simulated intelligence application that showed it was fit for mastering new abilities in a virtual world by replicating the activities of an embedded "master." Most artificial intelligence frameworks, like ChatGPT, gain their insight through openness to immense amounts of information, for example, from stores on the Web. However, such a methodology, as those in the business have noted, isn't exceptionally
Specialists at Seoul Public College have as of late attempted to prepare a man-made brainpower (simulated intelligence) specialist to make collections (i.e., fine arts made by sticking different bits of materials together), imitating prestigious craftsmanship and different pictures. Their proposed model was presented in a paper pre-imprinted on arXiv and introduced at ICCV 2023 in October. "Arrangement craftsmanship requires high human imaginativeness, and we considered what montage works of art made by simulated intelligence would seem to be," the writers told Tech Xplore by email. "Existing artificial intelligence picture-age devices like DALL-E or StableDiffusion can as of now produce collection