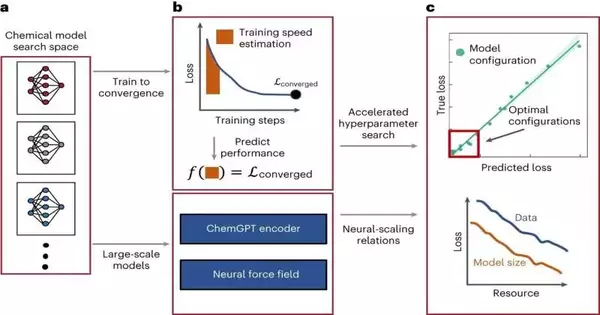
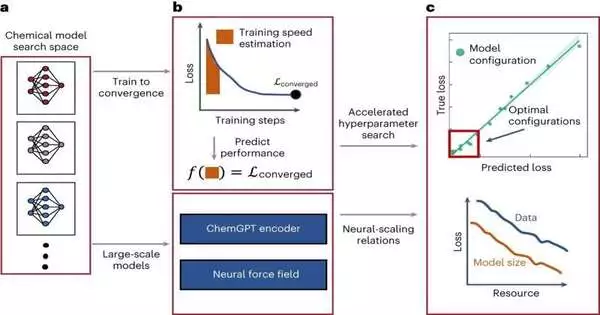
Profound brain organizations (DNNs) have ended up being exceptionally encouraging apparatuses for dissecting a lot of information, which could accelerate research in different logical fields. For example, throughout the course of recent years, some PC researchers have prepared models in view of these organizations to dissect substance information and distinguish promising synthetics for different applications. Scientists at the Massachusetts Establishment of Innovation (MIT) have, as of late, done a review researching the brain scaling conduct of enormous DNN-based models prepared to create invaluable compound structures and learn interatomic possibilities. Their paper, distributed in Nature Machine Knowledge, demonstrates the way that
Machine learning & AI
Profound brain organizations (DNNs) have ended up being exceptionally encouraging apparatuses for breaking down a lot of information, which could accelerate research in different logical fields. For example, throughout recent years, some PC researchers have prepared models in view of these organizations to examine synthetic information and distinguish promising synthetic compounds for different applications. Scientists at the Massachusetts Establishment of Innovation (MIT) have, as of late, done a review researching the brain scaling conduct of huge DNN-based models prepared to produce favorable compound creations and learn interatomic possibilities. Their paper, distributed in Nature Machine Knowledge, demonstrates the way that rapidly
In a noteworthy blend of atomic innovation and AI (ML), a group of researchers at the U.S. Branch of Energy's (DOE) Argonne Public Lab has uncovered a critical finding in keeping up with wellbeing and productivity in a kind of cutting-edge atomic reactor known as a sodium-cooled quick reactor (SFR). A SFR is a kind of atomic reactor that utilizes fluid sodium to cool its center and effectively makes power without carbon by dividing weighty iotas. While they aren't utilized economically in the U.S., many accept that these reactors could alter power creation and assist with diminishing atomic waste. Notwithstanding,
Engineers from the Software Engineering Division at Binghamton College, State College of New York, have customized a robot guide canine to help the outwardly hindered. The robot pulls on its chain. Binghamton College colleague Teacher Shiqi Zhang, alongside PhD understudy David DeFazio and junior Eisuke Hirota, have been dealing with a mechanical seeing-eye canine to increase openness for outwardly impeded individuals. They introduced an exhibit in which the robot canine drove an individual around a lab foyer, certainly and cautiously answering mandate input. Zhang made sense of a portion of the thinking behind beginning the venture. "We were shocked that
Scientists from MIT and NVIDIA have created two strategies that speed up the handling of scanty tensors, a sort of information structure that is utilized for elite execution processing undertakings. The corresponding strategies could bring about huge upgrades to the presentation and energy-proficiency of frameworks like the gigantic AI models that drive generative, man-made reasoning. Tensors are information structures utilized by AI models. Both of the new techniques look to proficiently take advantage of what's known as sparsity—zero qualities—in the tensors. While handling these tensors, one can skirt the zeros and save money on both calculation and memory. For example,
The most deadly element of any disease is metastasis, the spread of malignant growth cells all through the body. A new examination by Penn State uncovers interestingly the mechanics behind how bosom malignant growth cells might attack sound tissues. The revelation, showing that an engine protein called dynein powers the development of malignant growth cells in delicate tissue models, offers new clinical focuses against metastasis and can possibly, in a general sense, change how disease is dealt with. "This disclosure denotes a change in perspective in numerous ways," said Erdem Tabdanov, partner teacher of pharmacology at Penn State and a
Man-made brainpower now wears different caps in the work environment, whether it's composing promotion duplicates, taking care of client service demands, or separating requests for employment. As innovation proceeds with its climb and capacities, the idea of partnerships oversaw or possessed by computer-based intelligence turns out to be less implausible. The lawful structure as of now exists to permit "zero-part LLCs." How might an artificial intelligence-worked LLC be treated under the law, and how might computer-based intelligence answer legitimate liabilities or outcomes as the proprietor or chief of an LLC? These inquiries address a phenomenal test confronting legislators: the guideline
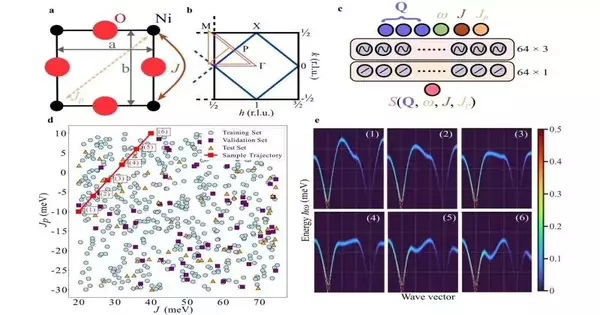
Specialists at the Branch of Energy's SLAC Public Gas Pedal Research Facility have exhibited another way to peer further into the mind-boggling conduct of materials. The group uses the force of AI to decipher sound excitations and the aggregate swinging of nuclear twists inside a framework. This pivotal examination, distributed as of late in Nature Correspondences, could make tests more productive, giving ongoing direction to specialists during information assortment, and is essential for a venture driven by Howard College, including scientists at SLAC and Northeastern College, to utilize AI to speed up research in materials. The group made this new
Disregard the cloud. Northwestern College engineers have fostered a new nanoelectronics gadget that can perform precise AI characterization undertakings in the most energy-effective way yet. Utilizing 100 times less energy than current advancements, the gadget can crunch a lot of information and perform man-made reasoning (computer-based intelligence) undertakings continuously without radiating information to the cloud for investigation. With its little impression, super low power utilization, and absence of slack opportunity to get investigations, the gadget is great for direct joining into wearable hardware (like brilliant watches and wellness trackers) for ongoing information handling and close-moment diagnostics. To test the idea,
To look at the worldwide province of computer-based intelligence morals, a group of scientists from Brazil conducted a methodical survey and meta-investigation of worldwide rules for man-made intelligence use. Distributing October 13 in the diary examples, the analysts saw that, while the majority of the rules esteemed security, straightforwardness, and responsibility, not very many esteemed honesty, licensed innovation, or kids' freedoms. Moreover, the majority of the rules depicted moral standards and values without proposing down-to-earth strategies for executing them or pushing for lawfully restricting guidelines. "Laying out clear moral rules and administration structures for the organization of artificial intelligence all