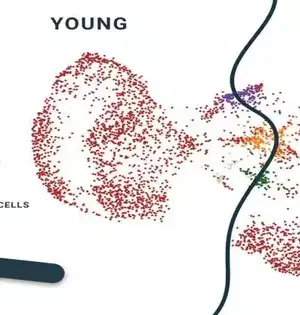
Articular cartilage is the smooth, white tissue that covers the ends of bones where they come together to form joints. When it gets damaged, it can lead to joint pain, stiffness, and other problems. The fact that researchers have uncovered new mechanisms for healing this tissue is an important step forward in understanding how to treat joint injuries and disorders. Understanding how the environment of the knee joint affects cartilage cells is critical for joint health. Understanding the mechanisms of cell-driven cartilage degeneration can aid in the development of effective pharmaceutical interventions for osteoarthritis. Musculoskeletal diseases, such as osteoarthritis, are
Medical research
Researchers have developed a new method for delivering drugs to brain tumors in children that involves using a type of nanoparticle called "lipid-calcium-phosphate" (LCP) nanoparticles. These nanoparticles are designed to carry drugs directly to brain tumors while avoiding healthy brain tissue. Researchers at Mount Sinai Health System and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center have developed a new drug delivery strategy that employs nanoparticles to enable more effective and targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs to children with brain tumors. The technology enables the targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs to specific brain tumor locations while sparing normal brain regions. According to their
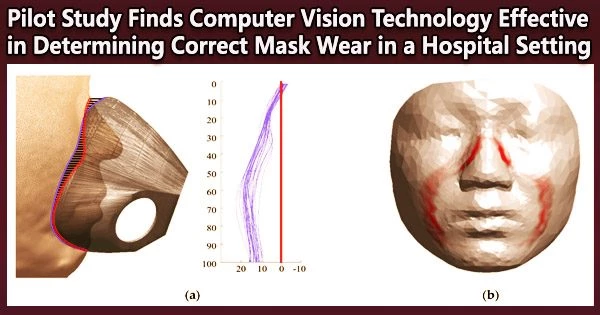
Universal mask use was a key tactic for stopping the spread of COVID-19 in early 2020, before COVID-19 vaccinations and efficient treatments were widely accessible. Hospitals and other places with mask requirements, however, had a problem. Manually reminding patients, guests, and employees to wear masks was necessary, which required a lot of time and labor. Researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) set out to test a tool to automate monitoring and reminders about mask adherence using a computer vision algorithm. The researchers
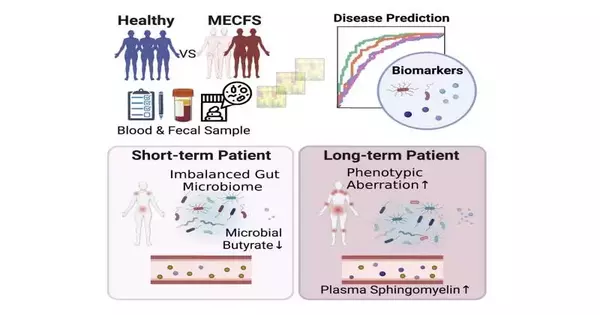
Throughout the course of recent years, the development of long-haul impacts related to the coronavirus has prompted an expanded center around an infection with comparative trademarks and side effects: myalgic encephalomyelitis/ongoing fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). Two examinations distributing February 8 in the diary, Cell Host and Microorganism, are investigating ME/CFS as it connects with the microbiome and the metabolites that microbial species produce. The two examinations tracked down the fact that ME/CFS is related to decreased levels in the gastrointestinal microbiome of microorganisms known to deliver the unsaturated fat butyrate. These microbiome disturbances could explain, to some extent, how the safe
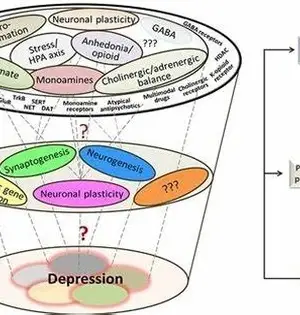
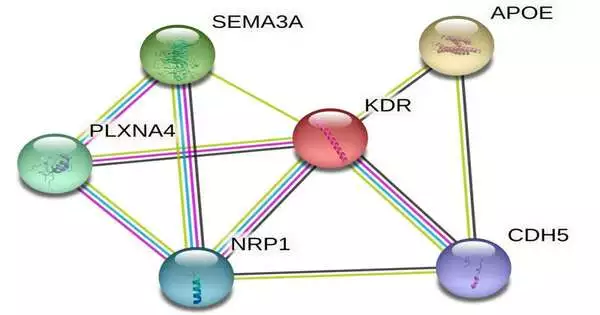
A University of New Mexico nervous system specialist, Rawan Tarawneh, MD, has distinguished an exceptional biomarker that could prompt new symptomatic tests to work on the recognition of nascent Alzheimer's illness before side effects show up. In a paper distributed in the Chronicles of Clinical and Translational Nervous System Science in November 2022, Tarawneh and her partners recognized another protein in the cerebrospinal liquid that can dependably distinguish endothelial injury—hharm to the cells covering the little veins in the mind—iin Alzheimer's illness. Utilizing this biomarker, Tarawneh's group observed that endothelial injury is a significant supporter of mental hindrance in even
Nanopore technology is a method for detecting and analyzing single molecules in real-time. In the context of neurodegenerative diseases, nanopore-based sensing devices can be used to explore disease-related changes in biomolecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins. Tau and tubulin proteins are one of the leading causes of many neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. The accumulation of these proteins in the brain is mostly responsible for the advancement of neurodegenerative diseases. Inspired by one of her doctoral students who wanted to explore tau and tubulin proteins, Jiali Li, a physics professor at the University of Arkansas, and her
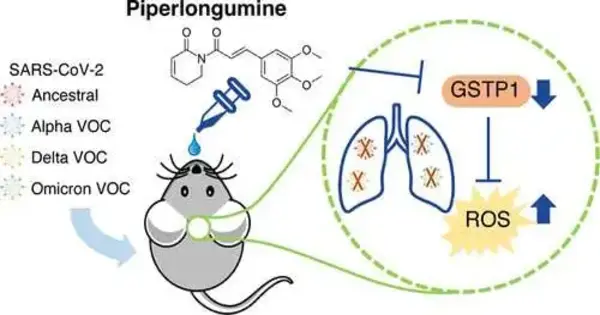
Another review, driven by Gonçalo Bernardes, bunch pioneer at the Instituto de Medicina Sub-atomic Joo Lobo Antunes (iMM; Portugal) and teacher at the College of Cambridge (Cambridge, UK), distributed as of late in the ACS Focal Science diary, reports the revelation of a compound effective in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 that could be extensively applied to treat various variations of the infection. The scientists found that the compound piperlongumine (PL), removed from the long pepper, the normal fixing utilized most widely in Indian clinical frameworks, has a strong antiviral impact in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 in mice. "We found that
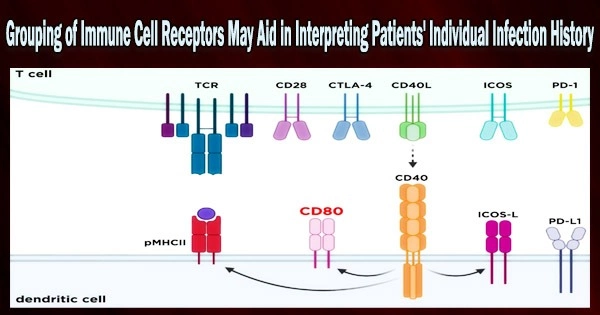
According to a study published today in eLife, grouping of pathogen-recognizing proteins on immunological T cells may be crucial for determining whether someone has ever been infected. The strength and targets of a person's T-cell response to infection or vaccination are more difficult to evaluate for researchers, but the findings point to a potential new strategy. Tests detecting antibodies against a pathogen are frequently used to discover symptoms of a prior infection. One day, this patient data might be helpful for diagnosing illnesses, directing care, or advancing the investigation and creation of fresh remedies and vaccinations. Immune T cells help
RNA Analysis is Automated Using New Open-Source Software to Speed Both Research and Drug Development
A new software tool has been unveiled by Scripps Research researchers to investigate RNA (ribonucleic acid) molecules, which play a variety of crucial roles in organisms. In situations such as fundamental research and drug development, the open-source program “Pytheas,” which was disclosed on May 3, 2022, in Nature Communications, expedites the process of defining and quantifying RNAs. The software is made primarily to examine RNA data obtained using the mass spectrometry technique. “Mass spec” is frequently used to analyze RNA molecules that are changed in some way rather than being just chains of unaltered RNA nucleotides. Among their demonstrations, the
A Michigan Medicine study identified another possible goal for treating osteoarthritis, a crippling joint disease that affects nearly 31 million Americans and is a major source of disability worldwide. A group of scientists led by Tristan Maerz, Ph.D., a biomedical designer and partner teacher in the Branch of Muscular Medical Procedure at Michigan Medicine, has revealed beforehand obscure cell types in the joint that arise after a physical issue and drive the beginning of osteoarthritis. Clinically, osteoarthritis presents as an intricate illness, with patients experiencing joint firmness, decreased versatility and capability, and most often, steady torment. Osteoarthritis patients usually live