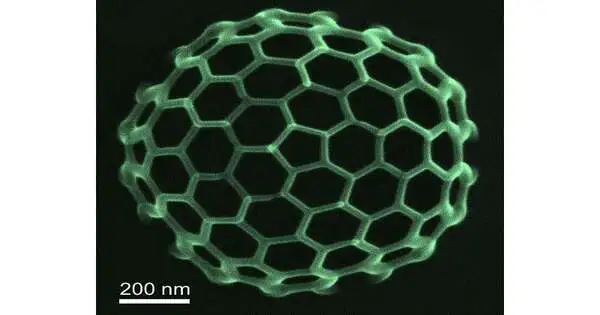
Specialists at the Georgia Organization of Innovation have fostered a light-based method for printing nano-sized metal designs that is fundamentally quicker and less expensive than any innovation presently accessible. A versatile arrangement could change a logical field long dependent on innovations that are restrictively costly and slow. The advancement can possibly free new innovations once again from labs and into the world. Mechanical advances in many fields depend on the capacity to print metallic designs that are nano-sized—a scale many times less than the width of a human hair. Sourabh Saha, aide teacher in the George W. Woodruff School of
Nanotechnology
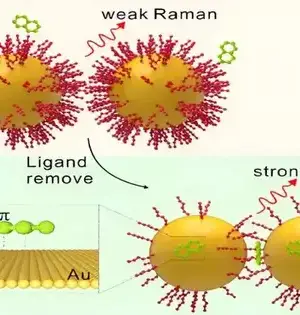
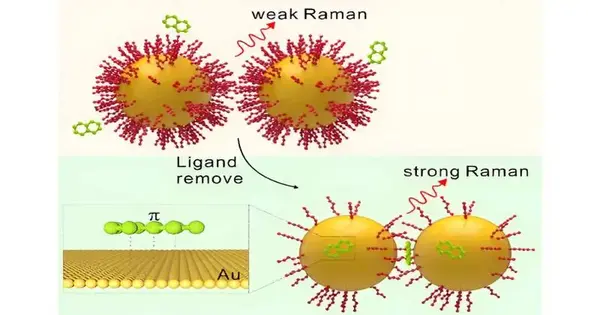
An exploration group led by Prof. Yang Liangbao from the Hefei Foundations of Actual Science at the Chinese Institute of Sciences (CAS) has noticed the communications between fragrant particles and Au surfaces on a solitary Au nanodimer by surface-improved Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The review is distributed in Scientific Science and was chosen as the title page of the issue. Interface connections between fragrant atoms and respectable metals are conspicuous in key science and mechanical applications. In any case, because of the limit of portrayal innovation and the intricacy of exploratory circumstances, there is as yet an absence of quantitative comprehension
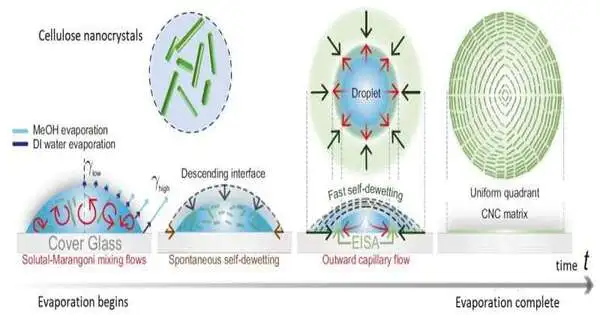
A KAIST research group has fostered an enemy of icing and de-icing film covering innovation that can apply the photothermal impact of gold nanoparticles to modern locales without the requirement for warming wires, intermittent splash or oil covering of liquid catalyst substances, or substrate plan changes. The gathering led by Teacher Hyoungsoo Kim from the Division of Mechanical Designing (Liquid and Connection Point Research Center) and Teacher Dong Ki Yoon from the Branch of Science (Delicate Material Get Together Gathering) uncovered that they have fostered a unique method that can consistently design gold nanorod (GNR) particles in quadrants through straightforward
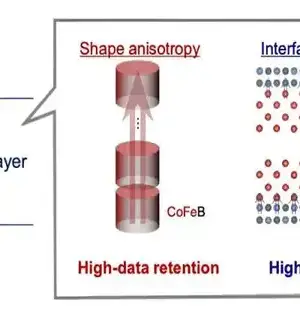
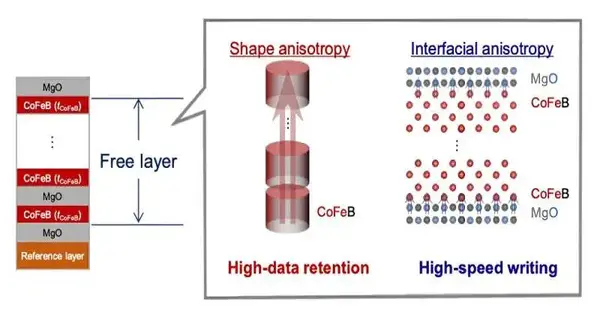
Specialists at Tohoku College have created rules for a solitary nanometer attractive passage intersection (MTJ), considering execution fitting to meet the prerequisites of different applications, going from computer-based intelligence (IoT) to cars and space innovations. The advanced will prompt elite execution of spintronic non-unstable memory, viable with cutting-edge semiconductor innovations. The subtleties were distributed in the diary of npj Spintronics on January 4, 2024. The vital quality of non-unstable memory is its capacity to hold information without even a trace of an outer power source. Subsequently, broad improvement endeavors have been coordinated towards non-unstable memory on account of its capacity
For around 20 years, it has been feasible to change surfaces through nanoparticles with the goal that they concentrate or control light in an ideal manner or trigger different responses. Such optically dynamic nanostructures can be tracked down in sun-based cells and natural or substance sensors, for instance. To extend the scope of uses for these nanostructures, specialists at the Foundation of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis (Graz College of Innovation) and the Graz Focus of Electron Microscopy (ZFE) have been working for over 10 years on assembling level nanostructures, yet specifically mind-boggling, detached 3D designs. The group led by Harald
Instruments smaller than a human hair are being intended to destroy infection-safe microscopic organisms and battle malignant growth. Dr. Ana Santos becomes profound while depicting what happened quite a while prior: Her granddad and an uncle passed on from urinary tract diseases, and an old buddy surrendered after an incidental cut got contaminated. She was stunned. During a time of anti-infection agents, such mishaps shouldn't have occurred. Rise and fall of anti-infection agents"My relatives were passing on from diseases," said Santos, a microbiologist at the Wellbeing Exploration Establishment of the Balearic Islands, or IdISBa, in Spain. "I began to understand
Specialists have shown that treated steel and other metal compounds covered with hexagonal boron nitride, or hBN, display non-stick or low-erosion characteristics while also working on long-term assurance against brutal consumption and high-temperature oxidation in air. The work has been distributed at cutting-edge material connection points. Metal composites—combinations of at least two metals—are made to have major areas of strength and are impervious to erosion or oxidation. By adding coatings, or "defensive layers," to make those materials much harder, researchers could upgrade existing items and empower the production of new, inventive ones. For instance, reinforcing may help the capacity of
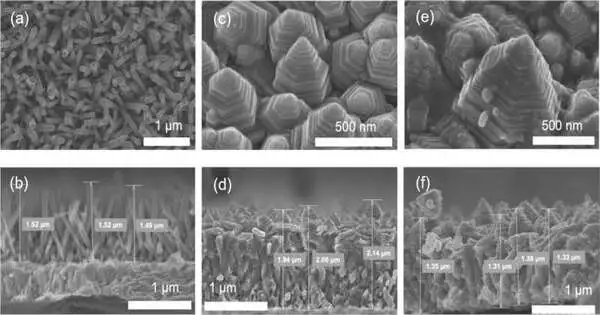
An exploration group comprising individuals from the Egyptian Oil Exploration Foundation and the Practical Materials Designing Research Center at the Toyohashi College of Innovation has fostered a clever, superior-execution photoelectrode by developing a zinc oxide nanopagoda exhibit with an interesting shape on a straightforward terminal and applying silver nanoparticles to its surface. The zinc oxide nanopagoda is characterized by having many step structures, as it includes piles of contrastingly estimated hexagonal crystals. What's more, it shows not very many gem surrenders and magnificent electron conductivity. By beautifying its surface with silver nanoparticles, the zinc oxide nanopagoda exhibits photoelectrode gains in
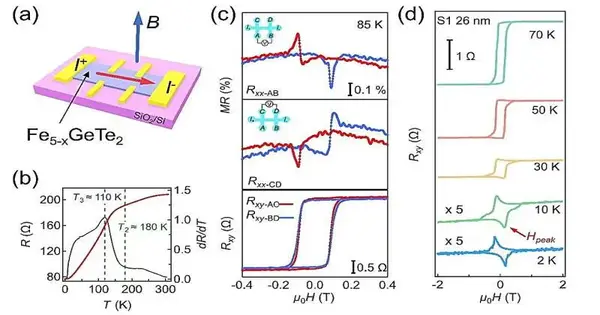
As per a review distributed in ACS Nano, an exploration group has uncovered a clever non-complementary antisymmetric magnetoresistance and eccentric Corridor impact in a two-layered (2D) van der Waals (vdW) ferromagnetic Fe5-xGeTe2, which might begin with the offbeat charge exchanging of the attractive spaces. 2D ferromagnets with high Curie temperatures give a rich stage to investigating the intriguing peculiarities of 2D attraction and the capability of spintronic gadgets. As an ordinary layered ferromagnetic material, Fe5-xGeTe2 has drawn in escalated consideration because of its high Curie temperature. Be that as it may, because of its mind-bogglingly attractive ground state and attractive
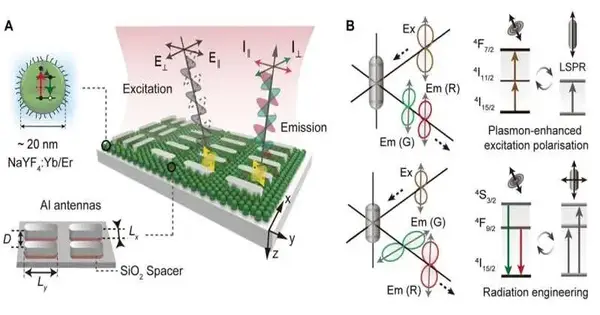
Public College of Singapore (NUS) scientists have acquainted themselves with an upconversion plasmonphore stage with precise command over the polarization of isotropic upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs). This is accomplished by coupling upconversion activators with painstakingly planned anisotropic hole plasmon mode-upheld metasurfaces. Photon-plasmon coupling in cross-breed frameworks is an incredible asset for exploring light-matter connections at the nanoscale, with possible applications in different fields, including scaled-down strong state lasers, ultracompact spectrometers, on-chip sub-atomic detection, and polarimetric imaging. Lanthanide-doped UCNPs are especially encouraging as quantum light sources because of their particular outflow tops, huge stir-up shift, and fantastic photostability. The trademark spectroscopic fingerprints