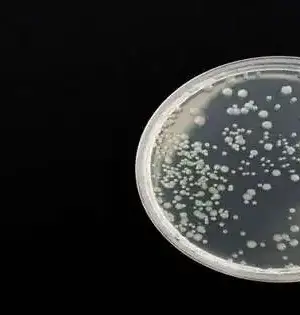
A Skoltech research group made a precise survey of distributions on in vitro biocompatibility of carbon nanotubes and recognized the assembling boundaries that could make them OK for living creatures. The researchers chose around 200 papers distributed throughout recent years and carried out a factual examination of the detailed exploration. It worked out that carbon nanotubes utilized as substrates are OK for living cells and, hence, could be utilized for wearable, implantable, and material gadgets. The paper highlighting the group's discoveries was distributed in the journal RSC Advances. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) hold a lot of promise for biomedical applications: tissue
Nanotechnology
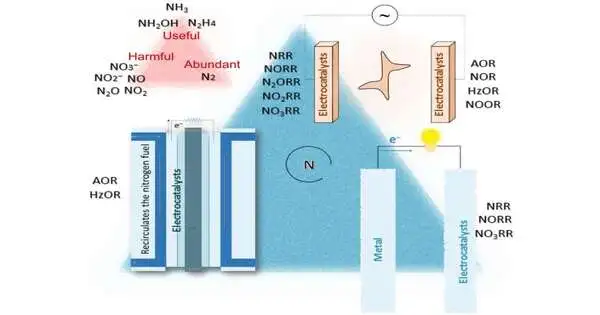
Over a long time ago, Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch industrialized a cycle that could deliver smelling salts from nitrogen promptly accessible in the air, making monetarily feasible compound manure fit for further developing yield creation. The Haber-Bosch process is still used to grow crops all over the world.It saved millions from starvation, yet it, alongside other human activities, is upsetting the planet's nitrogen cycle, warming the globe, and possibly gambling with the strength of millions. That is the reason this moment is an opportunity to audit the logical work in progress to rebalance the nitrogen cycle, as per Xuping
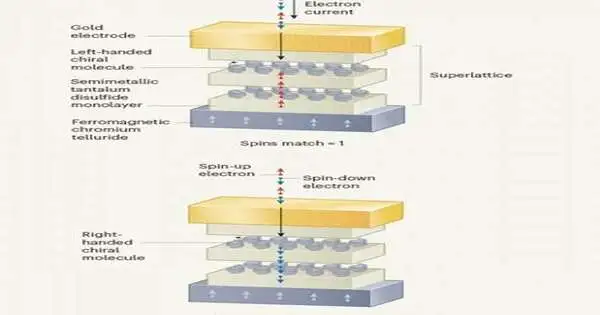
Chirality depicts a particle that can't be superimposed on its own perfect representation. Two mathematically unique chiral atoms of similar equation, recognized by the R-and S-design, display different optical properties. More intriguingly, a material block made of the equivalent chiral particles can work like a security door when electrons swarm through, giving admittance to electrons with a similar twist character. That is, electrons in the turn-up state will clear their path through the chiral atoms that favor the turn-up state, while electrons in the twist-down state will get impeded and avoided, or the other way around. This inborn sifting impact,
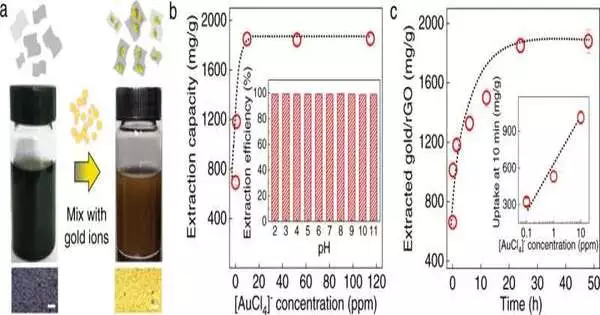
A long time ago, chemists trusted in the presence of the savant's stone, a substance that could transform modest substances into valuable gold. Presently, researchers from The University of Manchester, Tsinghua University in China, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences have shown that graphene can be a sort of savant's stone, permitting gold extraction from squander containing just the following measures of gold (down to a billionth of a percent). This new, apparently mystical use of graphene works clearly: add graphene into an answer containing hints of gold and, after a couple of moments, unadulterated gold shows up on graphene
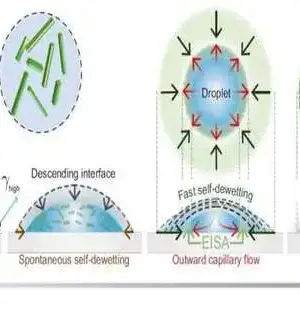
Scientists have published work in Advanced Materials depicting a fast and basic strategy to shape requested varieties of gold nanoparticles with plasmonic properties. Plasmonic nanoparticles arranged by colloidal science have favorable electronic, optical, and attractive properties, yet their execution into useful gadgets is restricted by tedious and difficult-to-scale steps like ligand trade, purging, and self-gathering. In this work, scientists from the Institute of Materials Science of Barcelona (ICMAB, CSIC) and the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), show the planning of gold nanoparticles requested exhibits straightforwardly on substrates utilizing an unusual bottom-up wet-compound engineered approach. The analysts applied warm nanoimprint
Multitudes of microrobots infused into the human body could unblock inner clinical gadgets and keep away from the requirement for additional medical procedures, as per a new exploration from the University of Essex. The review is from when researchers first developed appealing microrobotics to eliminate stores in shunts—normal inner clinical devices used to treat various conditions by emptying excess liquid out of organs. Shunts are inclined to fail, frequently caused by blockages due to the development of silt. The silt not just limits and deters fluid going through the shunt, but it also influences the shunt's adaptability. This prompts patients
CPU planners, materials researchers, scholars, and different researchers currently have an uncommon degree of admittance to the universe of nanoscale materials because of 3D perception programming that is associated straightforwardly with an electron magnifying lens, empowering scientists to see and control 3D representations of nanomaterials continuously. The capabilities are remembered for another beta version of Tomviz, an open-source 3D information perception device used by a large number of scientists.The new form rethinks the perception cycle, making it conceivable to go from magnifying lens tests to 3D representations in minutes rather than days. As well as creating results more rapidly, the
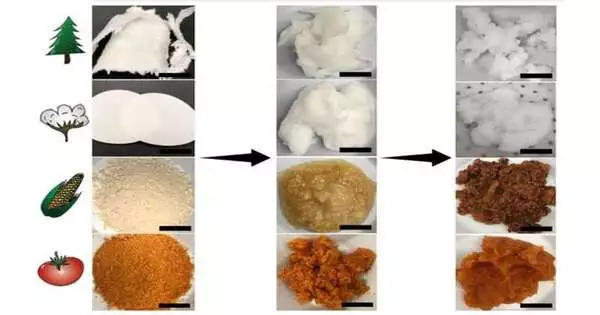
What do corncobs and tomato strips have to do with gadgets? The two of them can be utilized to rescue important uncommon earth components, similar to neodymium, from electronic waste. Penn State analysts utilized miniature and nanoparticles made from natural materials to catch uncommon earth components from fluid arrangements. Their discoveries, accessible web-based now, will likewise be distributed in the November issue of the Chemical Engineering Journal. Byproducts like corncobs, wood mash, cotton and tomato strips frequently end up in landfills or in manure, said related creator Amir Sheikhi, aide teacher of compound design. "We needed to change these byproducts
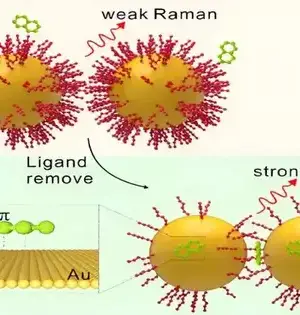
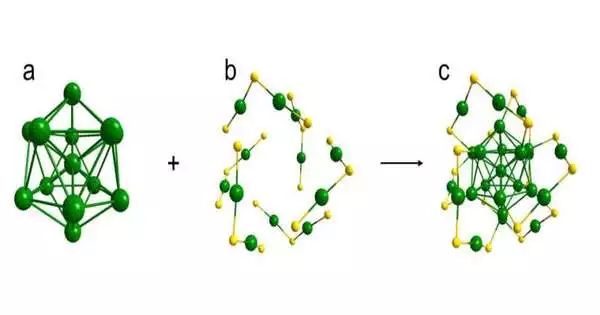
As per a review distributed in Nano Letters, scientists driven by Prof. Wu Zhikun from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) decreased palladium (Pd)-based amalgam nanoclusters (abridged as Au4Pd6 and Au3AgPd6) interestingly. As per the analysts, Au3AgPd6 is the smallest tri-metal amalgam nanocluster with an obvious piece/structure up to this point. Catalysis is firmly connected to the surface. For metal impetuses, expanding the extent of surface iotas can further develop the use efficiencies of metals, which is especially significant for honorable metal impetuses like gold and platinum. Hence, lessening the quantity of
A global research team led by the University of Göttingen discovered novel quantum effects in high-accuracy studies of normal twofold layer graphene and deciphered them in collaboration with the University of Texas at Dallas, utilizing their hypothetical work.This investigation adds to our understanding of the cycles in question by providing new insights into the connection between charge transporters and the various stages.The LMU in Munich and the National Institute for Materials Science in Tsukuba, Japan, were likewise engaged in the exploration. The outcomes were distributed in Nature. The clever material graphene, a skinny layer of carbon iotas, was first found