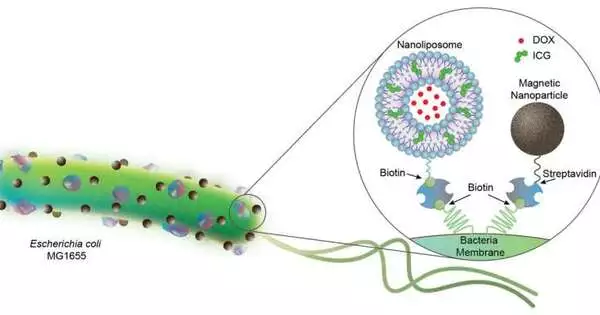
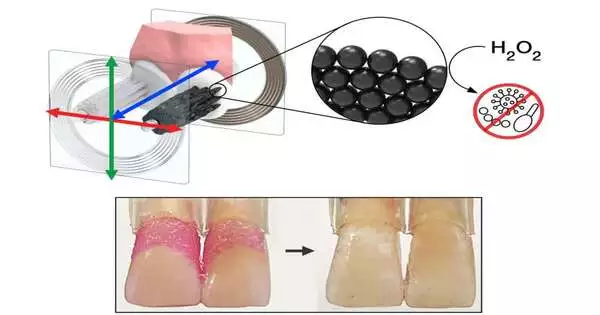
A group of researchers in the Physical Intelligence Department at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems have joined mechanical technology with science by preparing E. coli microbes with fake parts to build biohybrid microrobots. To start with, as should be visible in Figure 1, the group joined a few nanoliposomes to every bacterium. On their external circle, these round molded transporters encase a material (ICG, green particles) that softens when enlightened by close to infrared light. Further towards the center, inside the fluid center, the liposomes typify water solvent chemotherapeutic medication atoms (DOX). The second part the analysts joined
Nanotechnology
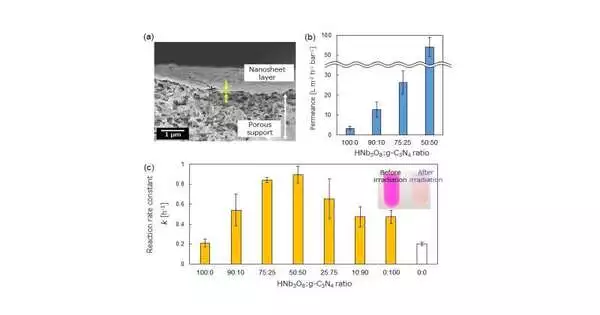
A global cooperation led by Kobe University scientists has effectively fostered a nanosheet-covered photocatalytic film that shows both great water permeance and photocatalytic action. The film's photocatalytic properties make it simpler to perfect, as illuminating the layer with light effectively lessens fouling. They cultivated this film by covering 2D nanomaterials (nanosheets) onto a permeable support. This progressive film innovation can be applied to water purging and hence can possibly contribute towards handling both worldwide natural and energy issues by assisting with guaranteeing safe drinking water supplies and clean energy. It is trusted that this will speed up the move towards
In the event that breast disease is thought, specialists do a biopsy. Nonetheless, this is intrusive, agonizing, and expensive. It likewise requires a few days to obtain the results. Later on, a finding could be made through a fluid biopsy of a patient's blood — a delicate, savvy strategy that would convey the outcomes inside only a couple of hours. A group of scientists at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Polymer Research IAP is working close to accomplices on this creative strategy. A biopsy is normally called for in the event that a dubious knot is found in a patient's
A shapeshifting mechanical microswarm could one day function as a toothbrush, wash, and dental floss all in one.The innovation, created by a multidisciplinary group at the University of Pennsylvania, is ready to offer a new and robotized method for carrying out the ordinary yet basic daily errands of brushing and flossing. A framework could be especially important for people who miss the mark on manual skills and can't clean their teeth properly themselves. The building blocks of these microrobots are iron oxide nanoparticles that have both reactive and attractive properties. Utilizing an attractive field, scientists could guide their movement and
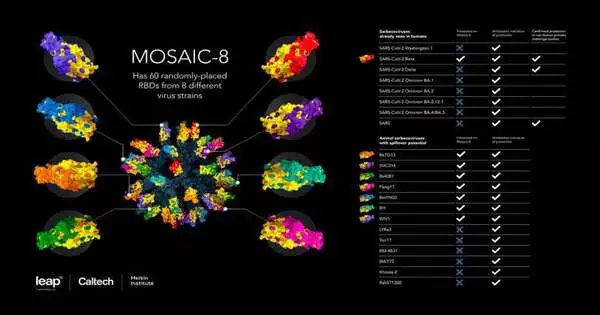
Another sort of immunization gives security against an assortment of SARS-like betacoronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2 variations, in mice and monkeys, as per a review driven by scientists in the lab of Caltech's Pamela Bjorkman, the David Baltimore Professor of Biology and Bioengineering. Betacoronaviruses, including those that caused the SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 pandemics, are a subset of COVIDs that taint people and creatures. The immunization works by giving the safe framework bits of the spike proteins from SARS-CoV-2 and seven other SARS-like betacoronaviruses, joined to a protein nanoparticle structure, to incite the creation of a wide range of cross-receptive antibodies. Rather,
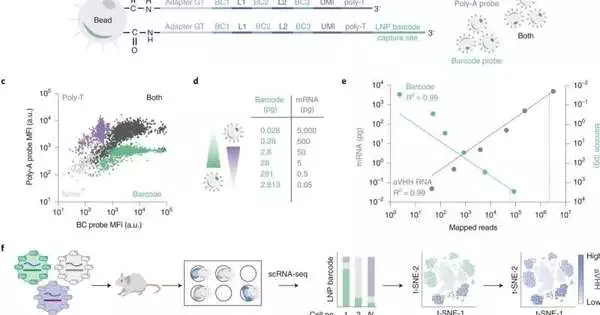
In view of messenger RNA, or mRNA, might possibly treat many ailments, including malignant growth, hereditary illnesses, and, as the world has learned lately, lethal infections. To work, these medications should be conveyed straightforwardly to target cells in nanoscale air pockets of fat called lipid nanoparticles, or LNPs—mRNA isn't a lot of good if it doesn't arrive at the right cell type. A group of scientists at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University's School of Medicine has moved toward further developing improvement of these hand-crafted conveyance vehicles, revealing their work June 30 in Nature Nanotechnology. Curtis Dobrowolski and
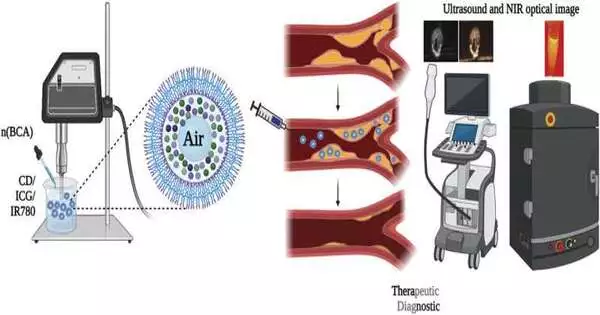
Cook Heart and Diabetes Institute scientists have planned and fostered a clever medication conveyance strategy that can immensely improve the viability of a medication used to treat atherosclerosis and can possibly recognize and treat different illnesses. The method, utilizing drug-stacked nanoparticles, straightforwardly focuses on the site of atherosclerosis in creature models, upgrading the cells' take-up of the medication hydroxylpropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CD) and altogether lessening cholesterol content more than the medication alone. High dosages of CD are expected during treatment of atherosclerosis, bringing about aftereffects including hearing misfortune, yet the supported and nearby arrival of this medication stacked nanoparticle (CDNP) wouldn't just
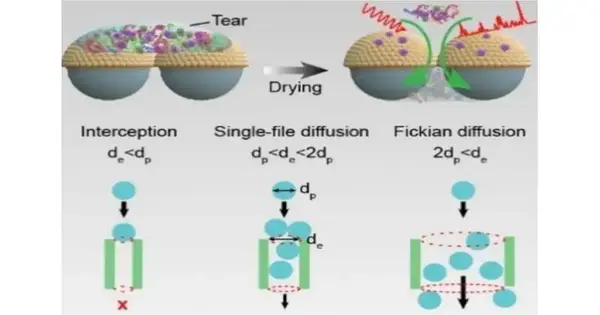
Human tear liquids contain numerous proteins, metabolites, and different atoms whose foci change essentially with specific illnesses. An examination group has now cultivated a convenient test pack for tears that can recognize patients with jaundice. Their prosperity depends on a half-and-half sensor that all the while eliminates pollutants from the example. This approach could give new strategies for early discovery and determination in light of perplexing organic liquids, as the group revealed in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition. One specific benefit of tear liquid conclusion is that examples can be gathered in an agreeable and harmless way. A technique
A Rice University group led by teachers Matteo Pasquali and Angel Mart has worked on the treatment of the profoundly important nanotubes to make them more reasonable for a huge scope of applications, including aviation, gadgets, and energy-effective materials. The analysts detailed in Nature Communications that boron nitride nanotubes, also known as BNNTs, gather themselves into fluid gems under the right circumstances, basically focusing over 170 sections for each million by weight in chlorosulfonic corrosive. These fluid gems are made up of adjusted BNNTs, which are far easier to process than tangled nanotubes, which normally structure in arrangement.The lab continued
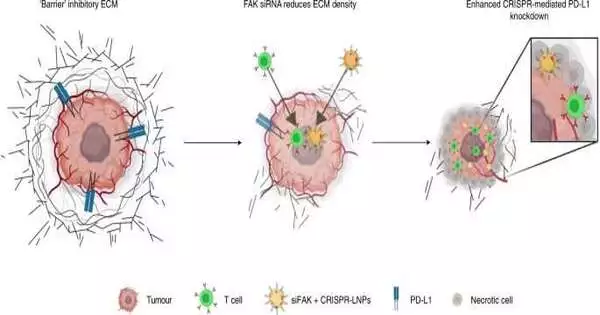
As they develop, strong cancers encircle themselves with a thick, difficult-to-enter mass of sub-atomic guards. Getting drugs past that blockade is notoriously troublesome. Presently, researchers at UT Southwestern have created nanoparticles that can separate the actual boundaries around growth to arrive at disease cells. When inside, the nanoparticles discharge their payload: a quality-altering framework that changes DNA inside the cancer, impeding its development and enacting the safe framework. The new nanoparticles, described in Nature Nanotechnology, really halted the development and spread of ovarian and liver tumors in mice. The framework offers another way ahead for the utilization of the quality