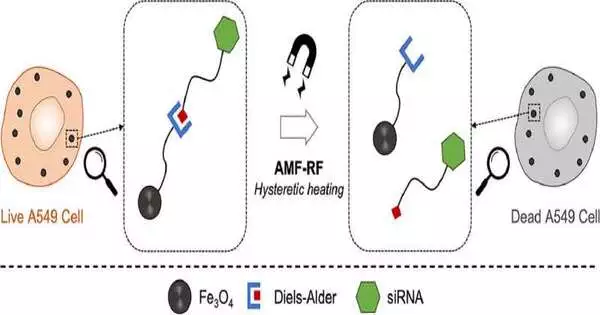
Specialists are seeking ever more refined therapies to handle cellular breakdown in the lungs. Customary chemotherapy can have serious aftereffects all over the body, so countless new medicines are exceptionally designated. These techniques allow for controlled delivery directly to the cancer, with specific specialists less likely to produce unexpected results. An article published in Biomedical Engineering Advances presents such a methodology. Daniel Hayes and partners at Pennsylvania State University in the United States made attractive nanoparticles that can be set off to deliver a helpful payload while invigorated utilizing an attractive field. The procedure should allow a doctor to administer
Nanotechnology
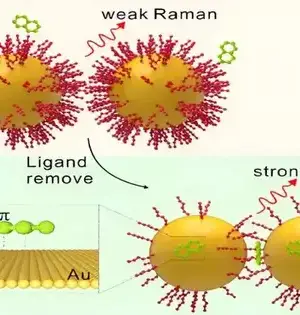
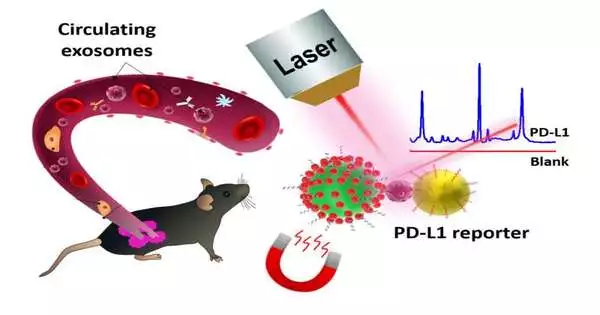
As of late, a group led by Prof. Huang Qing at the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has revealed the manufacture of ultrasensitive biosensors in view of Surface-improved Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) to recognize the malignant growth metastasis related customized passing ligand (PD-L1) biomarker. In this examination, researchers manufactured profoundly touchy and explicit aptamer-functionalized tests in view of Au/TiO2/Fe3O4 (shell/center) attractive nanocomposites and Ag/4-ATP/Au (shell/center) SERS nanotags. Using the "sandwich" approach, they caught the threatening exosomes between attractive nanocomposites and SERS nanotags, with which they could quantitatively quantify the
Having a decent eye for detail is a fundamental skill for some callings. Specifically, scholars utilize unique methods and cutting-edge innovation to dissect individual cells with uncommon accuracy. Impedance cytometry is one test strategy that can uncover explicit qualities of living single cells. This method requires an electrical entrance, in which high-recurrence flow can freely go through the cell film without harming the cell. Presently, analysts from Japan have decided on ideal circumstances to perform impedance cytometry. Their work might prompt the fast appraisal of cells during societal organic tests. A better strategy for estimating the morphology and biomass of
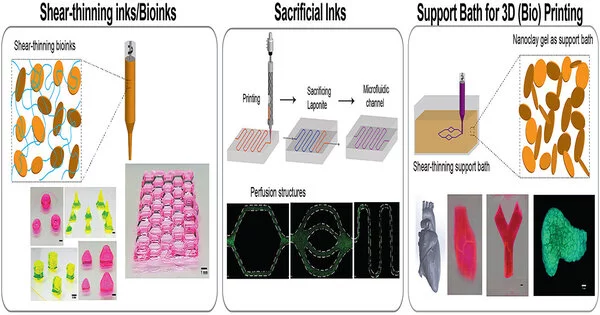
Expulsion-based 3D printing of bio solids, or "bioprinting," is a promising way to deal with creating patient-explicit, tissue-designed joins. In any case, a significant test in bioprinting is that most currently utilized materials come up short on flexibility to be utilized in many applications. New nanotechnology has been created by a group of scientists from Texas A & M University that uses colloidal connections of nanoparticles to print complex calculations that can copy tissue and organ structure. The group, led by Dr. Akhilesh Gaharwar, academic partner and Presidential Impact Fellow in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, has presented colloidal arrangements
The movement of carbon iotas on the outer layer of the nanomaterial graphene was recently estimated. the iotas move too quickly to be straightforwardly seen with an electron magnifying lens, their impact on the strength of the material can now be resolved by implication while the material is warmed on a tiny hot plate. The concentrate by analysts at the Faculty of Physics of the University of Vienna was distributed in the diary Carbon. Carbon is a component vital for all known life and exists in nature basically as graphite or diamond. Throughout the last several years, material researchers have
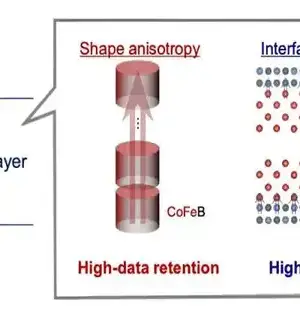
Non-unstable memories, which can store data even when power is lost, are widely used in PCs, tablets, pen drives, and a variety of other electronic devices.Among the different existing advances, magnetoresistive arbitrary access recollections (MRAM), at present utilized exclusively in unambiguous applications, is supposed to become widely available in the ten years to come. The most up-to-date MRAMs in light of spintronic systems—i.e., peculiarities connected with the twist, which is a natural property of electrons and different particles—can offer quicker tasks, lower power utilization, and long maintenance times, with possible applications in wearable gadgets, the auto industry, and the Internet
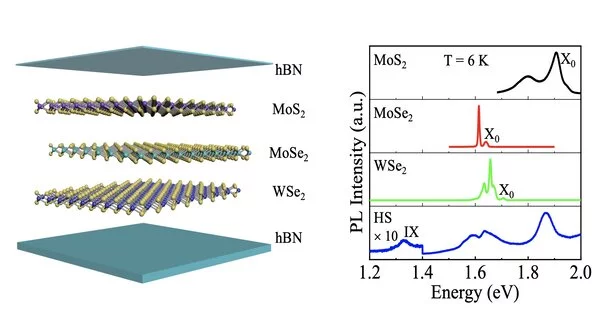
The arising field of valleytronics, which takes advantage of the force inclination of energized electrons, or excitons, in an assortment of optoelectronic gadgets, is intently attached to the creation of novel 2D materials just iotas thick. This month, a group of valleytronics scientists from Central South University in Changsha, China, created one such 2D material that essentially upgrades the utility of these thrilling particles. The subtleties of its creation and an explanation of its properties are depicted in the Nano Research Diary. In the domain of materials science, the term 2D materials refers to solids that are only one layer
A film only 250 nanometers thick (0.00025 mm) has given researchers a glimpse into the ultrafast world. The film is made of straight lead oxides, a class of material usually utilized for cell phone contact screens and photovoltaic frameworks. Nanophotonics specialists from Heriot-Watt's Institute of Photonics and Quantum Sciences have demonstrated that these materials can catch and gauge ultrafast events far superior to current frameworks. "The zero index materials that we utilised in our ultra-thin films. Because the refractive index, which is how we describe the interaction between light and matter, approaches 0 in these materials, light behaves entirely differently
A Rice University group led by teachers Matteo Pasquali and Angel Mart has worked on the treatment of the profoundly important nanotubes to make them more reasonable for a huge scope of applications, including aviation, gadgets, and energy-effective materials. The analysts revealed in Nature Communications that boron nitride nanotubes, also known as BNNTs, gather themselves into fluid gems under the right circumstances, basically focusing over 170 sections for each million by weight in chlorosulfonic corrosive. These fluid gems are made up of adjusted BNNTs, which are far easier to process than tangled nanotubes, which normally structure in arrangement.The lab continued
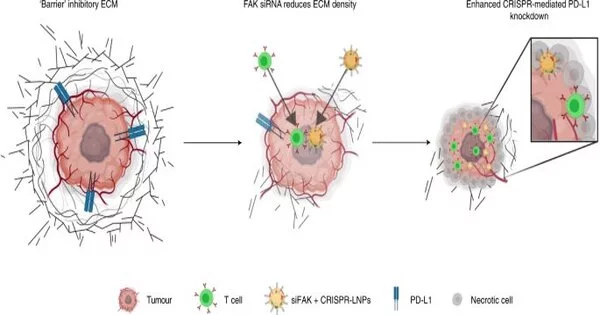
As they develop, strong cancers encircle themselves with a thick, difficult-to-enter mass of sub-atomic protection. Getting drugs past that blockade is notoriously troublesome. Presently, researchers at UT Southwestern have created nanoparticles that can separate the actual hindrances around growth to arrive at disease cells. When inside, the nanoparticles discharge their payload: a quality-altering framework that modifies DNA inside the cancer, hindering its development and initiating the safe framework. The new nanoparticles, described in Nature Nanotechnology, really halted the development and spread of ovarian and liver cancers in mice. The framework offers another way ahead for the utilization of the quality