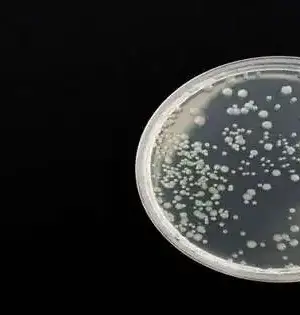
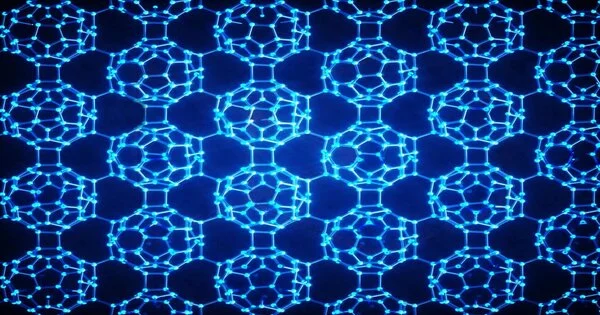
Manufactured carbon allotropes are interesting for their extraordinary properties and possible applications. Researchers have committed a very long time to integrating new kinds of carbon materials. In any case, a two-layered fullerene, which has an extraordinary design, has not been effectively blended as of not long ago. An examination bunch driven by Prof. Zheng Jian from the Institute of Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ICCAS) set up another interlayer holding cleavage system to set up a two-layered monolayer polymeric fullerene. The specialists arranged magnesium intercalated C60 mass gems as the antecedent to the shedding response. They then used
Nanotechnology
Cardiovascular illnesses are the main cause of death across the globe, accounting for around 17.9 million (32%) of all deaths overall consistently. Although screening and treatment may reduce the rate of death, medical care options are limited by the inflexibility and organic incongruence of common gadgets, such as pulse sensors.There might be a response in nanomaterials, as per scientists from Peking University in China, albeit more exploration is required before useful application. The group surveyed the present status of nanomaterial-based adaptable checking and treatment gadgets and prescribed the following stages to make such gadgets a useful possibility. Their paper was
Indistinguishable light particles (photons) are significant for some advances that depend on quantum material science. A group of scientists from Basel and Bochum has now delivered indistinguishable photons with various quantum specks—a significant step toward applications, for example, tap-confirmation interchanges and the quantum web. Numerous innovations that utilize quantum effects depend on precisely equivalent photons. Creating such photons, nonetheless, is very troublesome. In addition to the fact that they need to have a similar frequency (variety), their shape and polarization likewise need to coordinate. A group of specialists led by Richard Warburton at the University of Basel, in a joint
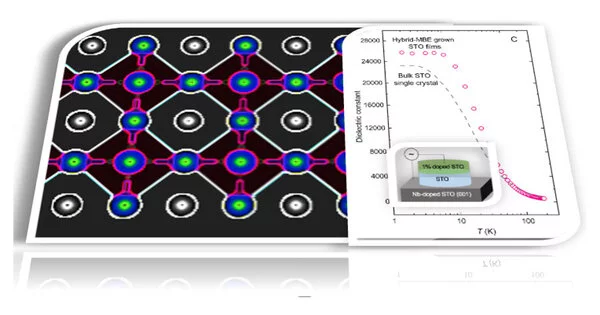
Researchers have solved the puzzle surrounding the dielectric characteristics of a rare metal oxide.
A University of Minnesota Twin Cities-driven research group has tackled a longstanding secret encompassing strontium titanate, a strange metal oxide that can be a cover, a semiconductor, or a metal. The exploration gives knowledge to future uses of this material for electronic gadgets and information stockpiling. The paper is distributed in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. When a cover like strontium titanate is set between oppositely charged metal plates, the electric field between the plates prompts the adversely charged electrons and the positive cores to arrange toward the field. This precise arranging of electrons and cores is
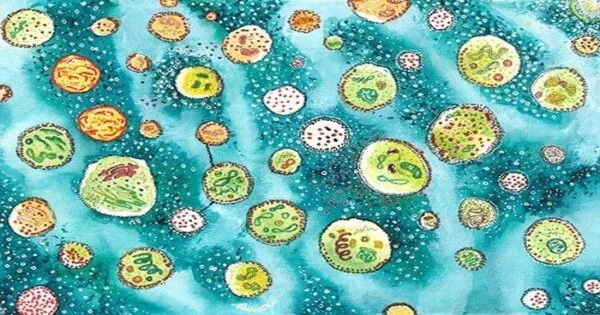
Another review from Imperial College London found that fake cells have been designed to copy the normal qualities of organic cells. Researchers from the Departments of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry have fostered a method for designing fake cells that copy how organic cells act because of natural changes. This could have huge ramifications for how we might interpret science, in treating disease and in drug conveyance. Delivering such cell models has been one of the definitive objectives of engineered science, as it would empower researchers to make planner cells with explicit capacities that are simpler to control and predict than
The familiar saying that oil and water don't blend isn't altogether accurate. While it is actually the case that the two mixtures don't normally consolidate, transforming them into one end result should be possible. You simply need an emulsifier—a fixing normally utilized in the food business. Yangchao Luo, an academic partner in UConn's College of Agriculture, Health and Natural Resources, is utilizing an imaginative emulsification process for the improvement of a better rack stable fat for food fabrication. Luo is working with something known as high interior stage Pickering emulsions (HIPEs). The high inside stage implies the combination is no
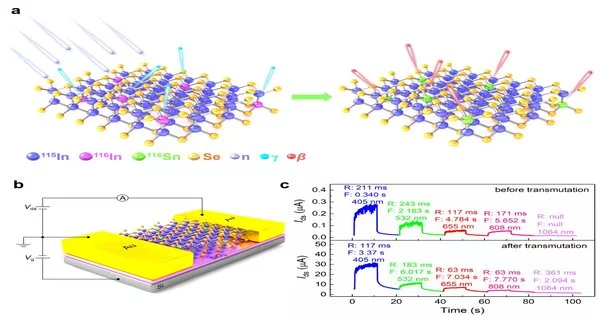
The library of two-layered (2D) layered materials continues to develop, from fundamental 2D materials to metal chalcogenides. 2D layered materials, unlike their mass-produced counterparts, have novel features that offer extraordinary potential in cutting-edge hardware and optoelectronics gadgets. Doping design is a significant and successful method for controlling the particular properties of 2D materials for their application in consistent circuits, sensors, and optoelectronic gadgets. However, extra synthetic compounds must be utilized during the doping system, which might pollute the materials. The strategies are only feasible at specific stages of material amalgamation or device manufacture. In another paper distributed in eLight, a
As electronic, thermoelectric, and PC advancements have been scaled down to the nanometer scale, engineers have confronted a test concentrating on essential properties of the materials in question; generally speaking, targets are too small to possibly be seen with optical instruments. Utilizing state-of-the-art electron magnifying lenses and novel methods, a group of specialists at the University of California, Irvine, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and different organizations have figured out how to plan phonons—vibrations in gem grids—in nuclear goals, empowering further comprehension of the manner in which intensity goes through quantum dabs, designed nanostructures in electronic parts. "This research represents
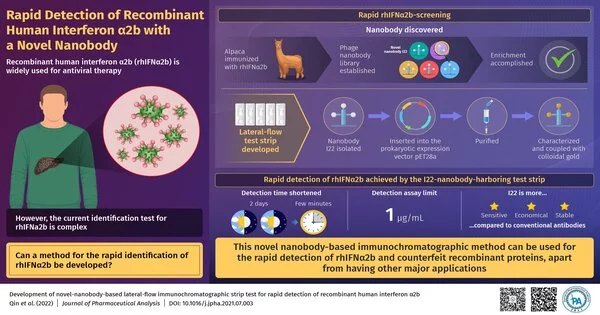
Interferons are proteins that play an important role in our normal defense mechanisms.These proteins also display a noteworthy antiviral action. The recombinant human interferon 2b (rhIFN2b) was endorsed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1986. From that point onward, it has been utilized as an antiviral specialist for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis C. In spite of its far-reaching applications, nonetheless, there remains an issue: the recognition of rhIFN2b is monotonous and tedious. In another review, scientists from China recently fostered a clever technique for the quick and proficient recognition of rhIFN2b. This paper was made
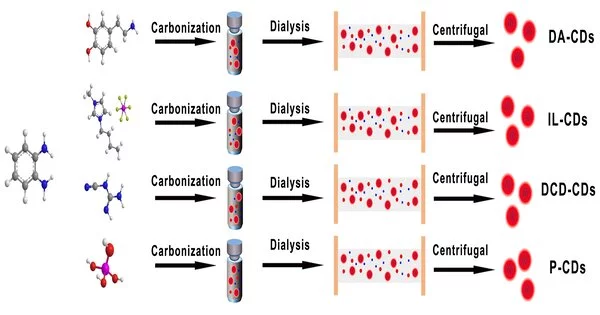
Universal red luminescence of o-phenylenediamine-based carbon dots aided by electron-phonon coupling
Carbon spots (CDs) are new carbon-based photoluminescence (PL) nanomaterials with a center shell theme. Because of their entrancing benefits, for example, substance idleness, high quantum yields (QYs), high water solvency, warm strength, and phenomenal biocompatibility, CDs stand out in different examination applications, like malignant growth analysis, phototherapy, and optoelectronic gadgets. Nonetheless, the fundamental PL peculiarities of CDs remain secret because of the polydispersity of the items and the trouble in finding out their nuclear designs. In another paper distributed in Light Science and Application, a group of researchers, led by Professor Siyu Lu and Yuxi Tian from the College of