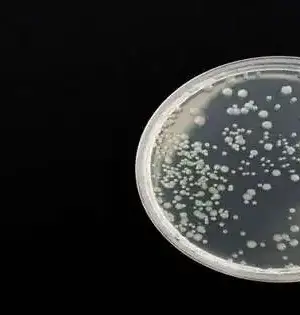
Scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have fostered an ultrasound-directed disease immunotherapy stage that produces fundamental antitumor resistance and works on the restorative adequacy of invulnerable designated spot bar. The discoveries from the preclinical review were published today in Nature Nanotechnology. As the first-of-its-sort, the Microbubble-helped UltraSound-directed Immunotherapy of Cancer (MUSIC) approach utilizes nanocomplexes joined with microbubbles to really convey cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP), an immunotransmitter engaged with anticancer resistance, into antigen-introducing cells (APCs). Inside the APCs, the microbubbles discharge cGAMP to enact the GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-trigger of interferon qualities (STING) pathway, which animates type
Nanotechnology
A nanoparticle immunization that consolidates two proteins that prompt resistant reactions against serious, intense respiratory conditions. Covid 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the infection that has caused the worldwide pandemic, can possibly be formed into more extensive and safe SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, as per specialists in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University. The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, which began around 2019, has resulted in over 6,000,000 deaths and is a global health concern.The infection is quickly advancing, as indicated by the development of a few huge variations. To battle the infection, the spike protein (S) is the favored objective antigen for immunization advancement
Mid-year is practically here, when many individuals attempt to beat the intensity. In any case, running climate control systems continually can be costly and inefficient. Presently, analysts detailing in the ACS journal Nano Letters have planned a lightweight froth produced using wood-based cellulose nanocrystals that reflects daylight, transmits assimilated heat, and is thermally protected. They recommend that the material could decrease structures' cooling energy needs by in excess of a third. In spite of the fact that researchers have created cooling materials, they have burdens. A few materials that latently discharge heat let a ton of intensity through to structures
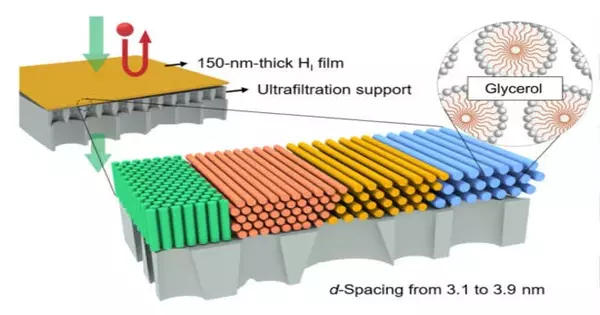
Water shortages are a developing issue all over the planet. Desalination of seawater is a laid out technique to deliver drinkable water, yet it comes with gigantic energy costs. Interestingly, specialists use fluorine-based nanostructures to channel salt from water effectively. Compared with current desalination techniques, these fluorous nanochannels work quicker, require less tension and less energy, and are a more powerful channel. In the event that you've at any point cooked with a nonstick Teflon-covered skillet, you've most likely seen the way that wet fixings slide around it without any problem. This happens on the grounds that the critical part
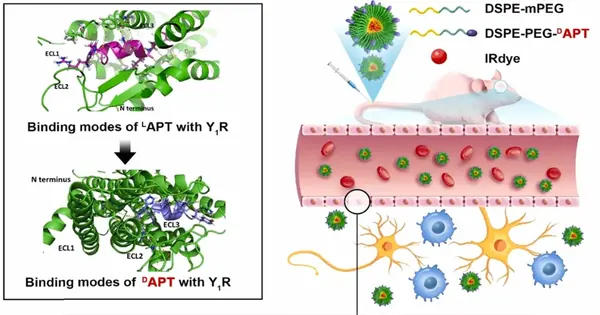
An exploration team led by Prof. Wu Aiguo at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. Dan Larhammar's gathering at Uppsala University, has proposed a D-peptide ligand of neuropeptide Y receptor Y1, which can act as nanocarriers to work with the crossing of the blood-cerebral obstruction (BBB) and hence targets gliomas productively. Results were distributed in Nano Today. Disease analysis and treatment of growth has turned into a significant logical issue of normal worry in multidisciplinary fields like science and materials science. The BBB limits the passage
A COVID-19 sensor created at Johns Hopkins University could change infection testing by adding precision and speed to an interaction that baffled many during the pandemic. In another review distributed today in Nano Letters, the specialists portray the new sensor, which requires no example readiness and insignificant administrator aptitude, as offering areas of strength for an over-existing testing technique, particularly for populace wide testing. "The procedure is pretty much as basic as putting a drop of spit on our gadget and getting a negative or a positive outcome," said Ishan Barman, an academic partner in mechanical design, who, alongside David
Substance partition processes are fundamental in the assembling of numerous items, from fuel to bourbon. Such cycles are vivaciously exorbitant, accounting for roughly 10–15 percent of global energy consumption.Specifically, the utilization of supposed "warm partition processes," for example, refining for isolating petrol-based hydrocarbons, is profoundly instilled in the compound business and has an exceptionally enormous related energy impact. Layer-based partition processes can possibly diminish such energy utilization fundamentally. Film filtration processes remove different impurities from the air we inhale and the water we drink. Notwithstanding, film innovations for isolating hydrocarbons and other natural materials are undeniably less evolved. Penn Engineers
We live in a world made and run by RNA, the similarly significant kin of the hereditary atom DNA. Truth be told, developmental researchers estimate that RNA existed and self-duplicated even before the presence of DNA and the proteins encoded by it. Quick forward to current people: science has uncovered that under 3% of the human genome is interpreted into messenger RNA (mRNA) atoms that are converted into proteins. Conversely, 82% of it is deciphered into RNA particles with different capacities, a significant number of which actually stay baffling. To comprehend what a singular RNA particle does, its 3D construction
For centuries, DNA has played a critical role in storing each cell's hereditary data. DNA is made up of strands with a specific sequence of four different structure blocks. These DNA strands are duplicated by the cell at every cell division in an incredibly perfectly tuned manner. However, incredibly, this complex hardware is administered by exceptionally basic guidelines. Lately, it has been found to use these straightforward standards with regards to hereditary design, in addition to building helpful DNA nanostructures by planning DNA strands. These DNA nanostructures have been demonstrated to have various valuable biomedical capacities, for example, the option
Nature might loathe a vacuum, but it sure loves structure. Mind-boggling, self-coordinated gatherings are viewed as all throughout the regular world, from twofold helix DNA particles to the photonic precious stones that make butterfly wings so beautiful and radiant. A Cornell-drove project has made manufactured nanoclusters that can imitate these various levels of self-get together as far as possible from the nanometer to the centimeter scale, crossing seven significant degrees. The subsequent engineered flimsy movies can possibly act as a model framework for investigating biomimetic progressive frameworks and future progress capacities. The gathering's paper, "Multiscale Hierarchical Structures from a Nanocluster