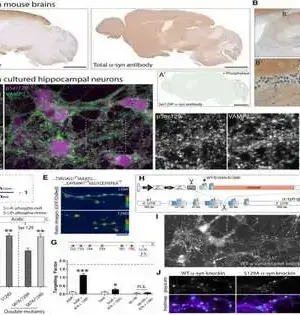
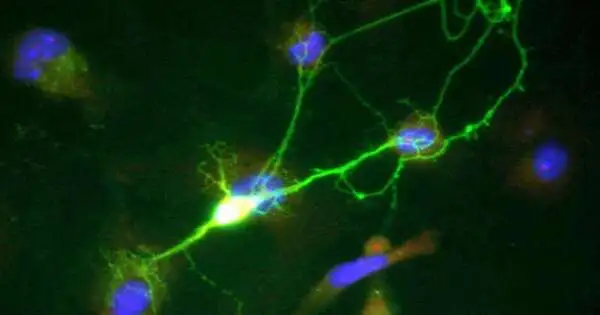
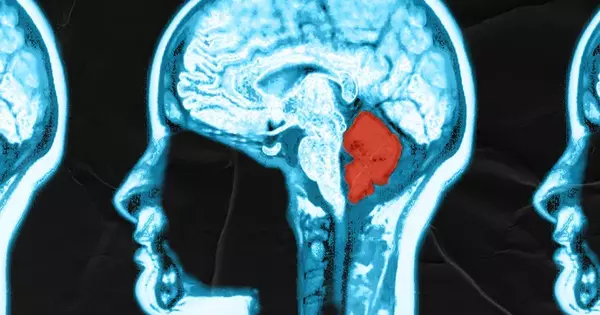
The mind is a refined natural framework known to create various encounters and discernments by means of complicated elements. Different mind locales and brain populations normally work in pairs, speaking with one another to create explicit ways of behaving and sensations at last. Specialists at the College of Oxford and the Maximum Planck Establishment for Elements and Self-Association have recently completed a review focused on better comprehension of the brain elements supporting this correspondence between brain populations. Their discoveries, assembled in Nature Neuroscience, show that the likelihood that mice will see something is connected to a fluctuation of brain movement
Neuroscience
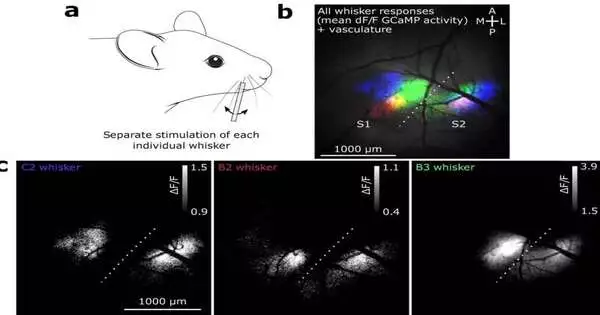
A new examination directed at the College of Liège, utilizing a super high-field 7 Tesla X-ray, gives a superior comprehension of how light invigorates our mind and could give new experiences into how it functions. An examination group at the ULiège GIGA Organization attempted to see better the way that light invigorates our discernment. Light behaves like espresso and assists us with stirring. That is the reason we suggest not utilizing an excessive amount of light on our cell phones and tablets at night. This can upset our rest. Then again, a similar light can help us during the day.
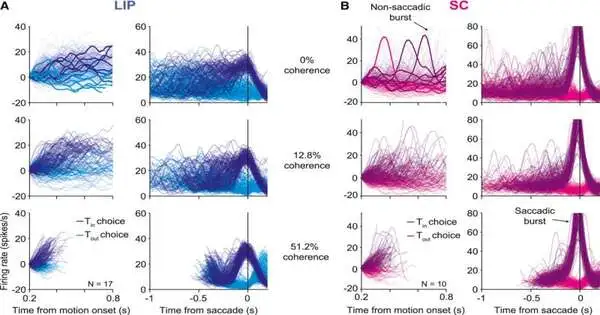
During navigation, the human mind basically amasses helpful data and weighs choices until it has sufficient proof to make a decision. Past examinations showed that decision-relevant proof is collected in unambiguous pieces of the cerebrum's external layer, known as the cortex, yet the brain components that form the last 'choice' of a choice remain ineffectively comprehended. Scientists at Columbia College completed a review focused on better grasping these brain instruments. Their paper, distributed in Neuron, features the job of the prevalent colliculus (SC), a design in the midbrain, in ending choices. "This work is the perfection of many years of
Another Northwestern medication concentrates on difficulties and a typical lack of confidence in what sets off Parkinson's illness. The degeneration of dopaminergic neurons is generally acknowledged as the primary cause of Parkinson's. However, the new review recommends that a brokenness in the neuron's neurotransmitters—the little hole across which a neuron can send a drive to another neuron—prompts shortages in dopamine and goes before the neurodegeneration. Parkinson's infection influences 1% to 2% of the populace and is characterized by a resting quake, unbending nature, and bradykinesia (gradualness of development). These engine side effects are because of the dynamic loss of dopaminergic
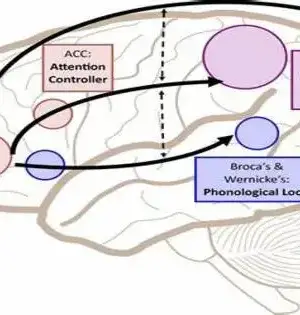
Analysis suggests that Knowledge of Word Building Blocks is vital when Deaf Youngsters Learn to Read
Understanding the building blocks of words, such as phonological awareness and phonics, is critical for all children, including deaf children, when learning to read. Research has consistently demonstrated that phonological awareness, which involves identifying and manipulating the sounds in language, is a strong predictor of reading achievement. An understanding of how words can be broken down into smaller units of meaning is important when deaf and hard-of-hearing children learn to read, according to research. This understanding of roots, prefixes, and suffixes, known as morphological awareness, assists children in learning new words and expanding their vocabulary. This is the first meta-analysis
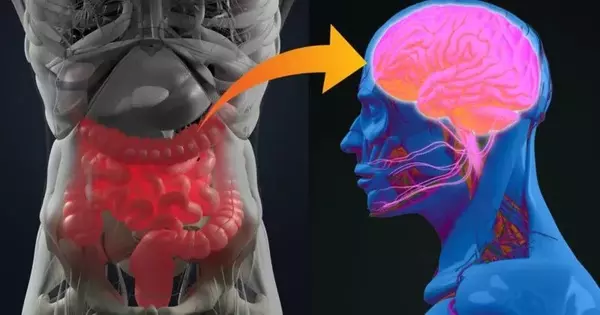
Recent research has suggested a possible link between the microbiome, the collection of microbes that inhabit our body, and baby brain development. The microbiome is composed mostly of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that live in various regions of the body, including the stomach. Levels of particular types of bacteria in babies' stomachs were shown to be connected with performance on early cognitive development assessments in a short, exploratory study. Sebastian Hunter and colleagues from the University of British Columbia in Canada published their findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE. A growing body of research suggests that the
Many states in the United States were enacting youth concussion laws to address concerns about the safety of young athletes participating in contact sports, particularly football. These laws typically mandate protocols for identifying and managing concussions in youth athletes, as well as education for coaches, parents, and players about the symptoms and risks of concussions. According to a recent study, states with college teams in strong conferences, particularly the Southeastern Conference (SEC), were among the last to implement regulations on youth concussions. The study, which looked at the relationship between youth sports participation and the passage of concussion legislation, discovered
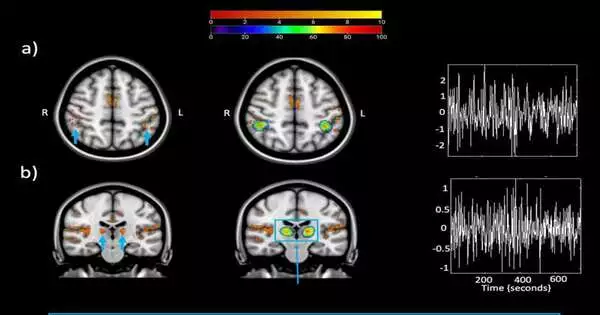
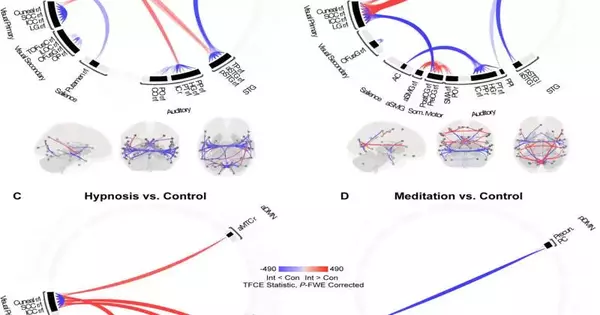
Changes in an individual's "typical" mental state subsequent to consuming medications, while pondering, during entrancing, or because of explicit ailments have been a subject of study for quite a while at this point. A portion of these psychological changes, which are known as modified conditions of cognizance, have been found to have possibly useful impacts, decreasing pressure and cultivating more prominent prosperity. Specialists at the College of Zurich's Mental Medical Clinic have as of late been investigating the capability of hallucinogenic medications like psilocybin and lysergic corrosive diethylamide (LSD) for treating wretchedness and other mental problems. In a new paper
The cerebellum is a brain area involved with motor coordination and balance, but it also plays a role in other cognitive activities. It includes an enormous number of neurons, accounting for roughly 10% of the total amount of neurons in the brain. These neurons make extensive and exact connections with one another, allowing for delicate and precise movement and coordination control. Although neuroscientists have long assumed that Purkinje cells had just one main dendrite that connects to a single ascending fibre from the brain stem, new research demonstrates that virtually all Purkinje cells in the human cerebellum contain numerous primary
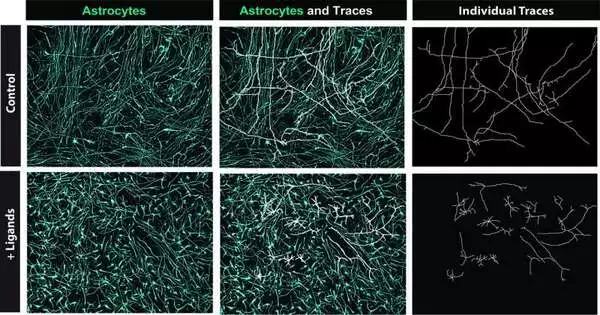
Astrocytes, a type of glial cell found in the central nervous system, are responsible for clearing out excess neurotransmitters, promoting the formation of synapses—the connections between neurons—and carrying out various other tasks. The improvement of astrocytes, similar to that of other glial cells, is incompletely upheld by extraneous ligands. Ligands are particles that tight spot to a getting protein, known as a receptor, getting different cell reactions. Scientists at Emory College Institute of Medication as of late decided to distinguish ligand-receptor coordinates that help the beginning and improvement of astrocytes in the human mind utilizing computational methods. Their paper, distributed