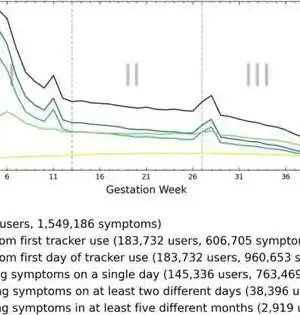
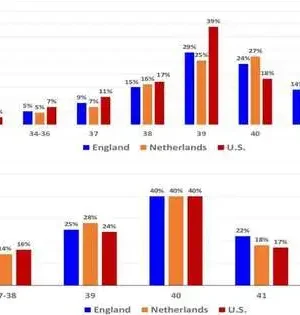
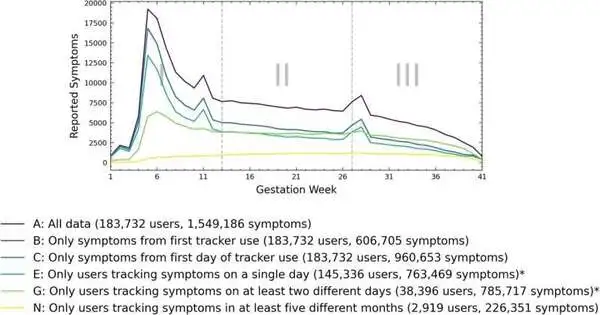
Exhaustion, spinal pain, or sleep deprivation—during pregnancy, practically all ladies experience the ill effects of these kinds of side effects, for example. An interdisciplinary group of scientists from FAU has now explored when such grumblings are especially normal and how they progress. The group utilized an anonymized, large information dataset from a pregnancy application. Every pregnancy is one of a kind, yet essentially all pregnant ladies experience the ill effects of comparable pregnancy side effects: they are drained, have spinal pain, and experience the ill effects of obstruction, inconvenience, resting, or windingness. "We have had some significant awareness of these
Obstetrics & gynaecology
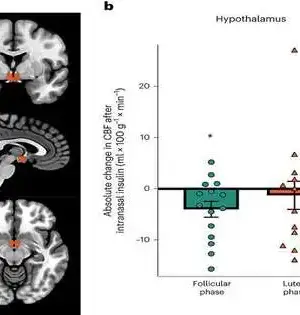
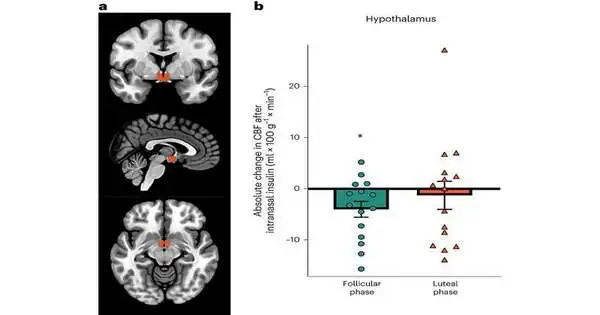
A joint group of diabetes experts from Eberhard Karls College Tübingen and Heinrich Heine College Düsseldorf, both in Germany, has found proof that suggests cerebrum aversion to insulin might be regulated by the monthly cycle in women. In their review, revealed in the diary Nature Digestion, the gathering directed a clinical preliminary, including checking the insulin levels of female workers. Nils Kroemer, with the College of Bonn, has distributed a News and Perspectives piece in a similar diary issue illustrating the work done by the gathering on this new exertion. Earlier examinations have proposed that the presence of insulin in
After trials of a similar GSK vaccine were halted due to an increase in preterm births and infant deaths, experts have called for additional investigation of the Pfizer vaccine, which is administered during pregnancy to prevent respiratory infections in infants. Pfizer claims that its vaccine is safe and effective, but experts interviewed for an investigation that was published today in The BMJ say that Pfizer's trial data should be looked at in light of the signal for preterm births seen in GSK's trial. The goal of the maternal RSV vaccine from Pfizer is to prevent severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
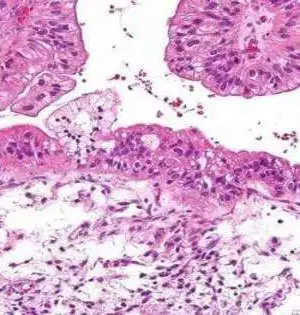
Ovarian cancer remains the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women despite recent advancements, and new treatment options are urgently required, particularly for advanced cancers that recur after standard treatment. A preclinical study that was carried out under the direction of researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania confirmed the existence of a brand-new target for drug-resistant ovarian cancer and provided data to support a treatment strategy that is currently being tested in clinical trials. The findings (Abstract #1133) will be presented by Sarah Gitto, Ph.D., an instructor of pathology and laboratory medicine, at
Two portions of mRNA from the coronavirus immunization during pregnancy are exceptionally successful against delta and decently viable against omicron contamination and are connected to a lower hazard of emergency clinic confirmation in newborn children under a half year old, finds a Canadian report distributed by The BMJ today. Security against omicron disease was most prominent when a mother got a subsequent immunization portion in the later phases of pregnancy and was likewise most prominent for babies in their first two months of life. Getting a third (sponsor) portion during pregnancy likewise supported security against omicron. Although most coronavirus cases
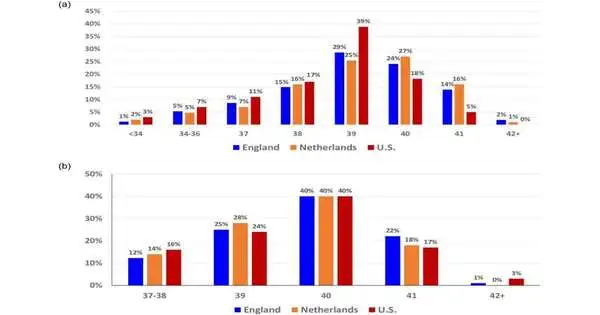
Maternal well-being outcomes in the United States continue to deteriorate, with maternal and infant mortality rates far exceeding those in Europe and other wealthy countries. Currently, another review driven by analysts at the Boston College School of General Wellbeing (BUSPH) and Harvard Clinical School-partnered Beth Israel Deaconess Clinical Center (BIDMC) is shedding knowledge on how clinic hierarchical designs and staffing inside US maternity care might influence the birthing system and perhaps add to unfriendly birth results. Distributed in the journal PLOS ONE, the review examined gestational age examples and timing of home and clinic births in three top-level salary nations:
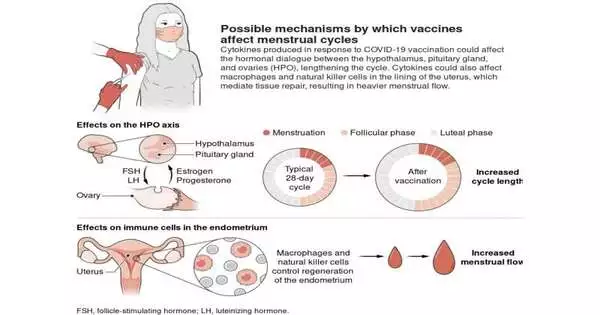
Victoria Male, a processing and digestion teacher at the Royal School of London, has distributed a Viewpoints piece in the journal Science tending to reports of coronavirus vaccinations differently affecting menstruation. In her article, she noted that research has shown that such antibodies can cause minor, brief changes in period. Soon after inoculations were introduced to safeguard individuals against the Coronavirus, ladies all over the planet started detailing changes to their periods subsequent to being immunized—aa few saw longer cycles and others heavier bleeding. The creators of the antibodies did not test for feminine effect during their preliminary studies because
While attempting to imagine, each subsequent tick that ticks by feels valuable. 65% of people seeking ripeness care at the end of their lives do so due to stress.That is the reason Penn Medication, as of late, founded a telemedicine-driven program pointed toward seeing patients more rapidly and beginning medicine sooner. The program, Quick Track to Ripeness, cut the time between when patients first connected for help to when they accepted their most memorable treatment considerably, getting them on the way to life as parents about a month and a half sooner, as per research distributed in NEJM Impetus by