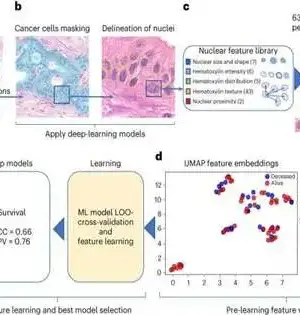
In a new report driven by Ravi Salgia, M.D., Ph.D., the Arthur and Rosalie Kaplan Seat in Clinical Oncology, a group of scientists from City of Trust, one of the biggest disease examination and therapy associations in the US, and different organizations found that nongenetic components are significant in cellular breakdown in the lungs of patients who foster protection from one malignant growth treatment. Their discoveries were distributed in the October 13 issue of the journal Science Advances. The group's review investigated protection from the counter-malignant growth medicine sotorasib in patients with non-little cell cellular breakdown in the lungs (NSCLC).
Oncology & Cancer
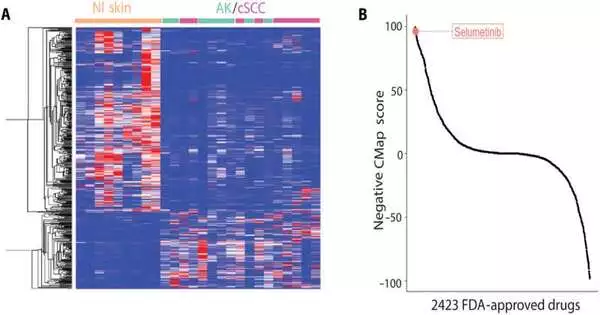
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is the second most normal kind of skin disease in the US, affecting roughly 700,000 individuals every year. While prescriptions exist to forestall the advancement of infection, they are related to incidental effects, recommending the requirement for new medications that can be securely used to forestall it. In another article distributed today in Science Translational Medication, a group of Moffitt Malignant Growth Community specialists, in a joint effort with NFlection Therapeutics and scientists at Stanford College, reports the distinguishing proof of another medication, NFX-179, that can be applied to the skin and was displayed to forestall
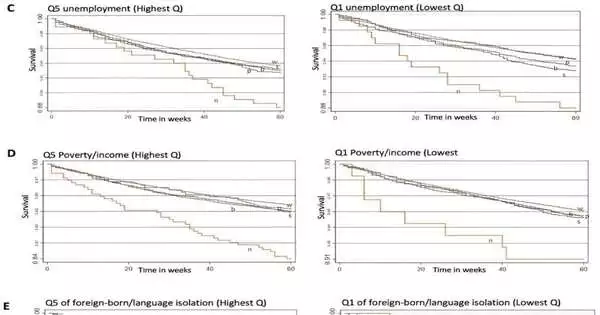
Living in a more walkable area safeguards against the risk of by and large heftiness-related malignant growths in ladies, explicitly postmenopausal bosom disease, yet additionally ovarian malignant growth, endometrial malignant growth, and numerous myeloma, as per another study by Columbia College Postal Workers School of General Wellbeing and NYU Grossman Institute of Medication. Corpulence has been connected to an expanded risk for 13 kinds of malignant growth in ladies, and active work, independent of body size, brings down the risk for a portion of these tumors. Neighborhood walkability is a bunch of metropolitan plans that include those that advance walker
Prostate disease has long held a scandalous standing as a prominent enemy of people of color—a dangerous stalker that has caused quite possibly the most profound uniqueness in endurance among all tumors influencing guys. New exploration from Stony Creek Medication, the wellbeing and clinical science venture of Stony Stream College in New York, has examined the purposes behind the unmistakable racial endurance contrasts for this type of malignant growth. The examination, distributed in the diary Malignant Growths, challenges the well-established view that people of color might be organically inclined to prostate disease. The epidemiological investigation discovered that the majority of
Scientists at the College of Arizona Disease Center found another class of iron-focusing intensifies that hamper the expansion of refined dangerous cells in a lab setting. The consequences of the review were distributed in the Diary of the American Compound Society. "Disease cells are what we call 'dependent on' iron, so we are making intensifies that can disrupt the accessibility of iron in malignant growth cells," said Elisa Tomat, Ph.D., teacher in the Branch of Science and Natural Chemistry at the UArizona School of Science and individual from the UArizona Disease Center. The revelation could prompt the advancement of a
In new discoveries from specialists at the American Disease Society (ACS), non-Hispanic Dark people determined to have a second essential malignant growth (SPC) experienced 21% higher malignant growth-related passing rates and 41% higher cardiovascular-related demise rates compared to their non-Hispanic white partners. The study likewise showed that Hispanic people determined to have a second essential disease additionally experienced 10% higher malignant growth-related death rates compared to their non-Hispanic white partners, but 10% lower cardiovascular-related passing rates. The paper was distributed in JAMA Organization Open. "These variations were, to some extent, inferable from ominous stage circulations at the second essential disease
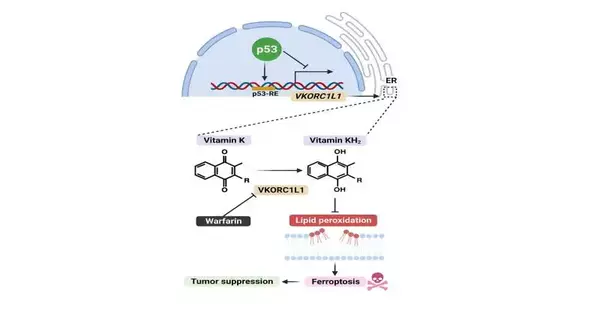
Warfarin, a broadly utilized blood thinner, seems to have strong anti-cancer growth properties, as indicated by a concentrate by Columbia College specialists. The review, conducted in human cells and in mice, found that warfarin prevents cancers from slowing down a fall-to-pieces component that cells start when they distinguish transformations or different irregularities. "Our discoveries recommend that warfarin, which is now supported by the FDA, could be reused to treat various diseases, including pancreatic malignant growth," says concentration on pioneer Wei Gu, Ph.D., the Abraham and Mildred Goldstein Teacher of Pathology and Cell Science (in the Foundation for Disease Hereditary Qualities)
Discoveries from the very first planned preliminary study, including a randomized pathway contrasting a medical procedure with non-careful therapy of dangerous entrail deterrent (MBO), give significant proof to assist with illuminating the clinical dynamic in dealing with this successive entanglement in patients with cutting-edge disease. The results are being published in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology and include information on clinical outcomes as well as patient quality of life. The S1316 study, a half-and-half preliminary that incorporated a randomized part, was driven by the SWOG Disease Exploration Organization, a clinical preliminary bunch. Robert S. Krouse, MD, chief of surgery at
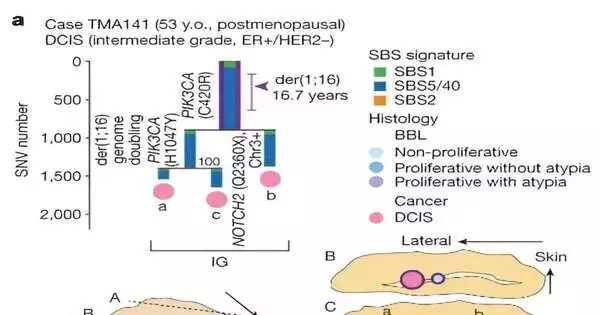
Common beliefs about how cancer grows are being challenged by Japanese research led by Kyoto University. In their paper "Transformative accounts of bosom malignant growth and related clones," distributed in Nature, the exploration group investigates the early transformative occasions prompting disease improvement and the job of non-malignant growth clones that share normal changes. The scientists utilized phylogenetic investigation to follow the advancement of bosom malignant growth and antecedent sores from procuring introductory driver changes to growing clinically analyzed infections. The researchers wanted to learn more about the driver events and their order of occurrence before these clones evolve into cancer,
Specialists from A*STAR's Establishment of Sub-atomic and Cell Science (IMCB) and Public Disease Community Singapore (NCCS) have found how the departure of a quality, PBRM1, can prompt the improvement of kidney malignant growth. The work is distributed in the journal Nature Cell Science. At the point when PBRM1 is dormant, it brings about the development of strange protein edifices that enact a malignant growth-causing pathway called NF-B. These edifices rearrange proteins all through the genome, prompting uplifted NF-B action and the statement of qualities that advance disease cell development. The PBRM1 quality is the second most often transformed quality in