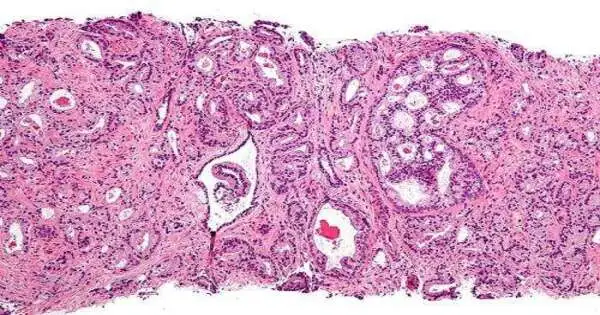
Scientists from the Barts Disease Foundation (BCI) at Sovereign Mary College of London, the Italian Organization for Genomic Medication, and the College of Milan recognized a clever part for a malignant growth-causing quality in controlling a significant hereditary cycle that supports hereditary variety in prostate disease. The discoveries, published today in Cell Reports, uncover what the quality means for the age of hereditary variations in prostate malignant growth that might anticipate illness backslide and address new medication focuses to work on quiet endurance. Co-senior creator Dr. Prabhakar Rajan, Gathering Pioneer at BCI and Expert Urological Specialist at Barts Wellbeing NHS
Oncology & Cancer
Another focus by UT Southwestern analysts proposes that fat cells, or adipocytes, that fill in nearness to bosom diseases, can move into other cell types that advance growth development. The findings, published in Cell Reports, could lead to better approaches to combating breast cancer, a disease that affects over 300,000 women in the United States each year and kills nearly 45,000 people. "We recognized novel adipocyte-determined cell types in the mammary organ that offer a ripe soil for bosom disease cancer attack and development," said concentrate on pioneer Philipp Scherer, Ph.D., teacher of inner medication and cell science and an
Ladies determined to have beginning phase bosom disease frequently decide to have a lumpectomy, which eliminates just the harmful tissue and a slim edge of encompassing solid cells rather than the whole bosom. Current disease rules for most ladies under 65 suggest keeping lumpectomy with radiation treatment, which targets stray malignant growth cells that could somehow make bosom disease repeat or spread to different pieces of the body. Another review introduced at the 2022 yearly gathering of the American Society of Clinical Oncology could ultimately increase the possibility of skipping radiation for certain women as youthful as 55. In any
The utilization of a wide range of anti-toxins in mice with harmful melanoma, a forceful type of skin disease, sped up their metastatic bone development, logical on the grounds that the medications drained the mice's digestive verdure and debilitated their safe reaction, as per another concentrate by scientists at Emory College in Atlanta. The discoveries highlight the significance of the stomach microbiome in general wellbeing and propose that specialists ought to painstakingly gauge the gastrointestinal impacts when they utilize anti-toxin treatments while treating malignant growth or different illnesses, according to one of the review's creators, Subhashis Buddy, Ph.D., a postdoctoral
Patients with high-risk melanoma who received the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab both before and after surgery to eliminate harmful tissue had a significantly lower risk of their disease recurring than comparable patients who received the medication only after surgery. These outcomes from an examination conducted by the SWOG Disease Exploration Organization, a malignant growth clinical preliminaries group financed by the Public Disease Foundation (NCI), will be introduced at an Official Conference at the European Society of Clinical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2022 in Paris on Sept. 11, 2022 (Unique LBA6). The review, known as S1801, was driven by Sapna Patel, MD, seat
Researchers said Saturday they had recognized the system through which air contamination triggers cellular breakdown in the lungs of non-smokers, a disclosure one researcher hailed as "a significant stage for science—and for society." The examination showed the health risk presented by the small particles created by consuming petroleum products, starting new calls for more atrocity to battle environmental change. It could likewise prepare for another field of disease avoidance, as per Charles Swanton of the UK's Francis Kink Foundation. Swanton introduced the exploration, which has not yet been distributed in a friend's survey, at the European Society for Clinical Oncology's
For many many years, an ever increasing number of grown-ups younger than 50 are creating disease. A review directed by scientists from Brigham and Women's Hospital reveals that the frequency of beginning stage tumors (those analyzed before age 50), including malignant growths of the breast, colon, throat, kidney, liver, and pancreas, among others, has emphatically expanded all over the planet, with this exceptional ascent starting around 1990. To figure out why so many younger people are being diagnosed with disease, researchers conducted extensive examinations of available information in print and online, remembering data for early life openings that could have
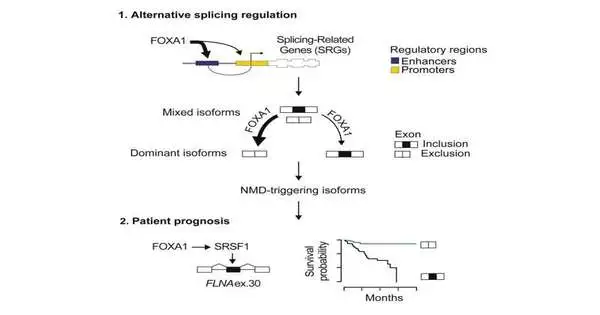
A Northwestern Medicine study has distinguished a sub-atomic component that manages the movement of emasculation-safe prostate malignant growth, as per discoveries distributed in the journal Oncogene. Specialists led by Jindan Yu, MD, Ph.D., professor of Medicine in the Division of Hematology and Oncology and of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, found that the downregulation of the protein FOXA1 manages hypoxia, or absence of oxygen, in prostate malignant growth cancers and advances growth movement. "The capability of FOXA1 in restraining genealogy versatility is significant in light of the fact that it is the metastasis and medication opposition of mutilation-safe prostate disease that
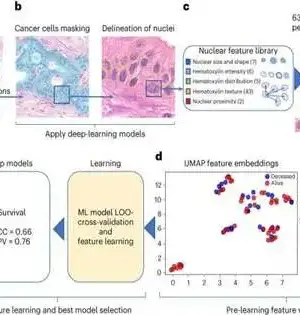
The most vital step in picking the proper therapy for a disease patient is to recognize their particular sort of malignant growth, including deciding the essential site — the organ or part of the body where the disease starts. In uncommon cases, the beginning of a disease is not set in stone, even with broad testing. Although these tumors of obscure essential will generally be forceful, oncologists should treat them with non-designated treatments, which regularly have cruel poison levels and result in low rates of endurance. Another profound learning approach created by scientists at the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer
Analysts have found that some immunotherapy therapies used to treat disease can cause ripeness harm. It implies these therapies could influence the future ripeness and hormonal strength of female disease survivors, inciting specialists to call for additional exploration and safeguard measures like freezing eggs. The pre-clinical study, driven by the Biomedicine Discovery Institute at Monash University and the Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, showed that safe designated spot inhibitors, a typical sort of immunotherapy drug, brought about long-lasting harm to mouse ovaries and the eggs put away inside. Customary disease treatments, like chemotherapy and radiotherapy, are now connected to long-lasting, negative