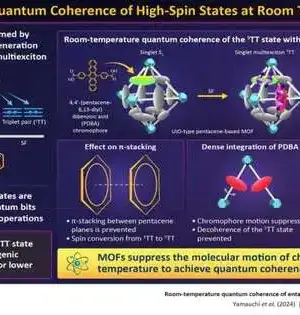
Specialists have utilized a quantum processor to make microwave photons strangely tacky. They got them to group together into bound states, then discovered that these photon groups worked in a system where they were supposed to break up into single states.The revelation was first made on a quantum processor, denoting the developing role that these stages are playing in concentrating on quantum elements. Photons—qquantum parcels of electromagnetic radiation like light or microwaves—nnormally don't interface with each other. Two crossed spotlights, for instance, go through each other undisturbed. Regardless, microwave photons can be made to collaborate in a variety of superconducting
Quantum Physics
Researchers from the College of Rostock, Germany, had the option of reproducing key actual properties from the domain of rudimentary molecule material science in a photonic framework. Natural and physical science outcomes are distributed. In their key examinations, trial physicists regularly carry monstrous yet complex hardware to bear, including: Molecule gas pedals of huge size crush together tiny particles at speeds near the speed of light, delivering impossible amounts of energy. Researchers are looking for signs of the universe's key powers in the remaining parts of these impacts. A genuine particle zoo has been discovered and incorporated into the standard
Optical photons are ideal transporters of quantum data. Yet, to cooperate in a quantum PC or organization, they need to have a similar variety (or recurrence) and transfer speed. Changing a photon's recurrence requires modifying its energy, which is especially difficult on coordinated photonic chips. As of late, scientists from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Designing and Applied Sciences (Oceans) have fostered a coordinated electro-optic modulator that can effectively change the recurrence and transfer speed of single photons. The device could be used for advanced quantum calculating and quantum organizations. The exploration is distributed in two parts: science
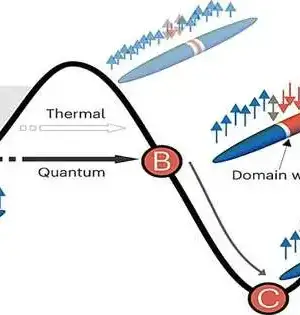
Water that just won't freeze, regardless of how cold it gets—aan exploration bunch including the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR)—has found a quantum express that could be depicted along these lines. Specialists from the Foundation of Strong State Physics Science at the College of Tokyo in Japan, Johns Hopkins University in the US, and the Maximum Planck Organization for the Physical Science of Perplexing Frameworks (MPI-PKS) in Dresden, Germany, figured out how to cool a unique material to approach outright zero temperature. They tracked down that a focal property of iotas—ttheir arrangement—didn't "freeze," not surprisingly, yet stayed in a "fluid" state. The
The secretive changes in periods of issuance—from strong to fluid and back once more—have entranced Eun-Ah Kim since she was in lower primary school in South Korea. Without cold drinking water promptly accessible, on hot days the youngsters would carry jugs of frozen water to school. Kim saw that when the water dissolved, the volume changed. "That revealed to me that there is something in there that I can't see with my eyes," said Kim, a physical science teacher at the School of Expressions and Sciences."Matter around me is comprised of imperceptible elements that communicate and do something together to
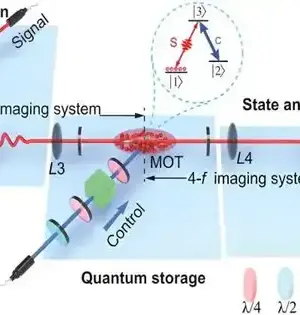
Quantum memory gadgets can store information as quantum states rather than two-fold states, as traditional PC memories do. While some current quantum memory innovations have accomplished profoundly encouraging outcomes, a few difficulties should be overcome before they can be carried out with enormous scope. Scientists at the AWS Place for Quantum Systems Administration and Harvard College have as of late fostered a promising quantum memory fit for blunder recognition and with a lifetime or rationality time (i.e., the ideal opportunity for which a quantum memory can hold a superposition without falling) surpassing 2 seconds. This memory, introduced in a paper
Researchers from QuTech and the Eindhoven College of Innovation have made strides in qubit research. Qubits are one of the fundamental components of a future quantum computer. The analysts, including Sasa Gazibegovic, Ghada Badawy, and Erik Bakkers from TU/e, have distributed their outcomes in Nature on November 23, 2022. A traditional PC performs tasks utilizing pieces, which can be either zero or one. A quantum computer, then again, utilizes quantum bits, or "qubits." Qubits can be photons, electrons, or any other framework that can exist in purported quantum states. Since these states can exist all the while, instead of traditional
On Friday, November 18, a test utilizing crashes of lead particles was done in the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) and gave an open door to the trials to approve the new finders and new information handling frameworks in front of the following year's lead material science run. After the fruitful beginning of Run 3 in July this year, which highlighted proton crashes at the record energy of 13.6 TeV, it was the turn of lead cores to flow in the LHC again last Friday, following a hole of four years. Lead cores have 208 nucleons (protons and neutrons) and are
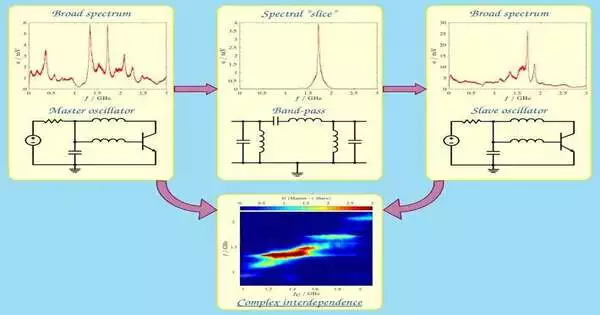
The theoretical idea that the entire thing can be found in each piece of it has long captivated scholars and played a role in all walks of reasoning and trial science, from Immanuel Kant on the concept of time to David Bohm on the concept of request, and from the self-similarity of fractal designs to the characterizing properties of 3D images. In any case, it has remained naturally unimportant to electronic design, which strives to cultivate always specific and effective circuits trading signals with profoundly controlled qualities.Conversely, the age of action having highlights that manifest themselves similarly over various worldly
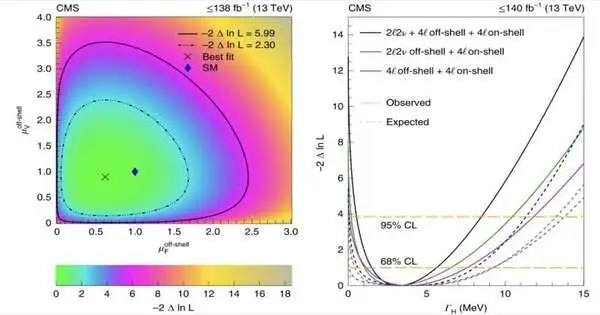
The Higgs boson, the key subatomic molecule related to the Higgs field, was first found in 2012 as a feature of the Map book and CMS tests, the two of which examine information gathered at CERN's Huge Hadron Collider (LHC), the most impressive atom smasher in existence. Since the revelation of the Higgs boson, research groups overall have been attempting to more readily grasp this novel molecule's properties and qualities. The CMS Collaboration, a large group of scientists working on the CMS Try, has recently updated its estimation of the width of the Higgs boson while also gathering the primary