A group of scientists affiliated with a few foundations in Alabama has connected 10 hereditary loci to the improvement of osteoarthritis. In their paper distributed in the journal Nature Hereditary Qualities, the gathering portrays their examination of information from the Million Veteran Program in the U.S. and, furthermore, the UK Biobank in the U.K.
Osteoarthritis is a dynamic joint illness brought about by irritation. It is one of the most widely recognized kinds of joint pain and regularly influences the knees, hips, spine, and hands. There is presently no fix, and medicines are restricted. Many individuals with the condition end up with joint substitutions. In this new effort, the specialists expand on earlier work into hereditary elements connected to the turn of events.
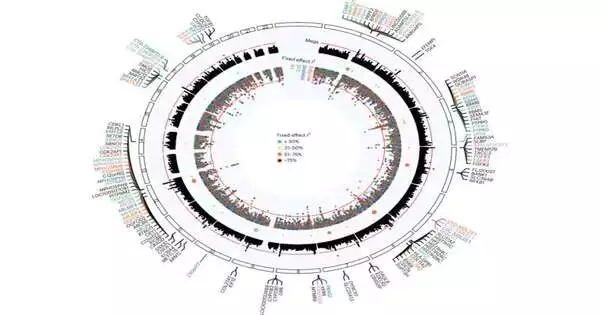
To figure out which qualities may be liable for the improvement of osteoarthritis, the scientists utilized information from the Million Veteran Program—aa data set of wellbeing data, hereditary information, and other data for roughly 163,000 U.S. veterans. They recognized 79,569 osteoarthritis patients from a benchmark group of 80,002 unaffected people.
The scientists then, at that point, did likewise with information from the UK Biobank. Subsequent to blending and breaking down the information from the two assets, the scientists separated 10 new hereditary loci related to osteoarthritis and affirmed 17 others recently distinguished by other examination gatherings.
When the experts directed family delineated examination of the information that could be associated with loci connected with tissue that were not related to joints, they discovered what they call critical affiliations.What’s more, they likewise led a quality set enhancement examination that assisted with featuring hereditary pathways associated with bone, ligament, and other connective tissue. They next investigated conceivable natural cycles engaged with the advancement of osteoarthritis and possible medicines for side effects.
The experts point out that recognizing the hereditary factors behind the progression of osteoarthritis is only the first step toward identifying the chain of events that causes joint damage—and, eventually, a method for breaking the chain and thus preventing it. They likewise note that more work is expected to be done to distinguish every one of the hereditary elements engaged in the sickness.
More information: Merry-Lynn N. McDonald et al, Novel genetic loci associated with osteoarthritis in multi-ancestry analyses in the Million Veteran Program and UK Biobank, Nature Genetics (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01221-w
Journal information: Nature Genetics