Long haul and extreme utilization of anti-toxins has caused the spread of anti-toxin opposition. The time-and cost-consuming course of new anti-toxin improvement brings about the much more slow rise of new antibacterial medications than that of bacterial opposition. The spread of superbugs has grown to become a major threat to human health.Tigecycline is viewed as the last line of defense to battle multidrug-safe Klebsiella pneumoniae. In any case, expanding use has prompted rising medication opposition and treatment disappointment. Tigecycline resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae is still a worldwide problem that needs to be resolved.
On June 29, 2022, Prof. Du Yongzhong from the College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Prof. Lu Xiaoyang and Jiang Saiping from The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine co-distributed an article titled “TPGS-based and S-thanatin functionalized nanorods for beating drug opposition in Klebsiella pneumonia” in the journal Nature Communications. Their examination demonstrates that D-alpha tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate(TPGS)-altered and S-thanatin peptide (Ts)-functionalized nanorods in the view of calcium phosphate nanoparticles can defeat tigecycline resistance of Klebsiella pneumonia.
“TPGS-based and S-thanatin functionalized nanorods for treating Klebsiella pneumonia medication resistance.”
Prof. Du Yongzhong from College of Pharmaceutical Sciences
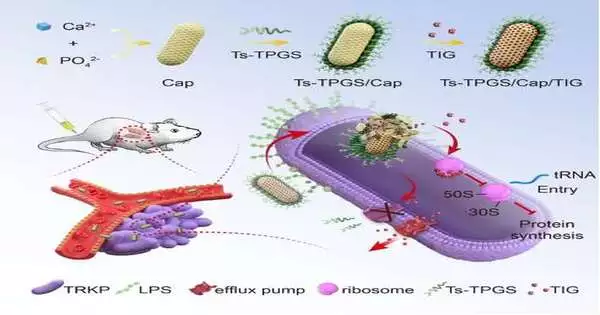
To begin with, the analysts arranged the tigecycline-stacked TPGS-changed and S-thanatin peptide-functionalized nanorods, Ts-TPGS/Cap/TIG (TTCT), and described the properties of TTCT. They found that the pre-arranged Ts-TPGS/Cap nanorods could really typify TIG and accomplish supported drug discharge. The TTCT, with a molecule size of 25 nm, wouldn’t dismantle when available for use and showed great security at room temperature.
Then, the analysts assessed the antibacterial action of TTCT and investigated the basic systems of beating opposition. They found that Ts-TPGS/Cap showed focus on and improved amassing in both Klebsiella pneumonia (KPN) and TRKP through the limiting of Ts and LPS. TPGS could apply its inhibitory limit on the action of efflux siphons and the outflow of acrA, acrB, and ramA in TRKP. Along these lines, the TIG focus inside microbes was altogether higher in the TTCT bunch than different gatherings. The synergistic antibacterial limit among Ts and TIG further upgraded the antibacterial action of TTCT, hence beating the medication opposition of TRKP.
In mice with pneumonia, Ts-TPGS/Cap was explicitly amassed in the lungs. White platelets and neutrophils in blood tests could be reduced by TTCT organization, as could total cell and C receptive protein (CRP) levels in bronchoalveolar lavage liquid (BALF).Also, TTCT was suitable for enhancing neutrophil penetration in the lungs and lessening bacterial states from BALF, hence clearly expanding the endurance paces of mice with pneumonia brought about by TRKP.
Generally, a TPGS-based and Ts-changed nanodrug conveyance framework was planned. The arranged nanorods can improve tigecycline amassing in microbes through the inhibitory impact on efflux siphons applied by TPGS and the focusing on limit of S-thanatin to microorganisms. The synergistic antibacterial limit between S-thanatin and tigecycline further upgrades the antibacterial action, hence defeating the tigecycline opposition of TRKP. The discoveries give a system to help prevent contamination illnesses brought about by MDR gram-negative microbes.
More information: Xiaojuan Wang et al, TPGS-based and S-thanatin functionalized nanorods for overcoming drug resistance in Klebsiella pneumonia, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31500-3
Journal information: Nature Communications