Mass eradications are fast worldwide abatements in Earth’s biodiversity, with five key occasions recognized over the planet’s set of experiences, seemingly the most popular of which happened ~66 a long time back during the Cretaceous, which finished the rein of dinosaurs. In any case, the biggest mass elimination is ascribed to the Permian, during which it is estimated that >95% of all life on Earth was killed.
The reason for this devasting occasion is as yet discussed, with advocates for both a huge space rock influence that made residue tuft into the climate, impeding daylight and producing corrosive downpour, and a critical volcanism that delivered plentiful measures of CO2 into the air and made the seas harmful to marine life.
The new exploration distributed in compound geography lends further support to the last hypothesis. Yu Wang, of Nanjing College, and associates led geochemical probe silt tests acquired from Zhigao Quarry in the area of the Upper Yangtze Waterway, China. Inside the examples, the researchers distinguished a significant mercury oddity, facilitated in natural matter, related to a top in carbon isotopes.
This negative carbon-13 isotope journey is deciphered as being brought about by gigantic arrivals of carbon into the climate, logically because of volcanic ejections, and these occasions are likewise significant wellsprings of mercury in nature. For sure, the planning of this journey matches the known volcanic action of the Emeishan Traps in Sichuan, a huge region (>250,000 km2) of flood basalts making an enormous molten territory.
Minor components, for example, molybdenum, uranium, and vanadium inside the residue tests, are vulnerable to diminishing and oxidizing conditions, with three recognizable spikes characteristic of anoxic circumstances when the seas were drained of oxygen. Moreover, huge worldwide ocean level falls during the Capitanian (~264 a long time ago) is proven by earthbound-determined natural carbon, while lower proportions of the components cadmium and molybdenum recommend debilitated or occasional upwelling of chilly, supplement-rich waters.
The geochemical information and decrease in calcareous green growth and fusulinacean foraminifera in the chert, mudstone, and limestone tests show marine anoxia and a more articulated delineation of the water section. In such circumstances, oxygen least zones were probably created, with steady areas of oxygen-unfortunate circumstances that would have repressed the endurance of living beings.

Field concentrate in the vicinity of Zhigao Quarry, China, and slim segment slides of dregs tests were imagined utilizing a petrographic magnifying lens to distinguish minuscule marine life forms like radiolarians, foraminifera, and green growth. Credit: Wang et al., 2024
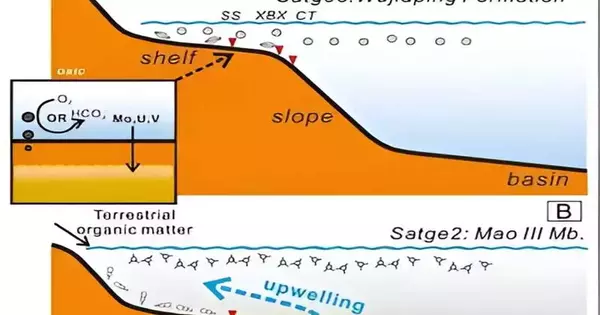
The exploration group proposes a three-step volcanic-climatic-maritime model to make sense of how the huge scope of volcanism prompted a biotic emergency in the seas during the Capitanian, paving the way to a definitive end-Permian mass termination. In stage 1, the review site was important for a carbonate stage that was associated with the Paleo-Tethys Sea, situated along the northern edge of the old supercontinent Gondwana. This oxygen-rich shallow marine climate experienced vivacious sea dissemination with upwelling of supplement-rich waters that were great for marine life to flourish, with proof of green growth, brachiopods, and corals in the Upper Yangtze areas.
During stage 2, the beginning of volcanism started in the early Capitanian, with the critical arrival of ozone-harming substances bringing about an environmental warming of 3°C–5°C. This concurred with the ocean level ascent brought about by territorial subsidence, hence the worsening definition of the water segment and marine anoxia as hotter seas decreased the centralization of broken-down oxygen. While supplements were brought to the surface by volcanic movement, essential efficiency at the sea surface spent the majority of this oxygen for breath and natural matter disintegration, producing exhausted oxygen least zones beneath.
Yet again, stage 3 is described by a winding down of volcanism and a re-visitation of shallower marine circumstances, with improved natural matter shipped from land to the sea as well as a fortified marine course that brought oxic conditions. This allowed marine organic entities to recuperate from the unfriendly anoxic circumstances and advance into new biological specialties.
The researchers seemingly recommend we are currently amidst a sixth mass elimination, and it is imperatively essential to keep investigating the role volcanism might play in influencing the equilibrium toward one more emergency for our marine domain.
More information: Yu Wang et al. Coupled volcanic activity and marine anoxia in the Upper Yangtze region prior to the Capitanian mass extinction, Chemical Geology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2023.121838