Specialists driven by the College of Toronto, Canada, have directed a randomized clinical preliminary to assess the viability of improved versus negligible nasal suctioning in treating babies with bronchiolitis after release from the crisis division.
In their paper, “Nasal Suctioning Treatment Among Babies With Bronchiolitis Released Home From the Crisis Division,” distributed in JAMA Organization Open, the group found that upgraded suctioning didn’t essentially affect the course of bronchiolitis compared with negligible suctioning.
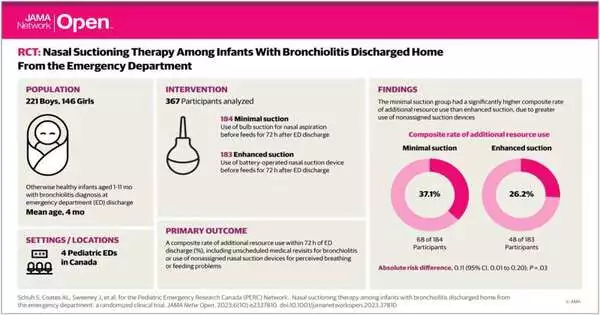
The review included in any case solid newborn children who matured from 1 to 11 months (middle age 4 months) and were determined to have bronchiolitis. Bronchiolitis was characterized as the primary episode of upper respiratory disease with nasal clogs and respiratory trouble.
Members were haphazardly relegated to one of two gatherings with either insignificant suctioning through a bulb pipetting gadget or improved suctioning by means of a battery-worked gadget.
The essential result was extra asset use, which was a composite of unscheduled returns to for bronchiolitis or the utilization of extra suctioning gadgets for taking care of or breathing worries.
Upgraded suctioning didn’t fundamentally change the sickness direction compared with insignificant suctioning. While there was a slight decrease in extra asset use with upgraded suctioning, it was not measurably huge. There was no tremendous contrast in unscheduled returns for bronchiolitis between the two gatherings, showing that upgraded suctioning didn’t prompt fewer returns.
Negligible suctioning brought about fundamentally higher utilization of non-appointed suctioning gadgets for saw breathing or taking care of hardships compared with upgraded suctioning, proposing that guardians in the improved attractions bunch were more happy with their allotted gadget than those in the insignificant pull bunch.
The fulfillment of or trust in the suctioning technique was irrelevant to different auxiliary results, including bronchiolitis returns, crisis office returns, and changes in typical taking care of and resting. While no massive contrasts were seen in essential or auxiliary results, parental consideration fulfillment was higher in the improved gadget bunch.
Bronchiolitis is a main source of newborn child hospitalizations and is related to critical medical service asset usage. Powerful treatments are restricted, prompting significant practice variety and the potential for ridiculous medicines. Nasal suctioning is ordinarily used to alleviate nasal blockage in newborn children with bronchiolitis, yet the adequacy of various suctioning techniques has been hazy.
The flow study outlines that when an improved suctioning gadget was utilized, it didn’t modify the sickness direction contrasted with insignificant suctioning; however, doling out negligible suctioning prompted a fundamentally higher utilization of non-relegated suctioning gadgets and a lower parental fulfillment with the allotted gadget. The creators recommend that negligible suctioning might be adequate for overseeing bronchiolitis in babies and feature the significance of parental fulfillment with saw contrasts in treatment choices.
More information: Suzanne Schuh et al, Nasal Suctioning Therapy Among Infants With Bronchiolitis Discharged Home From the Emergency Department, JAMA Network Open (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37810