The Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) instrument, locally available on NOAA’s GOES-18 satellite, is currently giving striking lightning perceptions of the Western Hemisphere. GOES-18 was sent off on March 1, 2022.
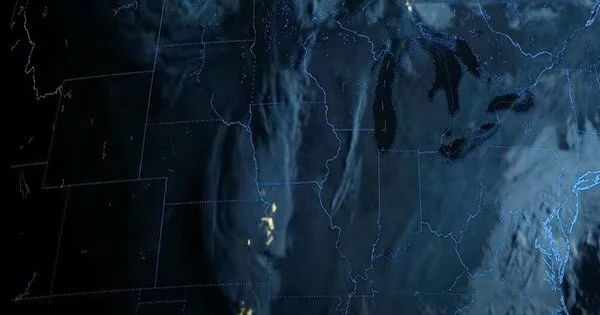
As of late, the GOES-18 GLM has recognized and observed lightning activity in extreme tempests across the U.S. A derecho traveled through the Northern Plains on May 12, especially influencing eastern South Dakota and western Minnesota. Derechos highlight strangely broad breeze harm, and as per NOAA’s National Weather Service, the May 12 occasion was one of the most outrageous models on record because of the quantity of huge breeze blasts. This derecho created straight-line twists somewhere in the range of 60 to 100+ miles per hour. A few cyclones were confirmed nearby, as well as huge blows of dust. The tempest evacuated trees, harmed property, caused blackouts, and brought about wounds and something like two deaths.
GLM distinguishes and maps complete lightning — in-cloud, cloud-to-cloud, and cloud-to-ground — over the Americas and adjacent sea districts on a consistent basis.GLM offers bits of knowledge past the presence of a lightning strike, uncovering the degree of lightning streaks and the distance they travel.
Quick expansions in complete lightning movement frequently precede extreme and tornadic tempests. Portraying lightning movement in storms permits forecasters to recognize escalating storms before they produce harmful winds, hail or cyclones. Forecasters can use GLM data to distinguish electrically dynamic storms, determine the extent of the lightning danger, recognize fortifying and debilitating storms, screen storm progression, and supplement radar information where inclusion is poor.
Researchers and forecasters have made extraordinary advances in a long time, starting from the primary GLM information opened up by GOES-16, including the capacity to extricate three-layered data from these locally two-layered perceptions. Flying alongside the tempests reveals exactly how well the GLM catches the development of the singular tempest cells that consolidate to frame enormous tempest frameworks. Quickly refreshing GLM information empowers forecasters to screen lightning streaks with pinpoint accuracy over a significant part of the Western Hemisphere.
Broad climate occasions present specific difficulties for the flight business. Expanded lightning streaks as seen by GLM happen in storms with additional fierce updrafts and downdrafts, which are a critical danger to airplanes. GLM symbolism assists pilots and aviators with dealing with regulators’ course trips to expand wellbeing and limit monetary effects.
GOES-18 is currently undergoing post-send off testing, approval, and alignment of its instruments and frameworks in order to be ready for operations. NOAA plans for GOES-18 to supplant GOES-17 as GOES West in mid-2023. Symbolism and data from GOES-18 should be regarded as preliminary and non-functional during the post-send off testing stage.