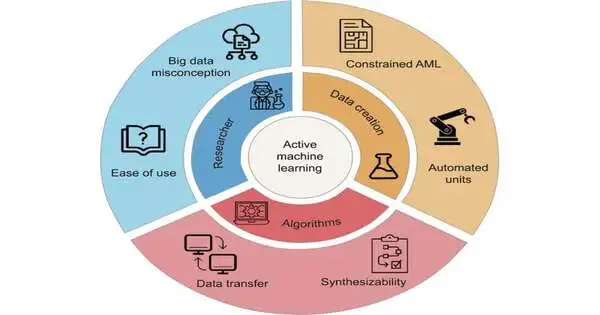
Synthetic design scientists have a strong new device available to them: dynamic AI. In a new viewpoint article distributed in Designing, Kevin M. Van Geem’s examination group at Ghent College investigates the capability of dynamic AI in changing the field of synthetic designing. By joining AI with the plan of analysis, dynamic AI vows to upgrade the productivity and cost-adequacy of exploration, crossing all lengths of compound design.
Dynamic AI calculations offer more noteworthy adaptability and better execution than customary analysis calculations. Nonetheless, notwithstanding their true capacity, the utilization of dynamic AI in synthetic design is as yet restricted. The article recognizes three key difficulties blocking its broad reception: persuading exploratory analysts, guaranteeing adaptability in information creation, and upgrading the power of dynamic AI calculations.
The study led by Van Geem’s group features an expansive range of dynamic AI applications in compound design. By the way, the article stresses the need to advocate for dynamic AI among trial analysts and overcome the current hindrances. To address these difficulties, the article proposes cooperative endeavors between AI specialists and synthetic designers.
The joint effort wouldn’t just bring issues to light about dynamic AI but additionally work with the customization and streamlining of calculations in view of explicit trial units and strategies.
To overcome the hindrance of poor starting exploratory choice, the incorporation of move learning and dynamic learning with multi-constancy models is proposed. Moreover, the article underlines the significance of adjusting general dynamic AI calculations to meet the imperatives of various arrangements, consequently expanding the application space of dynamic AI.
Dynamic AI can possibly reform different parts of substance design examination, from the particle and impetus plan to the response and reactor plan. Nonetheless, to open its maximum capacity, it is significant to overcome any barrier between AI specialists and compound architects. Thus, in addition to the fact that dynamic AI can allow calculations to be tweaked, the presentation of these calculations can also be moved along.
The article closes by highlighting the meaning of blending synthesizability and imagination in dynamic AI. Promising leaps forward in this field will empower substance specialists to use dynamic AI as a fundamental apparatus, working with independent and effective logical revelations. Eventually, this will contribute to a more feasible substance industry.
Nan Zhang, proofreader of the subject of synthetic, metallurgical, and materials design, remarked, “As dynamic AI keeps on developing, what’s to come looks splendid for compound architects. Expanding mechanization and the improvement of additional productive calculations will prepare for novel disclosures and headways in the field. With better cooperation and more extensive reception, dynamic AI is ready to turn into a confided-in resource in the synthetic specialist’s tool compartment.”
More information: Yannick Ureel et al, Active Machine Learning for Chemical Engineers: A Bright Future Lies Ahead!, Engineering (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.eng.2023.02.019