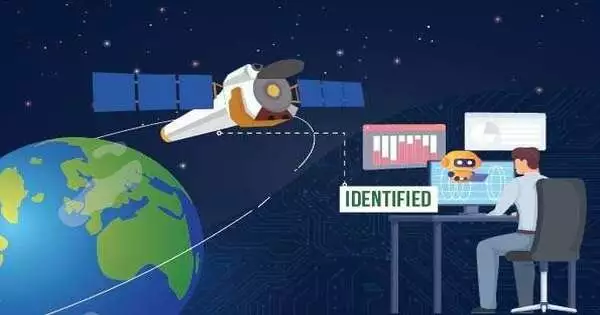
Researchers at the Goodbye Foundation of Essential Exploration (TIFR) in Mumbai, India, and the Indian Organization of Room Science and Innovation (IIST) have identified the concept of thousands of new large articles in X-beam frequencies using AI techniques.AI is a variation on or part of computerized reasoning.
Space science is entering another time as an immense measure of galactic information from a large number of enormous items is opening up. This is a consequence of huge studies, arranged perceptions with great galactic observatories, and an open information access strategy. Obviously, this information has an incredible potential for some disclosures and a new comprehension of the universe.
In any case, it isn’t pragmatic to investigate the information from this large number of articles physically, and automated AI methods are crucial for removing data from these sources. However, use of such strategies to gather galactic information is still exceptionally restricted and at a fundamental stage.
The TIFR-IIST group applied AI strategies to countless grandiose articles seen in X-beams with the USA’s Chandra space observatory. This demonstrated how a new and effective innovative advancement could assist and reform the critical and major logical exploration.The group applied these procedures to around 277,000 X-beam protests, of which the vast majority were obscure. An order of obscure items is identical to the disclosure of explicit classes’ objects.
Subsequently, this exploration prompted the dependable disclosure of a huge number of infinite objects of various classes—ffor example, dark openings, neutron stars, whiter people, and stars—wwhich opened up a gigantic chance for the stargazing local area to conduct additional nitty-gritty investigations of many fascinating new items.
This collaborative investigation has also been critical in laying out a cutting-edge capability to apply new AI methods to major cosmological exploration, which will be required to experimentally use data from current and upcoming observatories.
The review is distributed in the month-to-month notification of the Imperial Galactic Culture.
More information: Shivam Kumaran et al, Automated classification of Chandra X-ray point sources using machine learning methods, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad414