Drug advancement for lung infections is muddled. Most clinical preliminaries that test novel medications flop because research facility models can’t precisely repeat human physiology.
At present, unambiguous sub-atomic pathways are often demonstrated in exceptionally fake circumstances, utilizing a couple of various cell types in a culture dish in the lab. Such straightforward frameworks don’t completely imitate the tissue climate of the lung, and accordingly, these research facility models are inadequate with regards to the portrayal of restoratively pertinent cell correspondence pathways.
Upsetting pre-clinical medication improvement: an organotypic model framework for lung research
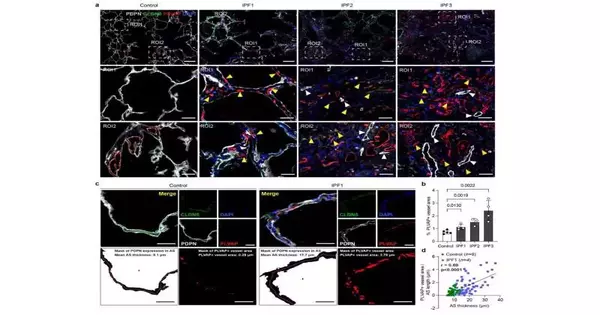
Another promising trial model to unthinkingly concentrate on lung sickness arose as of late: supposed human accuracy cut lung cuts (hPCLS). These are slender segments of lung tissue that can be utilized for tests in the lab.
“We are now working on scaling up these hPCLS perturbation experiments to learn more about the regulation of lung tissue states in health and disease, as well as providing an experimental model for drug testing directly in human lung tissue.”
Prof. Schiller says,
To create hPCLS, researchers from Helmholtz Munich worked with human lung tissue obtained from patients going through a medical procedure because of lung illnesses. The tissue gets cut into slight cuts that can be kept alive in the lab. hPCLS enjoy the remarkable benefit of holding the full cell variety and local three-layered construction of the lung.
The group of scientists led by Prof. Schiller and Dr. Burgstaller has now carried out a top-to-bottom investigation of all cells inside the hPCLS, consequently essentially propelling the potential outcomes and use of this lung sickness model.
They utilized the force of single-cell genomics, which records quality exercises in individual cells, to examine the movement of all cells in hPCLS after unambiguous trials and remedial medicines.
Figuring out treatment reactions: bits of knowledge from human accuracy cut lung cuts
The new high-level information about hPCLS was utilized by the group to comprehend how sickness-specific cell exercises that happen in lung fibrosis patients can be prompted in the hPCLS model framework and what these illness-specific cell states can be meant for by various enemies of fibrotic drugs.
The creators computationally coordinated a few single-cell transcriptomic datasets from numerous patient partners and utilized man-made brainpower (artificial intelligence)-based move learning ways to deal with comprehending how cells expresses that were prompted by cytokines and medication medicines in the hPCLS model, in contrast with the Human Lung Cell Map book (HLCA) of wellbeing and sickness.
The HLCA is a thorough guide specifying the qualities of all cell types inside the human lung and was delivered recently by Helmholtz Munich researchers and their global accomplices.
The new techniques and experiences from this study demonstrate the force of exploratory examinations in hPCLS to empower the investigation of tissue homeostasis, recovery, and pathology.
Prof. According to Schiller, “We are presently dealing with doing these hPCLS bother tests at scale to more deeply study the guidelines of lung tissue states in wellbeing and sickness and give a trial model to medicate testing straightforwardly in human lung tissue.” Eventually, these endeavors by Helmholtz Munich researchers will have the ability to fundamentally accelerate the improvement of novel treatments.
The work is distributed in the journal Science Translational Medication.
More information: Niklas J. Lang et al. Ex vivo tissue perturbations coupled to single-cell RNA-seq reveal multilineage cell circuit dynamics in human lung fibrogenesis, Science Translational Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adh0908