In order to generate mode-locked pulses, passive mode-locked technology regulates the loss and phase of the cavity by making use of the nonlinear absorption effect of saturable absorbers. Graphene has a very wide operating spectral range (300–2,500 nm), a low absorption coefficient, a significant modulation depth, and a unique energy bandgap structure.
When it comes to fiber lasers’ ultrashort pulse output, graphene has emerged as an ideal saturable absorber. Mode-locked pulses have been achieved by researchers in numerous graphene mode-locked technology experiments. According to patterns of energy distribution, laser pulses can also be divided into bright and dark pulses. Numerous bright pulses have been reported.
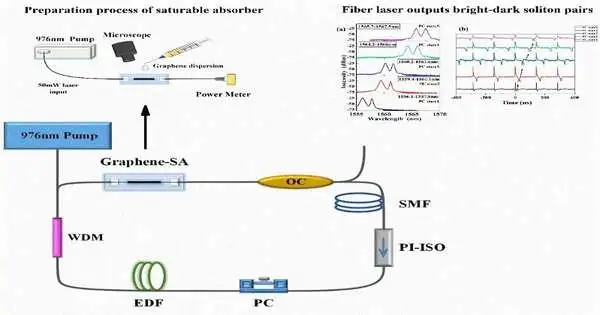
Graphene mode-locked fiber lasers are of interest to researchers at Changchun University of Science and Technology (CUST), China, led by Prof. Mingyu Li. Their plan is to use optical deposition to create a graphene microfiber composite structure that has an all-fiber structure and addresses the issue of saturable absorbers’ low modulation depth.
In the journal Frontiers of Optoelectronics, a paper titled “Generation of mode-locked states of conventional solitons and bright-dark solitons in graphene mode-locked fiber laser” was published.
In this manner, the output characteristics of two switchable mode-locked pulses in the graphene mode-locked fiber laser, the effects of pump power and polarization state on bright and dark soliton pairs, and dual-wavelength tunable characteristics were investigated. A graphene mode-locked fiber laser was constructed in the negative dispersion region. The use of graphene in fiber lasers will become even more widespread as a result of this study.
More information: Zixiong Li et al, Generation of mode-locked states of conventional solitons and bright-dark solitons in graphene mode-locked fiber laser, Frontiers of Optoelectronics (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s12200-023-00067-2