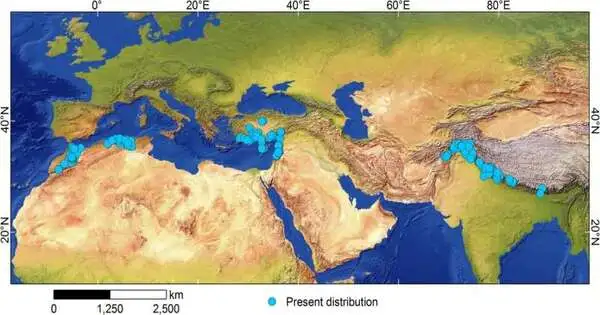
The family Cedrus Trew (Pinaceae) comprises four types of evergreen coniferous trees, which have significant social, stylistic, logical, and monetary qualities. The four species are disjunctively dispersed in the Mediterranean and western Himalaya. Understanding the verifiable conveyance of Cedrus and the driving variables can give important data for the preservation of these species.
In a review published in Ecological Indicators, specialists from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences utilized the MaxEnt (greatest entropy) model in a blend with environmental information and the ongoing circulation information of Cedrus to mimic the past, present, and future dissemination of possibly reasonable territories for Cedrus in the Mediterranean district and western Himalaya.
The models utilized in the review featured the key bioclimatic factors that influence the regular dispersion of Cedrus. Cedrus’s winter precipitation is the fundamental environmental variable that impacts the endurance and conveyance of Cedrus. The winter temperature was one more significant element controlling the conveyance of Cedrus in the two regions, and the limit conceivably goes from-10 °C to 5 °C.
“We believe that protecting Cedrus in the Mediterranean region should be prioritized. As soon as possible, some measures should be put in place to protect the natural distribution of Cedrus.”
Li Shufeng of XTBG.
The recreation results showed that the current dispersion of reasonable environments for Cedrus was to some degree bigger than the genuine circulation region. A few areas in the Mediterranean and western Himalaya are a long way past the ongoing circulation of Cedrus. The Quaternary dust record for Cedrus in the Mediterranean district demonstrated that Cedrus created a lot of dust that was shipped over significant distances.
Additionally, the dispersion of Cedrus would be diminished in light of worldwide environmental change from now on. From the Last Glacial Maximum to the present, the dispersion of Cedrus in North Africa has diminished fundamentally, compared to the eastern Mediterranean area.
“We propose that attention be given to the security of Cedrus in the Mediterranean area.” “A few measures ought to be carried out to safeguard the normal dissemination of Cedrus straightaway,” said Li Shufeng of XTBG.
More information: Shumei Xiao et al, Cedrus distribution change: past, present, and future, Ecological Indicators (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109159