Specialists have prevailed with regards to creating a covering material that can be composed on utilizing UV light and the composing eradicated again utilizing oxygen. Changes to rewritable paper could assist in lessening paper squander in a wide assortment of uses. The material is produced using three non-harmful parts and is delivered in a solitary combination venture, as portrayed in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
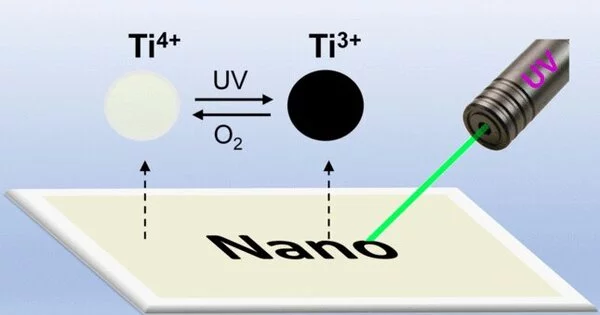
Yadong Yin and his group based at the University of California, Riverside (U.S.) zeroed in on titania (TiO2) nanocrystals to deliver a light-delicate, rewritable framework. Nanocrystalline TiO2, a semiconductor, obscures when illuminated with bright (UV) light because of charge detachment and a decrease of titanium molecules. Basically, the variety change isn’t extremely durable on the grounds that oxygen in the air re-oxidizes the titanium and makes it less straightforward.
“When exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, nanocrystalline TiO2, a semiconductor, darkens due to charge separation and reduction of titanium atoms. Importantly, the color change is not permanent because oxygen in the air re-oxidizes the titanium, causing it to return to its original transparency.”
Yadong Yin and his team based at the University of California
The group of specialists focused on supporting the variety of changes for a more extended timeframe. They used nitrogen as a dopant, which they got from urea, and embellished the gems with a typical non-harmful substance called diethylene glycol. This substance, which was added to the mixture as a dissolvable, also played an important role in the variety change; experts discovered that it searched for excess electron openings, postponing reoxidation and a return to the straightforward state.
When applied to glass or paper, the nanocrystals form a uniform covering that could be composed of utilizing UV light. All that was necessary to deliver the composition was 30 seconds of brightening with a light source at a frequency of under 400 nm. The group underscored that it was not important to utilize areas of strength for a source; lights in the power scope of LEDs were adequate to create an elevated degree of difference on the material.
The group investigated two light-composing strategies. In the first place, they delivered designs or printed text by enlightening the paper or glass substrate through a photomask. They likewise created freehand composition using a laser pen. The two choices gave a high-contrast design that was steady for a long time and could either be deleted by warming or blurred gradually in light of oxidation. The group showed that broadening the existence of the printing is conceivable by covering the film surface with a defensive layer of a non-harmful polymer, diminishing its openness to oxygen.
The primary benefit of the framework delivered by Yin and his group is its reusability. The review showed that up to 50 composing eradicate cycles could be finished with no eminent loss of differentiation. This implies that the innovation could be applied in various fields where reusable/rewritable surfaces are expected; for instance, day-to-day transport tickets, data loads up, information capacity, or sensor innovation. The creators feature a straightforward creation strategy, utilizing normal, non-harmful beginning materials, and a serious level of similarity with different materials.