Following quite a while of quiet, NASA has heard from Explorer 2 in interstellar space, billions of miles away. Flight regulators inadvertently sent an off-base order almost fourteen days prior that shifted the space apparatus' receiving wire away from Earth and cut off contact. NASA's Profound Space Organization, a monster radio receiving wires across the globe, got a "heartbeat signal," meaning the 46-year-old art is alive and working, project director Suzanne Dodd said in an email Tuesday. The news "floated our spirits," Dodd said. Flight regulators at the Stream Drive Lab in California will presently attempt to turn Explorer 2's
Astronomy & Space
Fast radio bursts are still one of the most exciting and puzzling astronomical phenomena. They are short, strong bursts of radio waves that originate in faraway galaxies and last barely a few milliseconds. Despite multiple detections, the precise cause and origin of FRBs has remained mostly unknown. An international team reports on a radio pulsar phase of a Galactic magnetar that generated a rapid radio burst in 2020; data show distinct origins for 'bursts' and 'pulses,' adding to the idea of FRB generation. More than 15 years after the discovery of fast radio bursts (FRBs), which are millisecond-long cosmic explosions
Black holes, among of the most fascinating things in the universe, with such a tremendous gravitational attraction that not even light can escape. The discovery of gravitational waves in 2015, created by the merger of two black holes, offered a new window into the universe. Since then, scores of such observations have fueled astrophysicists' search to comprehend their cosmic origins. Using the POSYDON code's recent major advances in simulating binary-star populations, a team of scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Northwestern University, and the University of Florida (UF) predicted the existence of merging massive, 30 solar mass black hole
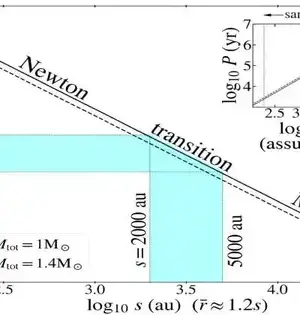
Gravitational waves are disturbances in the fabric of spacetime created by enormous objects colliding, such as black holes or neutron stars. These waves were predicted by Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity in 1915, but were not directly detected until 2015 by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO). You can't see or feel it, but everything around you is gradually shrinking and increasing, even your own body. According to a new study from the NANOGrav Physics Frontiers Centre of the National Science Foundation, it's the strange, spacetime-warping effect of gravitational waves travelling across our galaxy. The North American Nanohertz Observatory
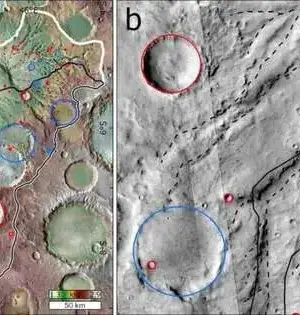
Astronomers all over the world have been scouring the universe for clues about how and why fast radio bursts (FRBs), which are millisecond-long cosmic explosions of electromagnetic radiation, were first discovered more than 15 years ago. Practically all FRBs distinguished have begun in profound space outside our Smooth Way system. That is, until the first Galactic FRB, FRB 20200428, was discovered in April 2020. This FRB was created by a magnetar (SGR J1935+2154), a thick, city-sized neutron star with an extraordinarily strong attractive field. Some people were led to believe that magnetars could also produce FRBs found at cosmological distances
Gravitational waves are ripples in spacetime created by the acceleration of enormous objects such as black holes or neutron stars during severe events such as mergers or supernova explosions. These occurrences generate enormous amounts of energy in the form of gravitational waves. Although astrophysicists should theoretically be able to detect gravitational waves from a single, non-binary source, these elusive signals have yet to be discovered. Researchers now propose looking at a new, unexpected, and completely unknown location: the tumultuous, energetic cocoons of material that encircle dying big stars. Now, researchers from Northwestern University propose looking at a new, unexpected, and
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a powerful space observatory launched by NASA that is designed to study distant objects in the universe such as planets, stars, and galaxies. Given its advanced capabilities, it is possible that JWST will capture breathtaking images of Saturn and its rings, providing new insights and detailed observations of this magnificent gas giant. Saturn's iconic rings appear to glow eerily in this incredible infrared image, which also reveals unexpected features in Saturn's atmosphere. Please see the image link below. This image provides context for an observing program that will put the telescope's ability to
Dark openings are the most puzzling items known to mankind, with highlights that sound like they come directly from a science fiction film. Heavenly mass dark openings with masses of around 10 suns, for instance, uncover their reality by eating materials from their sidekick stars. Furthermore, in certain examples, supermassive dark openings amass at the focal point of certain cosmic systems to shape splendid smaller districts known as quasars with masses equivalent to millions to billions of our sun. A subset of accumulating heavenly masses of dark openings that can send off planes of exceptionally polarized plasma are called microquasars.
Researchers reveal a theoretical breakthrough that may explain both the nature of invisible dark matter and the cosmic web, the large-scale structure of the universe. The result forges a new link between these two long-standing astronomical problems, opening up new avenues for understanding the universe. According to the findings, the 'clumpiness problem,' which concerns the unexpectedly even distribution of matter on large scales throughout the universe, could be a sign that dark matter is made up of hypothetical, ultra-light particles known as axions. The implications of proving the existence of difficult-to-detect axions go beyond understanding dark matter and may raise
Helium nuclei research contributes significantly to our understanding of cosmic ray origin and propagation. Cosmic rays are high-energy particles that constantly bombard the Earth and other celestial bodies, originating primarily from outside the Solar System. They are made up of protons, helium nuclei (alpha particles), heavier nuclei, electrons, and gamma rays. Since 2015, the CALorimetric Electron Telescope (CALET) on the International Space Station's Kibo's Exposed Facility (EF) has been measuring the flux of cosmic ray particles. An international team of researchers has published the results of a direct measurement of the cosmic ray helium spectrum using CALET data in a