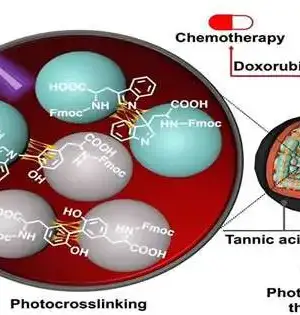
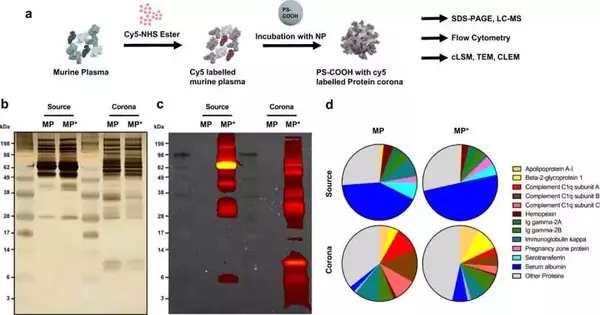
Novel medications, like immunizations against Coronavirus, among others, depend on drug transport utilizing nanoparticles. Whether this medication's transport is harmed by a gathering of blood proteins on the nanoparticle's surface was not explained for quite a while. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Exploration have now followed the path of a molecule into a cell using a combination of microscopy techniques.They had the option to notice a cell-interior interaction that successfully isolates blood parts and nanoparticles. Nanoparticles are a momentum field of examination, and envisioning current medication without them is incomprehensible. They act as minuscule medication containers that
Bio & Medicine
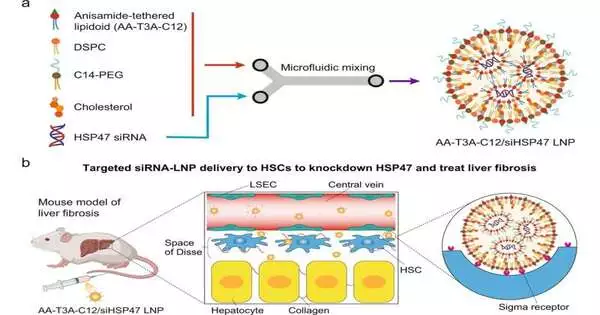
Since the outcome of the coronavirus antibody, RNA treatments have been the object of expanding interest in the biotech world. These treatments work with your body to focus on the hereditary basis of illnesses and diseases, a promising elective treatment strategy compared to that of conventional drug therapy. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have been effectively utilized in drug conveyance for quite some time. FDA-endorsed treatments use them as vehicles for conveying messenger RNA (mRNA), which prompts the cell to make new proteins, and little meddling RNA (siRNA), which trains the cell to quiet or hinder the outflow of specific proteins. The
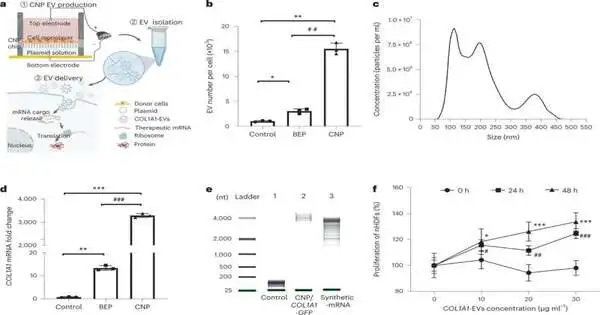
A group of scientists drove by the College of Texas, MD. Anderson Malignant Growth Place has fostered a clever conveyance framework for courier RNA (mRNA) utilizing extracellular vesicles (EVs). The new strategy can possibly conquer large numbers of the conveyance obstacles looked at by other encouraging mRNA treatments. In the review, distributed today in Nature Biomedical Designing, the specialists describe using EV-typified mRNA to start and support collagen creation for quite a long time in the cells of photoaged skin in lab models. It is the principal treatment to exhibit this capacity and addresses a proof-of-idea for sending the EV
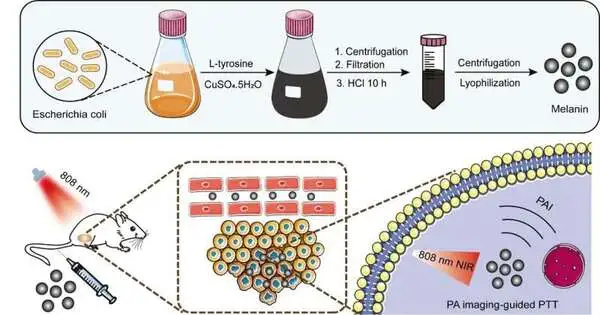
Photothermal treatment (PTT) has drawn significant consideration for the treatment of growths since it is negligibly obtrusive and has spatiotemporal selectivity. Melanin is a sort of multifunctional color tracked down generally in vertebrates, plants, and microorganisms, with extraordinary possibilities as a PTT specialist for disease treatment. Unfortunately, industrially available melanin is primarily obtained through substance blends or extraction from sepia, which limits its wide range of production and poses some potential health risks. As of late, an exploration group led by Prof. Yan Fei from the Shenzhen Foundation of Trend Setting Innovation (SIAT) of the Chinese Institute of Sciences, along
Another tiny nitrogen dioxide sensor could help protect the environment from vehicle toxins that cause lung disease and corrosive rain. Scientists from TMOS, the Australian Exploration Board's Focus of Greatness for Extraordinary Meta-Optical Frameworks, have fostered a sensor produced using a variety of nanowires, with a starting point of a fifth of a millimeter for each side, and that implies it very well may be handily integrated into a silicon chip. In research distributed in the most recent issue of Cutting Edge Materials, Ph.D. researcher at the Middle's Australian Public College group and lead creator Shiyu Wei depicts the sensor
Due to their large surface area and high surface awarenesses, as well as their novel electrical, optical, and electrochemical properties, two-layered materials, similar to change metal dichalcogenide, have applications in general wellbeing.An examination group has embraced a survey investigation of strategies used to tweak the properties of two-layered transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD). These techniques have significant biomedical applications, including biosensing. The cooperation is distributed in the diary, Nano Exploration Energy. The group will likely present a complete outline of this promising field and show the difficulties and open doors accessible in this exploration region. "In this audit, we center around
According to new research, adolescents who underwent sleeve gastrectomy, a type of weight-loss surgery that involves removing part of the stomach, were less likely to visit the emergency room or be admitted to the hospital in the five years following their operations than those who had their stomachs divided into pouches through gastric bypass surgery. The rates of complications, death, and subsequent surgery were comparable in both groups, according to a study published in JAMA by University of Michigan researchers. All of the patients studied were covered by Medicaid, the nation's largest health insurance provider for those under the age
Antioxidants such as amino acids, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin C are abundant in healthy diets, but the extent to which these micronutrients benefit cardiovascular health has long been debated. A new meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology sheds some light on the subject. Researchers systematically reviewed and analyzed data from 884 studies on micronutrients taken as dietary supplements that have been published to date. They discovered several micronutrients that do reduce cardiovascular risk, as well as others that have no benefit or even are harmful. The combined studies included more than 883,000 patients. "For
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-based messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) immunizations have as of late emerged as a promising system for the counteraction and therapy of tumors, as well as other irresistible illnesses. LNPs are carriers that safely and effectively deliver nucleic corrosive immunizations, gaining areas of strength for a reaction. One achievement is the clinical utilization of driving LNP mRNA antibodies against the Coronavirus, which shows various levels of security adequacy as well as a few secondary effects. As these antibodies are known to be protected, effective, and easily created, they have been broadly utilized as security against different human illnesses, particularly
Engineers at Duke College have fostered a gadget that utilizes sound waves to separate and sort the tiniest particles tracked down in blood in no time. The innovation depends on an idea called "virtual support points" and could be an aid to both logical examination and clinical applications. Little natural nanoparticles called "little extracellular vesicles" (sEVs) are released from each sort of cell in the body and are accepted to play a huge part in cell-to-cell correspondence and illness transmission. The new innovation, named Acoustic Nanoscale Division through Wave-Support Point Excitation Reverberation, or Reply for short, not just pulls these