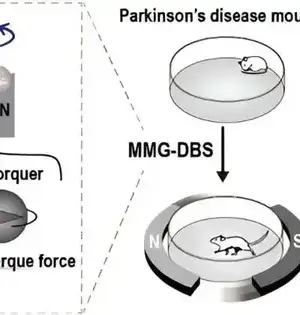
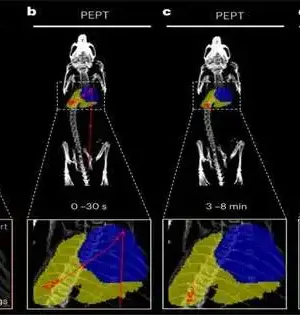
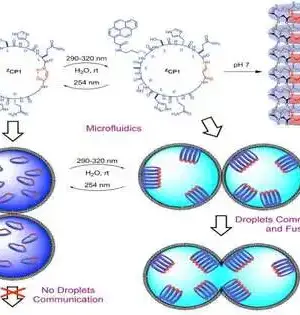
Scientists have for some time been dealing with how to treat weight, a difficult condition that can prompt hypertension, diabetes, ongoing irritation, and cardiovascular illnesses. Studies have likewise uncovered areas of strength for both weight and disease; late revelations show that smoking, drinking liquor, and heaviness are the greatest supporters of malignant growth around the world. The improvement of fat cells, which are created from a small fibroblast-like begetter, enacts the fat cells' particular qualities as well as develops them by putting away more lipids (in adipocytes and fat tissue). Truth be told, lipid capacity is the defining capability of
Bio & Medicine
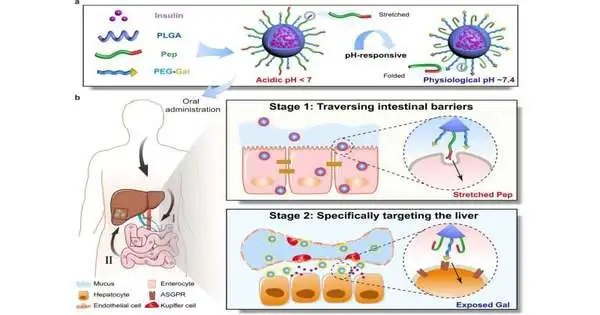
Clinically, type 1 diabetes (T1DM) and high-level type 2 diabetes (T2DM) patients require various everyday insulin infusions to keep up with blood glucose levels, which might cause incredible agony, is a bother to patients, and can prompt hyperinsulinemia. In comparison, oral insulin treatment is very consistent. There are two bottlenecks in accomplishing the desired oral insulin treatment. One is the gastrointestinal boundary that generally limits the oral retention of insulin; the other is the lack of amassing of insulin at target sites after ingestion. Under physiological circumstances, the liver is exposed to a 2–3 fold higher insulin level than the
The effectiveness of mRNA vaccines and medications, such as those used to treat cancer, Covid-19, or other genetic diseases, will be significantly increased with even less dosage of the mRNAs, according to recent research from a team of synthetic biologists at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST). Since mRNA can be created to instruct cells to produce any type of protein, including antigens, enzymes, and hormones that are crucial for preventing infections and controlling bodily processes, mRNA is undoubtedly a preferred alternative for vaccines and the treatment of many different diseases. However, mRNA medications and vaccines frequently
Surgery is widely regarded as the gold standard for solid tumor treatment. Intraoperative imaging has been used to overcome difficulties in identifying small lesions, surgical margins, and cancer-positive lymph nodes in order to improve surgical oncology precision. Dr. Benjamin Rotstein and colleagues present a simple method for producing carbon isotope-labeled versions of drugs and diagnostics. The ability of scientists to design elegantly specific drugs for targeted clinical trials is critical in the development of new pharmaceuticals. In this overall effort, isotopic labeling of drug candidates in research labs is critical. Dr. Benjamin Rotstein's lab at the University of Ottawa Faculty
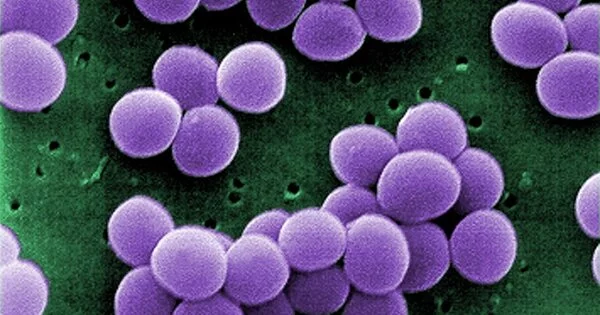
Antibiotic discovery in the previous century reduced mortality and morbidity due to infectious diseases, but their inappropriate and irrational use resulted in the emergence of resistant microbial populations. Pathogenic bacteria develop intrinsic antibiotic resistance through the modification of target sites, active efflux of drugs, and enzymatic degradations. Antibiotic resistance is currently a major public health issue. Since the discovery of new antibiotics does not appear to be a sufficient tool in the fight against multidrug-resistant infections, adjuvant therapy, which reduces bacterial virulence, is gaining importance. Silymarin is a flavonolignan complex found in milk thistle that has a wide range of
Nanoparticles, or small particles that can convey a payload of medication therapies and different specialists, show incredible promise for treating tumors. Researchers can fabricate them in different shapes with various materials, frequently as permeable, gem-like designs framed by a grid of metal and natural mixtures, or as cases that encase their items inside a shell. When infused into a tumor, these particles can deliver therapies that assault disease cells straightforwardly or supplement different therapies like immunotherapy and radiation. In a cooperative effort by disease-trained professionals and physicists, scientists at the College of Chicago have formed a high-level sort of nanoparticle
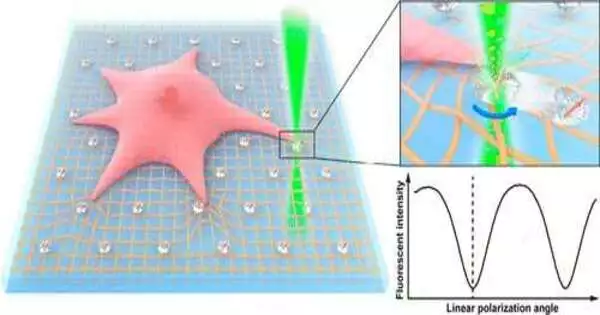
Mechanics plays a key role in cell science. Cells explore these mechanical powers to investigate their surroundings and sense the way of behaving encompassing living cells. The actual qualities of a cell's current circumstances thus influence the cell's capabilities. Understanding how cells interact with their current surroundings provides valuable experience in cell science and has broader implications in medicine, including disease detection and treatment. Up to this point, analysts have fostered various devices to concentrate on the exchange among cells and their 3D microenvironment. One of the most famous advances is footing force microscopy (TFM). It is a main strategy
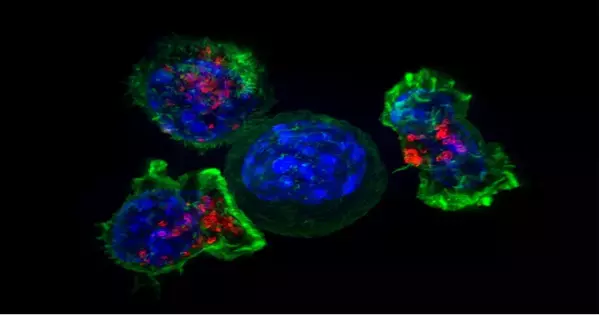
Cancer Cachexia is a progressive disorder marked by loss of body weight, fat, and muscle. Cachexia causes metabolic disruptions that are both similar and dissimilar to those seen in cancer, obscuring both diagnosis and treatment options. As systemic mediators of cancer-induced muscle wasting, inflammation, hypogonadism, and physical inactivity are all being studied. According to UTHealth Houston research, targeting a specific enzyme in the muscle could help cancer patients preserve muscle mass and potentially prolong their survival. Yi-Ping Li, Ph.D., professor in the Department of Integrative Biology and Pharmacology at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, led a study that discovered
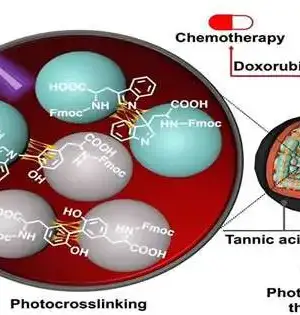
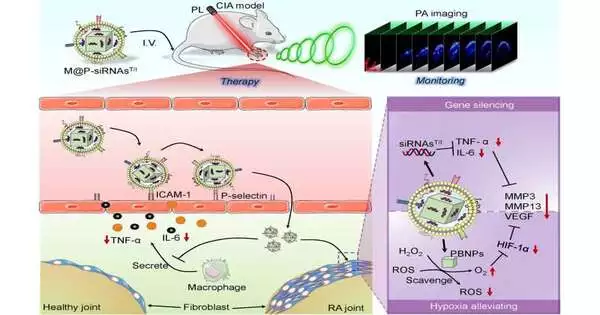
The elevated degree of responsive oxygen species (ROS) in the rheumatoid joint inflammation (RA) microenvironment and its diligent fiery nature can cause harm to joints, bones, and the synovium. Methodologies that coordinate viable RA microenvironment guidelines with imaging-based checking could prompt enhancements in the analysis and treatment of RA. A joint exploration group from the Shenzhen Establishment of Cutting-edge Innovation of the Chinese Foundation of Sciences and the College of Texas at Austin has proposed another methodology that can accomplish designated treatment of rheumatoid joint pain. The specialists coordinated little meddling RNAs (siRNAsT/I) and Prussian blue nanoparticles (PBNPs) to quiet
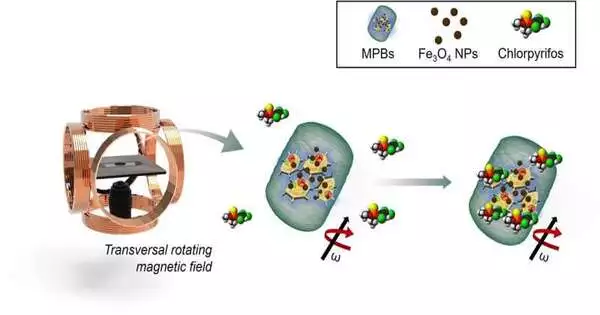
Biohybrid miniature/nanorobots that coordinate organic substances with counterfeit nanomaterials have shown extraordinary potential in the area of biotechnology. Notwithstanding, regularly utilized actual hybridization approaches can prompt blockages and harm to organic points of interaction, obstructing the ideal double-dealing of innate capacities. In another review from the College of Science and Innovation in Prague, the evacuation of the pesticide chlorpyrifos was exhibited by utilizing plant-based robots. To deliver attractive plant biobots, specialists developed plant calli on media containing ferromagnetic material. This material (iron oxide) was taken up inside the plant cells during their development. Additionally, these materials were not harmful to