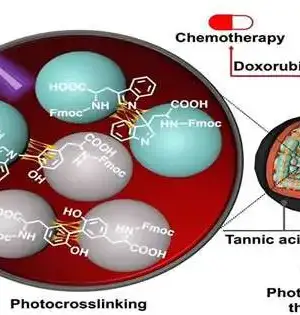
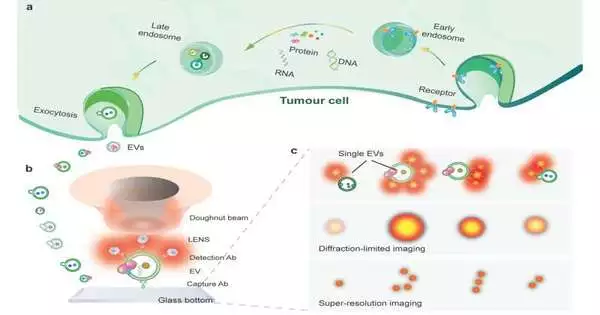
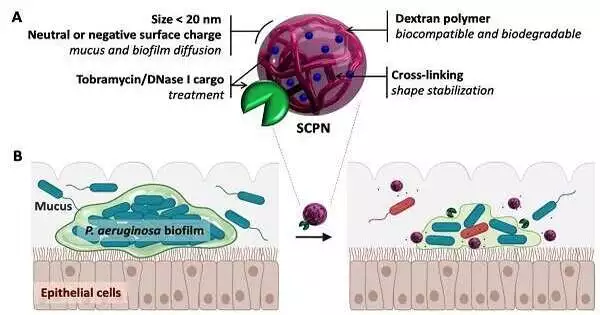
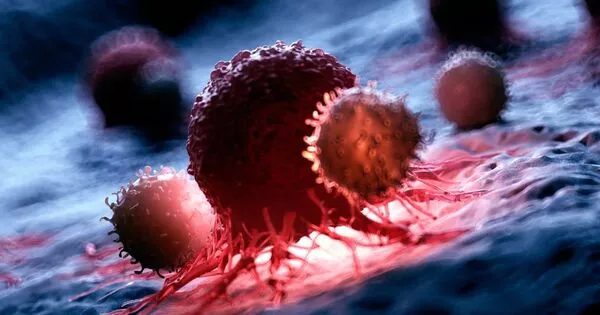
It has been generally acknowledged that tumorigenesis and disease movement comprise a multistep cycle. The most commonly involved strategy for disease finding and guessing to direct treatment choices depends on an intricate mix of imaging and obtrusive tissue biopsies. Nonetheless, the techniques are not generally delicate for beginning-phase disease finding. Little extracellular vesicles (sEVs) are nanometer-sized, bilayer lipid transporters and contain a wide assortment of freight, including lipids, proteins, metabolites, RNAs, and DNA. sEVs let out by unique disease cells exist in practically all body liquids. They can turn into the likely flowing biomarkers in fluid biopsies, as they remarkably
Bio & Medicine
Optical tweezers (OTs), otherwise called optical snares, are profoundly engaged laser rays that can be utilized to trap and control tiny items with a noncontact force. Utilized in an extensive variety of nano and small-sized tasks, OTs have become especially helpful in the control of organic items, including human cells. Another audit distributed in The European Actual Diary in addition to passing the most recent accomplishments in OTs over the last many years. The audit was written by analysts from the School of Data Science and Designing, Northeastern College, Shenyang, China—Sheng Hu, Jun-yan Ye, Yong Zhao, and Cheng-Liang Zhu .
Steady lung diseases, ongoing injuries, and medical care-related contaminations are normally considerably harder to treat than different kinds of bacterial diseases. This is on the grounds that they are frequently brought about by biofilms, or at least, states of microorganisms — mostly microbes — that fill up a self-created grid that shields and detaches them from the outer climate. As of now, another triple-acting anti-toxin specialist has figured out how to get through the biofilm extracellular grid and kill over half of the microorganisms in a single shot, as per a review distributed in the journal npj Biofilms and Microbiomes.
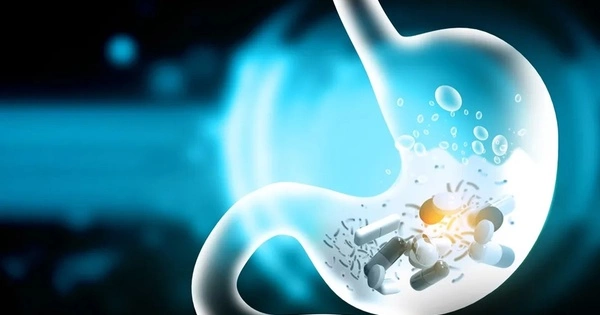
A common, economic, and easy method of administering drugs is orally, by swallowing a pill or capsule. But oral administration is the most complex way for the human body to absorb an active pharmaceutical ingredient, because the bioavailability of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract depends on the medication's ingredients and the stomach's dynamic physiological environment. In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Johns Hopkins University and Johns Hopkins School of Medicine employ a biomimetic in-silico simulator based on the realistic anatomy and morphology of the stomach -- a "StomachSim" -- to investigate and quantify the effect of
Stanford University researchers have discovered a rapid and sustainable way to synthetically produce a promising cancer-fighting compound right in the lab. The compound's availability has been limited because its only currently known natural source is a single plant species that grows solely in a small rainforest region of Northeastern Australia. The compound, designated EBC-46 and technically called tigilanol tiglate, works by promoting a localized immune response against tumors. The response breaks apart the tumor's blood vessels and ultimately kills its cancerous cells. EBC-46 recently entered into human clinical trials following its extremely high success rate in treating a kind of
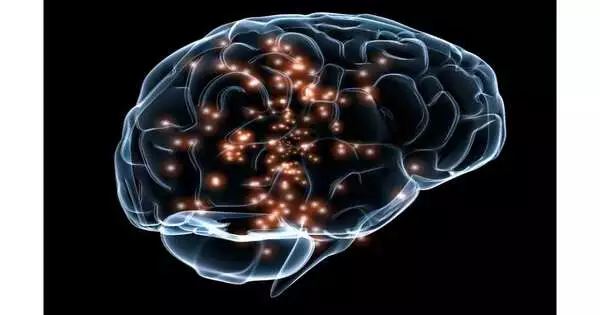
In a new report, scientists from Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool College and different colleges in China have revealed that mind feeling joined with a nose shower containing nanoparticles can further develop recuperation after ischemic stroke in a creature model. The nasal splash is a harmless strategy for conveying attractive nanoparticles into the mind that the review finds can build the advantages of transcranial attractive feeling (TMS). TMS is a strategy for painless mind feeling previously utilized clinically or in clinical preliminaries to deal with neurological circumstances like stroke, Parkinson's illness, Alzheimer's sickness, gloom, and habit. Rodents that were given joined nanoparticle and
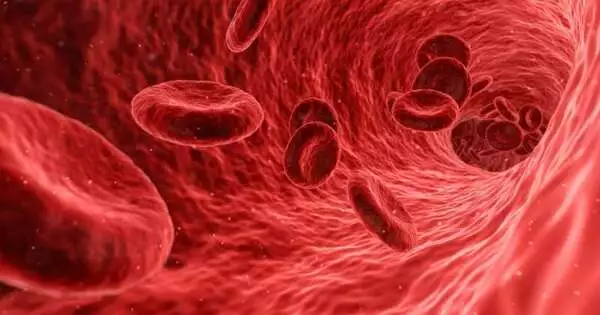
A nanoparticle treatment created by examiners at College Clinics (UH) and Case Western Hold College targets overactive neutrophils, a particular sort of white platelet, to forestall practically a wide range of blood clumps while causing no increased risk of dying. The preclinical discoveries, published in Science Translational Medication, may prompt more secure ways of really focusing on patients affected by blood clumps. As per the Centers for Infectious Prevention and Avoidance (CDC), about 900,000 individuals in the U.S. experience the ill effects of perilous blood clumps every year. "What we are observing interestingly is that neutrophils are key drivers of
Treating mice models of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (a condition found primarily in type 1 diabetes) with a combination of leptin and a drug called PTP1B inhibitor, researchers found that blood glucose levels normalized without the use of insulin. A research group at Nagoya University in Japan has discovered a new treatment for type 1 diabetes that uses leptin, a hormone secreted by fat cells. Treating mice models of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (a condition found primarily in type 1 diabetes) with a combination of leptin and a drug called PTP1B inhibitor, they found that blood glucose levels normalized without the use
Specialists at the MIT Media Lab have planned a scaled-down receiving wire that can work remotely within a living cell, opening up conceivable outcomes in clinical diagnostics and treatment and other logical cycles in light of the recieving wire's true capacity for checking and, surprisingly, coordinating cell movement continuously. "The most interesting part of this exploration is that we can make cyborgs at a cell scale," says Deblina Sarkar, colleague teacher and AT&T Profession Improvement Seat at the MIT Media Lab and head of the Nano-Computerized Biotrek Lab. "We can combine the adaptability of data innovation with the degree of
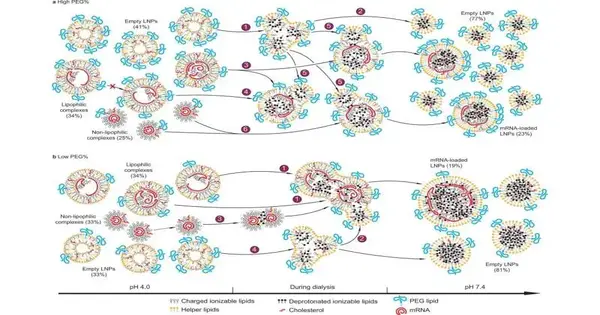
A significant part of the immunizations safeguarding individuals against SARS-CoV-2 infection and its variations are lipid nanoparticles, or LNPs. These roundabout particles convey restorative mRNA payloads, the scraps of hereditary material that trigger our insusceptible frameworks to protect against Coronavirus. Indeed, even with their prosperity, certain qualities of the particles, like payload dispersion, are obscure. Scientists and the Food and Medication Organization maintain that more bits of knowledge about these qualities should further develop measurements detailing drug fabrication. Another atomic identification stage created by two Whiting School of Design teachers is noting the FDA's call. To assist specialists with planning