A formerly unidentified hereditary transformation in a little protein gives critical security against Parkinson's illness and offers another course for investigating expected medicines, as per another USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology review. The variation, situated in a mitochondrial microprotein named SHLP2, was viewed as profoundly defensive against Parkinson's illness; people with this change are half as prone to fostering the sickness as the individuals who don't convey it. The variation type of the protein is generally uncommon and is tracked down principally in individuals of European plummet. The discoveries show up in the journal Atomic Psychiatry. First found by
Genetics
A review driven by VA Connecticut Medical Care Community/Yale scientists uncovers parentages all over the planet have a common hereditary design for tricky liquor use (PAU)—constant weighty drinking, joined by unsafe results. The discoveries, distributed in Nature Medication, could assist researchers with understanding the hereditary premise of PAU, a significant reason for medical conditions in many age groups. It is a main source of death in those it torments. This study is the biggest to date for PAU—it distinguished many new gamble qualities and revealed a lot of new science. With a superior comprehension of PAU science, researchers will have
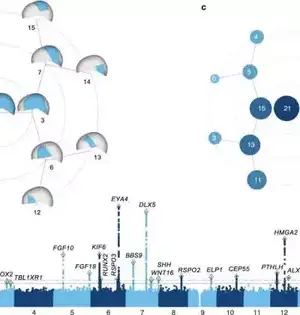
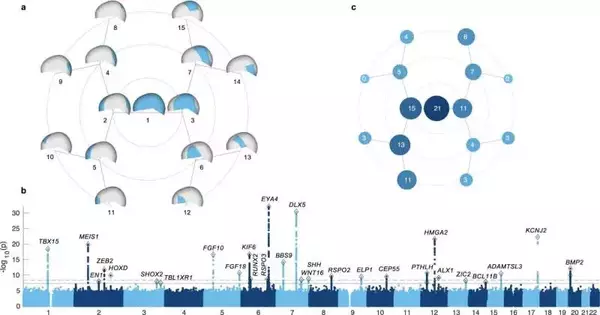
Scientists at the College of Pittsburgh and KU Leuven have found a set-up of qualities that impact head shape in people. These discoveries, distributed for the current week in Nature Correspondences, assist with making sense of the variety of human head shapes and may likewise offer significant hints about the hereditary premise of conditions that influence the skull, for example, craniosynostosis. By breaking down estimations of the cranial vault—the piece of the skull that frames the adjusted top of the head and safeguards the mind—the group distinguished 30 areas of the genome related to various parts of head shape, 29
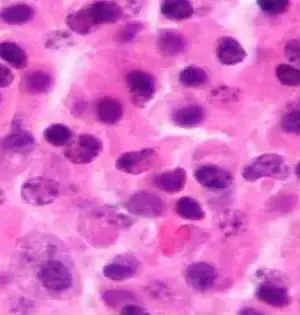
All malignant growth cells—even those inside a similar growth—contrast from one another and shift in the direction of malignant growth sickness. Researchers at Heidelberg College Clinic, the Clinical Personnel in Heidelberg, and the German Malignant Growth Exploration Center found sub-atomic changes in numerous myeloma cells that help individual disease cells endure treatment. The review was distributed in the diary Blood. Indeed, even inside one sort of malignant growth, no two cells are the same. Although a patient's disease cells are cell clones, coming about because of the division of a unique cell, they are different at a sub-atomic level. Subsequently,
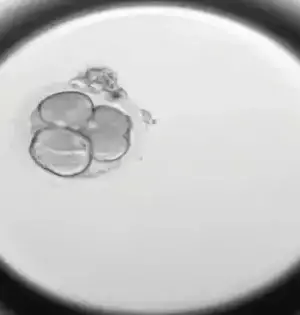
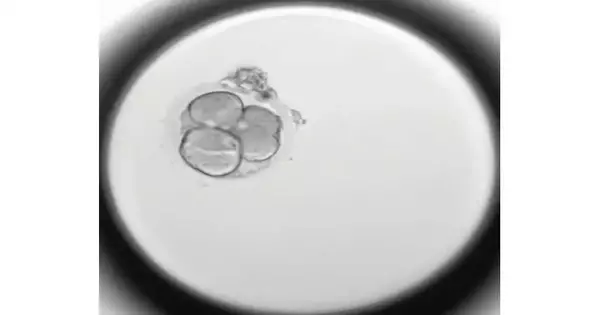
By hereditarily testing almost 1,000 undeveloped organisms, researchers have given the most point-by-point examination of incipient organism destiny following human in vitro preparation. Almost a portion of the undeveloped organisms contemplated went through formative capture due to hereditary setbacks in the early stages of events—a noteworthy understanding that proposes more IVF children could come to terms with changes in the fruitfulness of the treatment process. The novel mix of information from captured undeveloped organisms likewise reveals new insight into the still, to a great extent, baffling earliest phases of pregnancy through normal means. "We think this additionally occurs in normal
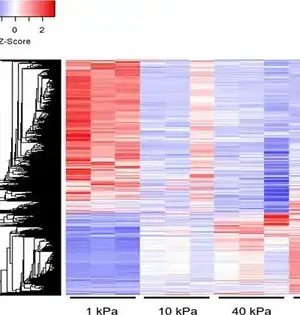
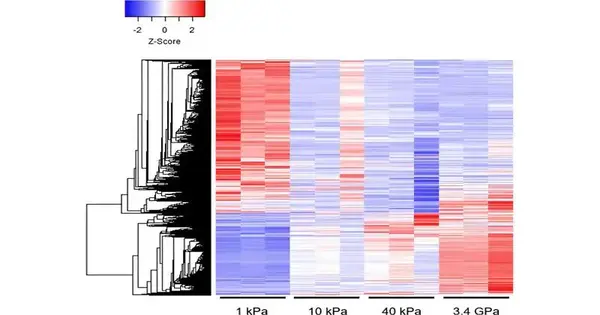
Most strong growths become solid as the disease advances. In spite of the fact that analysts perceive that the climate around the malignant growth cells impacts their way of behaving, the way in which it does so is muddled. In another paper, distributed in Logical Information, specialists from the College of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have gathered quality articulation information in light of mechanical solidity in cancers. Their work can assist with directing comprehension; we might interpret the crosstalk between malignant growth cells and their environmental factors. By and large, specialists have zeroed in on how disease cell qualities change their
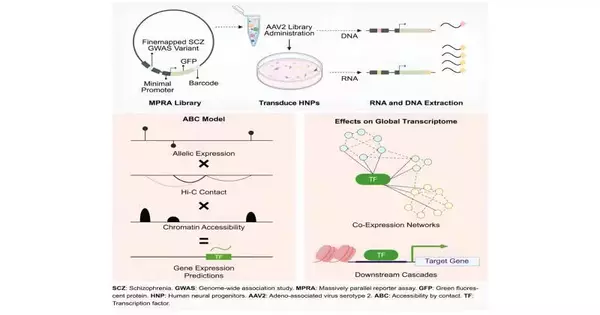
Hereditarily speaking, we are people not quite the same as one another in light of slight variations in our DNA groupings—supposedly hereditary variations—some of which have sensational impacts we can see and understand, from the shade of our eyes to our gamble for creating schizophrenia, a crippling mental condition influencing a large number around the world. For quite a long time, researchers have concentrated on the whole genomes of thousands of individuals—called broad affiliation studies, or GWAS—to find roughly 5,000 hereditary variations related to schizophrenia. Presently, UNC Institute of Medication researchers and partners are sorting out which of these variations
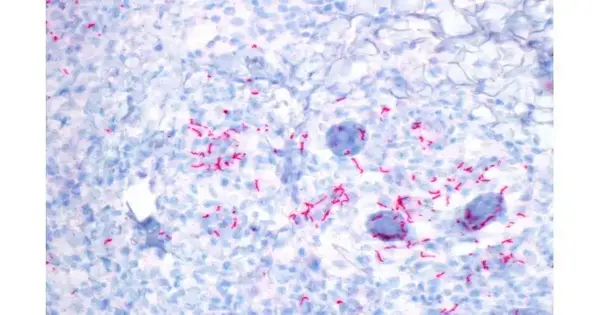
Researchers have utilized genomics to uncover unmistakable sexual organizations for syphilis transmission, characterized geologically or by sexual inclination, as a foundation for more extensive dissemination in Britain. They likewise show the presence of medication obstruction in most cases. By gathering firmly related types of the bacterium that causes syphilis—Treponema pallidum—specialists exhibit how an enormous number of cases are connected together. Specialists from the Wellcome Sanger Establishment and their partners at the UK Wellbeing Security Organization (UKHSA) sequenced 237 entire genome tests and coordinated this with epidemiological information to plan the bacterium's development and spread through a populace. They show particular
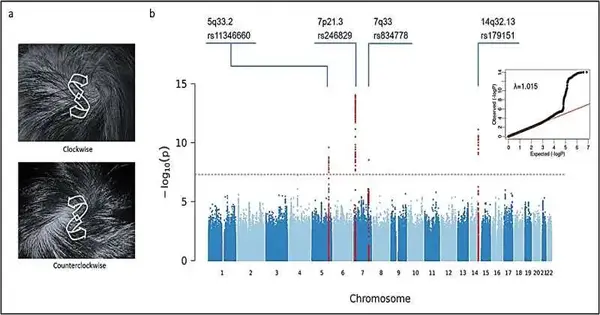
The main quality planning focuses on human scalp hair whorls, which not only shows that the hair whorl course has a hereditary premise but also that it is impacted by different qualities. Four related hereditary variations that are probably going to impact hair whorl course are recognized, as announced in the Diary of Analytical Dermatology. A hair whorl is a fix of hair filling in a roundabout example around a point determined by hair follicle directions. As an effectively noticed human quality, scalp hair whorl design is regularly characterized by the whorl number (single or twofold whorl) and whorl heading
It's hard to completely foresee who will foster Alzheimer's disease ahead of time. Presently, another review recommends that specific markers in the blood might happen 10 to 20 years before the beginning of side effects and could assist specialists with figuring out who is at high risk for dementia. For the review, specialists broke down 4,800 or more proteins in the blood of in excess of 10,000 moderately aged individuals (matured 45–65) north of 25 years. They distinguished 32 proteins connected to the risk of dementia sometime down the road. "The organic changes happen outside the mind as soon as