In conventional vision frameworks, optical data is captured by a casing-based computerized camera, and the computerized signal is later handled utilizing AI calculations.In this situation, a lot of information (for the most part repetitive) must be moved from an independent detecting component to the handling units, which prompts high dormancy and power utilization.
To resolve this issue, much effort has been put into fostering a productive methodology where a portion of the memory and computational errands are offloaded to sensor components that can see and handle the optical signal at the same time.
In another paper distributed in Light: Science and Applications, a group of researchers, led by Teacher Weida Hu from the School of Physical Science and Optoelectronic Designing, Hangzhou Establishment for Cutting Edge Review, College of Chinese Foundation of Sciences, Hangzhou, China, State Key Lab of Infrared Physical Science, Shanghai Foundation of Specialized Physical Science, Chinese Foundation of Sciences, Shanghai, China, and colleagues, have fostered a non-unstable photograph memristor, in which the reconfigurable responsiveness can be tweaked by the charge or potentially photon motion through it and further put away in the gadget.
“Our innovative notion of a two-terminal photo-memristor not only offers all-in-one sensing-memory-computing techniques for neuromorphic vision hardware, but also brings considerable convenience for high-density integration,”
The scientists
The non-unstable photomemristor has a straightforward two-terminal design, in which photoexcited transporters and oxygen-related particles are coupled, prompting an uprooted and squeezed hysteresis in the current-voltage qualities. Interestingly, non-unstable photograph memristors carry out computationally complete rationale with photoresponse-stateful tasks, for which a similar photograph memristor fills in as both a rationale entryway and memory, utilizing photoresponse as an actual state variable rather than light, voltage, and memresistance.
Extremity inversion of photograph memristors shows extraordinary potential for in-memory detecting and figuring with highlight extraction and picture acknowledgment for neuromorphic vision.
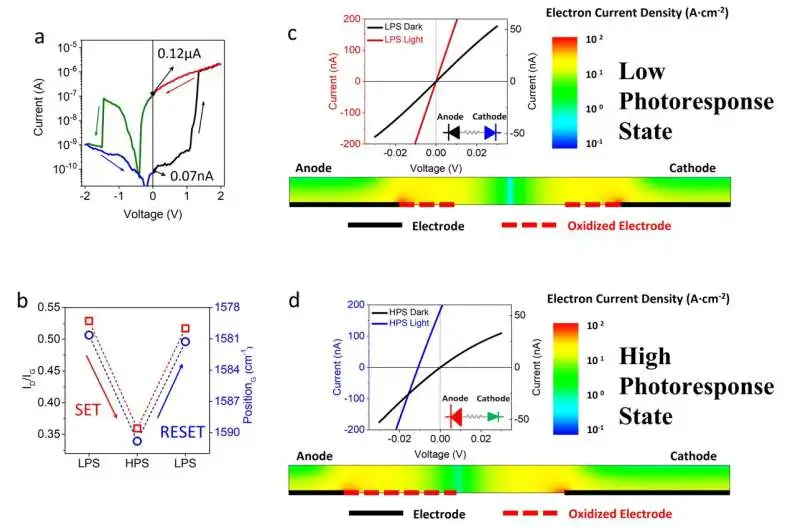
a, I-V quality of a G/M/G device with double photoresponse exchanging when the voltage changes from 0 to 2 V, 2 V to – 2 V, and back to 0 V.b, relationship between changes in the proportion of Raman dissipating forces and moves of the G method of graphene cathodes and non-unpredictable photoresponse conditions. TCAD-reenacted electron current densities dissemination of the low photoresponse state under illumination. TCAD-created dim/photograph current of the G/M/G gadget for a high photoresponse state; TCAD-created electron current densities conveyance of LPS under light.
The photographed memristor shows tunable short-out current in a non-unpredictable mode under brightening. By mimicking the organic functions of the human retina and designing explicit gadget structures, the gadgets can function as a brain network for neuromorphic visual handling and execution of completely photoresponse-stateful rationale activities triggered by electrical and light advancements. It can support various types of detection tasks using a variety of memory-registering approaches. These researchers sum up the functional guidelines and elements of their gadget as follows:
“We plan a two-terminal gadget with MoS2-xOx and explicit graphene for three purposes in one: (1) to give low boundary energy to the movement of oxygen particles; (2) to proceed as calculation deviated metal-semiconductor-metal van der Waals heterostructures with multi-photoresponse states; and (3) as an expansion of a memristor, this gadget gives tunable conductance, yet in addition exhibits reconfigurable photoresponse for perusing at zero predisposition voltage,” the writers state
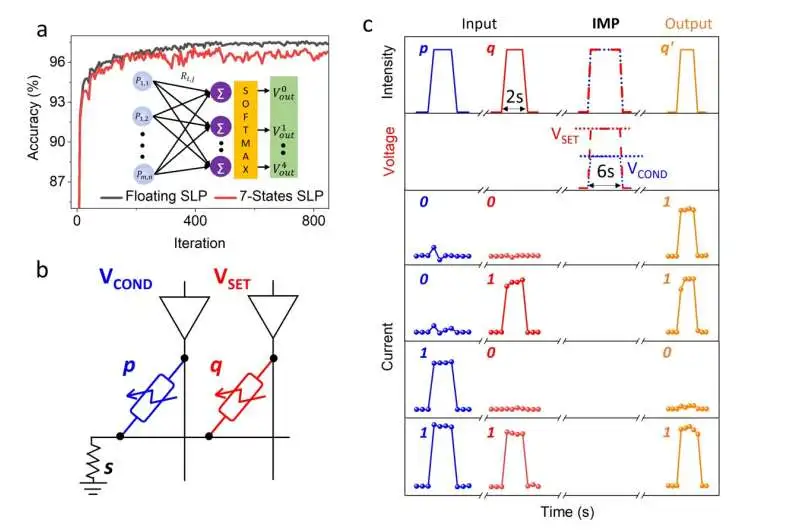
Solitary layer perceptron (SLP) brain network design schematics and the precision of the SLP classifier during preparation with drifting point weight and discrepant 7-level photoresponse state b. Delineation of an in-memory Pixie activity in view of a bunch of photomemristors set off by light upgrades. c, A graph depicting the optical and electrical heartbeats used in the devil’s activity. The blue and red bends show the optical and electrical sign of gadgets p and q previously and during the Devil activity, and the orange bends show the change in photoresponse states after Demon tasks, duplicating the Pixie truth table.
“In addition, the tunable short-out photocurrent and photoresponse can be expanded to 889.8 nA and 98.8 Mama/W, separately, which are a lot higher than that of other reconfigurable phototransistors in view of 2D materials. The channel semiconductor should be sufficiently delicate to invert the channel extremity and obtain an entryway tunable short out photocurrent. As a result, it is difficult to use the thick film required to retain enough light to produce a large sign. For our situation, the system of the two-terminal gadget modification depends on particle relocation, which isn’t restricted by the thickness. “We can expand the thickness of the film to retain more photons and get a huge short-out photocurrent,” they added.
“This new concept of a two-terminal photograph memristor not just enables all-encompassing memory-processing approaches for neuromorphic vision equipment, but additionally brings incredible comfort for high-thickness incorporation,” the researchers write.
More information: Xiao Fu et al, Graphene/MoS2−xOx/graphene photomemristor with tunable non-volatile responsivities for neuromorphic vision processing, Light: Science & Applications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41377-023-01079-5