Video-conferencing stages, for example, Skype, Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and Google Meet, permit individuals to discuss from a distance with others in various areas of the planet. The COVID-19 pandemic and the social separating measures that followed prompted a further ascent in the utilization of these stages, as they expanded remote working and virtual joint efforts.
Most video-conferencing stages currently likewise permit clients to utilize virtual foundations, so they don’t have to show their home surroundings to their collaborators and to diminish the chance of interruptions. These virtual foundations can be genuine (momentum), virtual (e.g., an ocean side scene or space), or counterfeit (a truly but not flowing foundation).While having the option to change the foundation expands clients’ protection, counterfeit foundations can likewise be utilized with vindictive aim to give the impression of a misleading area, for example, recommending that a client is at the workplace when he is entirely home.
Analysts at Sabanci University in Turkey, Florida International University in the United States, and the University of Padua in Italy have as of late fostered an apparatus that could be utilized to recognize genuine and virtual foundations in video-conferencing stages. Their strategy, presented in a paper pre-distributed on arXiv, was found to effectively distinguish between genuine and “counterfeit foundations” in two particular and normal assault situations.
As of late, researchers have demonstrated that most machine and profound learning methods are powerless against ill-disposed assaults in media criminology,” Ehsan Nowroozi, Berrin Yanikoglu, Yassine Mekdad, Selcuk Uluagac, Simone Milani, and Mauro Conti, the analysts who completed the review, told TechXplore by means of email. As a matter of fact, with the pandemic circumstances, a few gatherings have been brought out somewhat through video conferencing programming that empowers members to involve a virtual foundation for protection concerns.
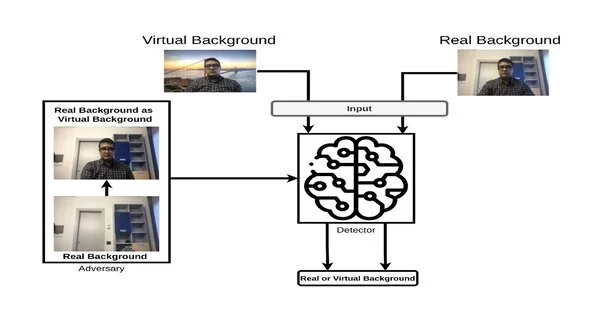
Some previous investigations exhibited the chance of enemies uncovering the genuine climate of a member by spilling pixels from the virtual foundation. However, organizations may have a genuine need to be aware if the client is unquestionably in the introduced foundation.
The critical goal of the new work by Nowroozi and his partners was to fabricate a framework that can powerfully recognize a genuine foundation versus a virtual or counterfeit one in a video-conferencing call. The strategy utilizes profound learning procedures to recognize genuine versus phony or virtual foundations with elevated degrees of exactness. What’s more, their finder can be utilized to identify ill-disposed assaults and phony foundations across a wide scope of video-conferencing stages.
“The framework works by considering the six co-event grids between the three variety channels of the foundation,” the specialists made sense of. “In a phony or virtual foundation, because of the static idea of the foundation picture, we don’t see the progressions in the ghastly space,” says Nowroozi, “however it tries to track down the connection between channels.” Hence, the main way is to utilize cross-band co-events across the channels and feed them to the profound learning-based indicator. “
“We are the primary group that gives a CNN-based model equipped for recognizing a genuine foundation versus a virtual or counterfeit one in a videoconferencing call,” Nowroozi and his partners said. “In addition, we accomplished a high precision of 99.80% for the situation where the identifier knows about the assault and high power even on account of an ignorant indicator.”
Later on, the CNN-based identifier created by this group of specialists could be utilized to affirm the validity of video-conferencing foundations in proficient settings as well as in policing and legal settings. Meanwhile, Nowroozi and the remainder of the group intend to keep chipping away at their identifier to work on its presentation and generalizability further. Preferably, they believe this identifier should be material to the most famous video-conferencing stages, including Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams.
“Our future examination will initially consider the instance of whether a foe can delude the locator in the event that it can get to the cross-band co-events,” Nowroozi and his partners added. Furthermore, we intend to assess our locator in a situation where the assailant thinks about a moving virtual foundation (e.g., cuts).”