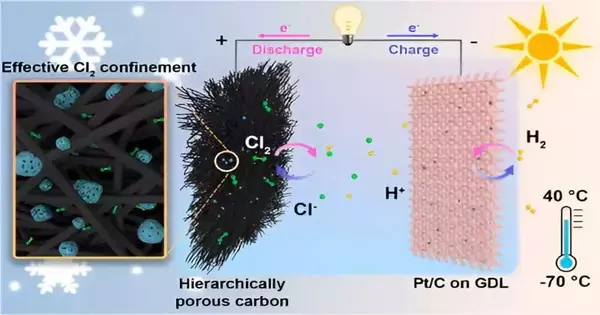
An exploration group led by Prof. Chen Wei from the College of Science and Innovation of China (USTC) of the Chinese Foundation of Sciences (CAS) planned a battery-powered hydrogen-chlorine (H2-Cl2) battery that can work in temperatures ranging from -70°C to 40°C. The review was distributed in the Diary of the American Substance Society as the cover article.
Hydrogen energy components are a promising innovation important for their maintainability and the overflow of hydrogen, among which H2-Cl2 power devices stand apart because of their quick electrochemical energy, high redox potential, and high unambiguous limit of the Cl2/Cl-redox couple. Nonetheless, the unstable chlorine gas can’t be held during the charging system, bringing about poor Coulombic productivity (CE) and reversibility. There is a pressing need to foster watery chlorine batteries with elite execution and pertinence at various temperatures.
The examination group originally found that because of the absence of restricting destinations with a solid fondness for Cl2, conventional adsorptive cathodes experience issues immobilizing Cl2, causing low reversibility. To handle this issue, the group planned a progressively permeable carbon cathode made out of exceptionally miniature/mesoporous carbon (HPC) and macroporous carbon felt (CF), really binding the Cl2 on the cathode and working on the reversibility.
The group showed that the H2-Cl2 cells kept a high CE and dependability, working consistently for 500 cycles at a release limit of 3 mAh cm2. Likewise, the cells work well at ultralow temperatures, maintaining a release level of 1.1 V and a high, unambiguous limit of 282 mAh g1 at -70 °C.
To additionally comprehend the system of reversibility improvement, the group joined X-beam photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) with hypothetical estimations and uncovered that the Cl2/Cl-response happens alongside the reversible arrangement and breakage of C-Cl bonds, which upgrades the reversibility of the Cl2/Cl-cathodes.
This work gives another heading to the plan of fluid chlorine batteries and high-energy-thickness hydrogen batteries in a wide temperature range.
More information: Zehui Xie et al, Rechargeable Hydrogen–Chlorine Battery Operates in a Wide Temperature Range, Journal of the American Chemical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c09819