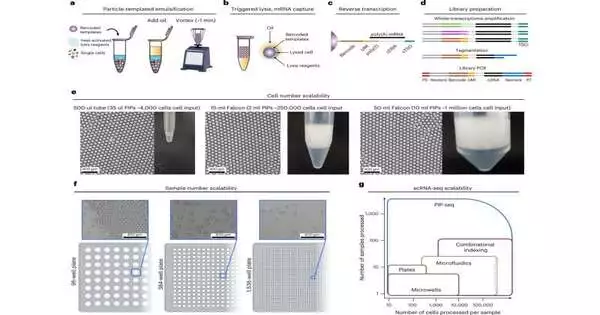
Another single-cell epitome, lysis, and barcoding technique for cDNA is quicker and requires less gear, equipment, cost, and ability. It has been demonstrated to be viable and adaptable with any size compartment, from 500 L microcentrifuge cylinders to 50 mL tapered cylinders, and works with 96-, 384-, or 1,536-well microtiter plates, too.
In their paper, “Sans microfluidics: single-cell genomics with templated emulsification,” distributed in Nature Biotechnology, the specialists gauge that 3,500 cells can be barcoded with 35 l of hydrogel layouts in a 500-l tube, 225,000 cells with 2 ml of layouts in a 15-ml cone-shaped cylinder, and 1 million cells with 10 ml of layouts in a 50-ml tube. No matter what the cylinder size, just 2 minutes of vortexing is expected for cell catch.
Molecule templated moment segment sequencing (PIP-seq) catches cells, barcoded formats, and lysis reagents in uniform oil-covered water drops with a couple of moments of vortexing. The interaction involves hydrogel particles comprising a >95% water arrangement as a template to get these obvious beads. The hydrogels with pre-functionalized dabs are filled by single cells and intensity-actuated lysing arrangements during vortexing.
The cells are then lysed by expanding the temperature to 65 °C, which initiates a proteolytic chemical (proteinase K) that separates the cell plasma layer, delivering the mRNA. The mRNA is then caught on polyacrylamide dabs enhanced with barcoded groupings.
PIP-seq emulsions can be stored at 0 °C with practically no adjustment of information quality (72 hours), permitting numerous examples to be stacked for succession. In the wake of continuing, oil is eliminated, dots are moved into a converse record support, and full-length cDNA is orchestrated, enhanced, and ready for sequencing.
Single-cell transcriptomics is acquiring an undeniably elevated degree of concentration in research as it permits researchers to comprehend exhaustively what’s going on inside a phone. Applications range from arranging dynamic cell capabilities to deciding sickness cause or movement to uncovering stowed-away RNA controllers and explicit associations, a lot of which must be roughly deduced in mass cell studies.
In the paper, the specialists demonstrate that PIP-seq delivers high-immaculateness transcriptomes in a mouse-human cell blending test. Searching for how much pre-lysed cells could bring about mRNA cross-tainting The preliminary study found the small portion of mouse peruses in human transcriptomes was below 3%.
PIP-seq was likewise tried in single-cell transcriptional profiling of blended aggregate intense leukemia. Here the analysts distinguished transcriptional contrasts from past immunophenotype perception. The regulation of ribosomal qualities, beforehand detached from this kind of leukemia, could assume a part in treatment opposition and propose a remedial objective to the scientists — a great find for a technique testing concentrate on that represents a blind spot of different strategies.
Problematic advancement
At the point when researchers discuss problematic developments or innovation, they by and large allude to another strategy that changes how exploration is sought after. Commonly, this implies making a current cycle less expensive, quicker, more exact, or at an expanded throughput of information assortment. Similar to how cells supplanted landlines, web-based video stores supplanted video stores, or cutting-edge sequencing supplanted Sanger sequencing, troublesome advancements are frequently immediately embraced and increment the quality and pace of exploration work.
PIP-seq emulsion capture is identical to what can be accomplished with microfluidic frameworks yet for a portion of the expense with no significant hardware venture, making it a basic, adaptable, and versatile cutting-edge sequencing work process that stretches out single-cell sequencing to new applications — making it a genuinely troublesome development in single-cell research. The PIP-seq designers trust this cycle will open up the field of single-cell sequencing to more modest, less-resourced research associations and scholarly foundations so they can be allowed to seek after the following influx of logical revelations.
More information: Iain C. Clark et al, Microfluidics-free single-cell genomics with templated emulsification, Nature Biotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-01685-z