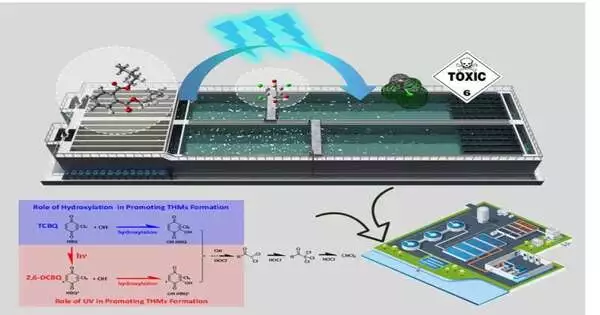
Halobenzoquinones (HBQs), as new arising sanitization results (DBPs), are often identified in consumable and pool waters. As a matter of fact, HBQs are likewise forerunners of other DBPs, for example, right now managed trihalomethanes (THMs), which represent a high gamble to the general wellbeing and the climate. At the point when UV is applied during the chlorination cycle, the DBPs arrangement might be very not the same as that under chlorine alone or UV alone. In any case, there stay many inquiries that require further examination. For example, does UV/chlorine joined sanitization advance or cutoff the change of HBQs into DBPs contrasted and chlorine-just sterilization? Especially, does UV assume a huge part in the change of natural forerunners and the development of DBPs upon chlorine sanitization?
To address these inquiries, Prof. Ching-Hua Huang from the Georgia Institute of Technology, Dr. He Zhao from the Institute of Process Engineering Chinese Academy of Sciences and their colleagues have worked together and uncovered efficiently the atomic system of THMs created from HBQs in chlorination or joined UV/chlorine. Their work recognized the advancing impact of UV on HBQs in THMs arrangement, which gave important knowledge to the likely gamble during the use of joined UV/chlorine in water treatment. The review was distributed in Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering.
In this review, the examination group found UV upgraded by almost multiple times the CHCl3 arrangement yield of 2,6-dichloro-1,4-benzoquinone (2,6-DCBQ, one of the most often recognized HBQs in drinking water). They likewise led top to bottom examination of the response system utilizing integral trial estimations and thickness useful hypothesis (DFT) computations, and uncovered different arrangement examples of THMs from four types of HBQs during chlorine-just and UV/chlorine processes. Their examination showed that UV had an incredible impact as per the compound design of HBQs, straightforwardly influencing the hydrolysis rate, change pathways, intermediates, and the ensuing creation of THMs. Their outcomes likewise divulged the hydroxylation of HBQ to be a vital middle pathway in advancing THM development.
This study explored completely and efficiently the arrangement of THMs from HBQs during chlorination or joined UV/chlorine processes interestingly, which ought to be viewed as in the use of consolidated UV and chlorine processes in water treatment. It has extended how we might interpret the advancing jobs of UV light and hydroxylation of HBQs in THMs development, which gives another knowledge to the likely dangers for UV sanitization of drinking water treatment.
More information: He Zhao et al, Enhanced formation of trihalomethane disinfection byproducts from halobenzoquinones under combined UV/chlorine conditions, Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering (2021). DOI: 10.1007/s11783-021-1510-7